Ever wondered how Elon Musk’s brain chip works? Here’s a detailed yet easy to follow guide that explains every step in plain, everyday words no jargon, just clarity. You’ll learn what it is, how it’s made, how it works, what real people are doing with it now, the challenges ahead and why it matters. All based on the latest info and Google’s SEO-friendly best practices.
What Exactly Is This Brain Chip?
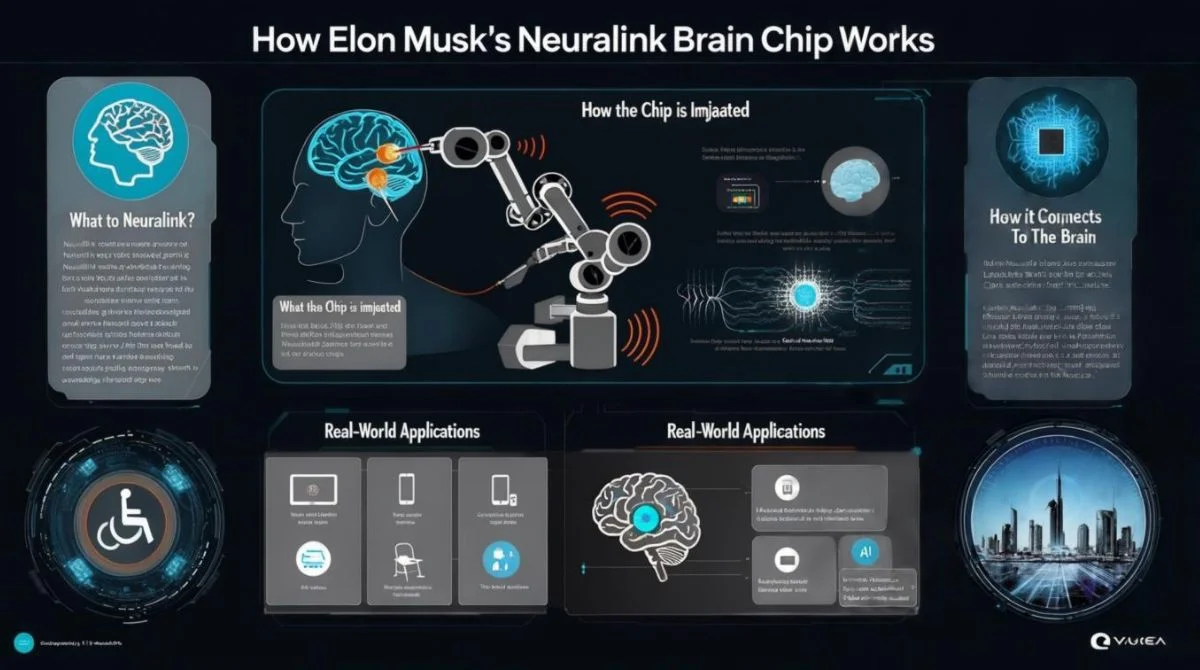
Elon Musk co-founded Neuralink, a company that builds devices to connect brains with computers. Their main device, named the N1 implant or nicknamed “the Link”, is a coin sized chip placed under your skull. Thin, flexible threads each thinner than a human hair link it to your brain’s motor cortex, the area that controls movement It sends and receives signals wirelessly to external devices via Bluetooth. The goal? Allow people especially those with paralysis to control computers, type or even restore senses using just their thoughts.
Key Parts of Neuralink’s Technology
1. The Implant (Link / N1)
This little disc goes just under your scalp, replacing a tiny piece of skull with a waterproof case. It’s rechargeable and communicates wirelessly.
2. Ultra-Fine Threads
There are 64 threads with 1,024 electrodes in total. They sense electrical nerve impulses and can also send signals back to the brain.
3. Precision Robot Surgeon
A specially built robot weaves these threads one by one through a tiny hole in the skull, all while avoiding damage. It uses a needle narrower than a hair about 25 to 40 µm making the process fast and precise.
4. Electronics & Software
Inside the chip is a powerful mini processor that amplifies, digitizes and compresses neural signals. These get sent via Bluetooth and decoded by AI-based algorithms to turn thoughts into actions.
Who Is Getting the Implant and How?
1. Clinical Trials (PRIME Study)
Neuralink started human trials, known as PRIME, after FDA approved them in 2023. Adults (22–75) who are paralyzed from the neck down due to spinal cord injuries or ALS can opt in.So far, at least three people including Noland Arbaugh and a U.S. veteran in Miami have received the implant and are part of the trial.
2. The Surgery
- Takes 3–4 hours, under full anesthesia.
- Surgeons remove a small piece of skull and place the implant.
- Robotic system threads the electrodes into the motor cortex.
