In today’s fast-moving digital world, having a fast and reliable internet connection isn’t just a luxury; it’s a necessity. Whether you’re working from home, attending virtual classes, gaming online, or managing smart devices, your internet connection plays a crucial role in how smoothly things run.
Fiber Internet vs 5G is a hot topic today, as both technologies offer high-speed connections but with different strengths. Both offer high-speed connections but operate in different ways and come with distinct pros and cons. So, which one should you choose?
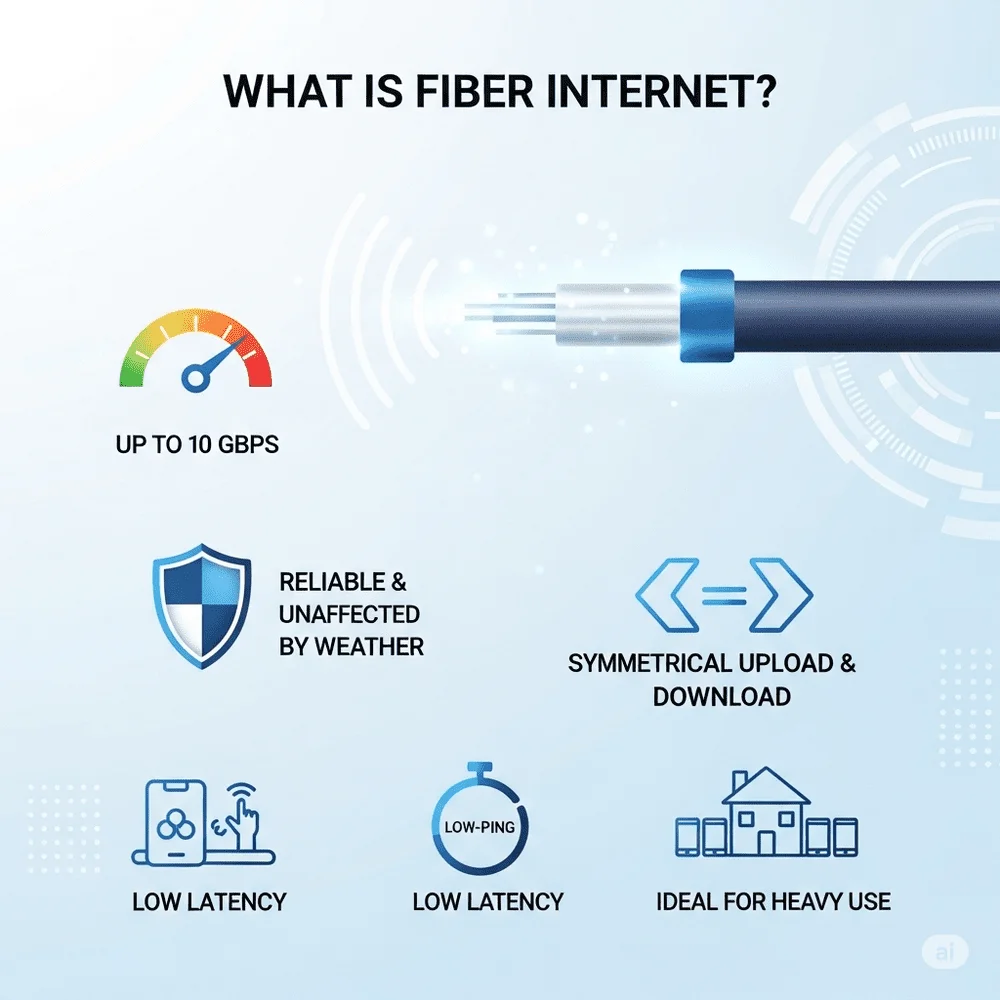
What is Fiber Internet?
Fiber Internet is a wired broadband connection that uses fiber-optic cables to transmit data. These cables are made of thin strands of glass or plastic that carry data using light signals, making them incredibly fast and efficient.
Key Benefits of Fiber Internet:
- Blazing fast speeds: Up to 1–10 Gbps, depending on your plan and provider.
- Highly reliable: Weather or electrical interference won’t affect the connection.
- Symmetrical speeds: Upload and download speeds are typically the same.
- Low latency: Low latency makes both options suitable for real-time activities such as online gaming and video calls.