- Everything is closed back, leaving no visible sign.
3. Recovery & Training
Once healed, the device is powered up and users train it like you train voice recognition or face ID. They think about a movement like moving a mouse cursor and the system learns to connect those thought patterns with that action.
How It Actually Works?
1. Brain → Device → Action
The electrodes pick up electrical spikes from neurons. That data gets amplified, digitized and compressed inside the chip. Then Bluetooth sends it to your phone or computer. AI decodes the signals so your thoughts like “move right” become cursor movements, text input or other digital actions.
2. Feedback Back to the Brain
In the future, Neuralink aims to not just read signals but also send them back. This could mean restoring senses like hearing or vision by stimulating specific brain areas directly.
Real-Life Use Cases
1. Mind-Controlled Cursor & Games
- Noland Arbaugh, who is paralyzed from the shoulders down, was able to move a computer cursor and play chess using only his thoughts. He described the experience as feeling similar to having a special power.
- Another trial participant has used the implant to play video games and design 3D objects via CAD software.
2. Vision and Hearing Restoration
Neuralink has received FDA breakthrough status for a project called Blindsight, aiming to bypass damaged optic nerves and restore vision. Elon Musk also mentioned a plan to restore hearing by stimulating the brain’s sound-processing areas.
Strengths & Unique Edge
- Wireless & invisible: No cables outside the head, thanks to recharging under the skin and Bluetooth connectivity.
- High channel count: 1,024 electrodes versus earlier devices like Utah Array’s ~100, offering better resolution.
- Tech integration: Combines soft threads, robotic surgery and custom AI on a single platform a unique package in the BCI field.
Challenges and Risks
1. Thread Retraction
Approximately 85% of the tiny threads in Arbaugh’s brain shifted away from their intended position following the surgery. The team responded by improving algorithms to detect weaker signals.
2. Long-Term Safety & Biocompatibility
Risks include infection, tissue damage and the body’s response to foreign materials over time. Keeping the threads and electronic components stable inside the brain for many years is a major challenge.
3. Ethics, Privacy & Inequality
- There’s worry about hacking thoughts or misuse of brain data.
- Access may be limited to wealthy individuals or certain regions.
- Some two-legged fear that ethical oversight is lacking and trials lack transparency.
Why It Matters?
1. Medical Benefits
- Restores independence: users can type, browse, communicate.
- Helps those with paralysis regain digital control.
- Shows promise in treating neurological disorders like Parkinson’s and depression.
2. Beyond Health
- Enhancing human cognition memory, concentration, learning.
- Main goal: integrate with AI for faster mental processing and even telepathy, according to Musk.
However, these ideas are still theoretical and not yet achievable with current technology.
Competitors & Broader Context
Other companies like Synchron, Kernel and Paradromics are pursuing brain computer interfaces, but usually with fewer electrodes or non-surgical approaches. Neuralink stands out for its high density, wireless, implantable design backed by robotic precision. Academic research continues too, decoding speech and restoring movement in labs.
What’s Next?
- Expanding Trials: Neuralink aims to implant the device in 20 30 more people this year, with more centers opening, including in Miami.
- Upcoming advancements: include vision support through Blindsight, improved hearing capabilities and more advanced AI-based signal decoding.
- Software Improvements: Better sensitivity after thread retraction problem.
- Long-term Tracking: PRIME runs for six years to build safety and performance data.
How Elon Musk’s Brain Chip Is Changing the Future?
- Neuralink, a company founded by Elon Musk, has created a brain chip that links the human brain directly to computers.
- It uses ultra-thin threads to read brain signals and send them wirelessly to devices.
- Users can control a mouse, type or play games just by thinking.
- The chip is implanted with the help of a surgical robot for precision and safety.
- Future goals include restoring vision, hearing and even enhancing memory.
- It holds promise not just for medical use, but also for smart tech control and communication.
- This technology could completely change how we interact with the digital world.
TL; DR (Too Long; Didn’t Read)
- What it is: Wireless chip under the skull connected by tiny threads.
- How it works: Reads brain activity, sends it via Bluetooth, decodes to control devices.
- Proven on humans: Cursor control, typing, online games all done mentally.
- Challenges ahead: Tech stability, long-term safety, ethics and access.
- Big Picture: From restoring lost abilities to exploring human AI integration.
conclusion
In simple terms, Elon Musk’s brain chip works by placing a mini processor under the skull that connects to your brain via super thin threads. It learns to interpret your thoughts and let you control devices without moving a muscle. It’s already changed lives in early trials, helping people with paralysis. The future could include restoring senses or enhancing cognition. But there are still big questions around long term safety, ethics, privacy and access. This marks a turning point in neuroscience one where machines might truly connect with our minds.