- Ideal for heavy users: Perfect for large households, remote work, or streaming 4K+ content.
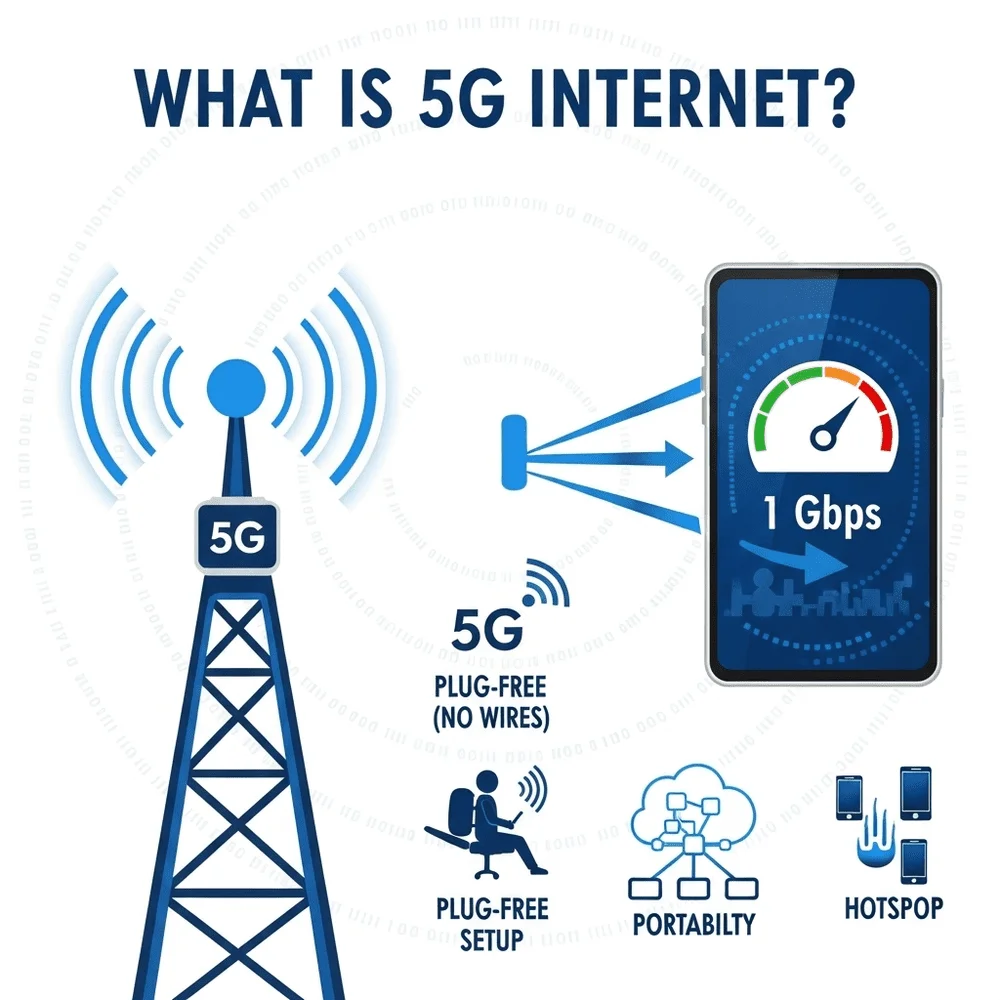
What is 5G Internet?
5G refers to the fifth generation of mobile networking technology. Unlike fiber, which is wired, 5G is a wireless technology that delivers internet using radio signals transmitted from nearby cellular towers or small cells.
Key Benefits of 5G Internet:
- Fast wireless speeds: Typically range from 100 Mbps to over 1 Gbps, depending on location.
- Quick setup: No need for cables or professional installation.
- Portable: Great for people who move often or live in temporary homes.
- Future-ready: Designed to handle many connected devices simultaneously.
- Excellent for mobile use: Supports smartphones, tablets, and hotspots seamlessly.
Fiber Internet vs 5G: Speed Comparison
Both technologies are fast, but speed depends on more than just advertised numbers. Here’s how they stack up in real-world use:
| Feature | Fiber Internet | 5G Internet |
| Download Speed | 300 Mbps – 10 Gbps | 100 Mbps – 2 Gbps (varies by location) |
| Upload Speed | Upload and download rates are equal (symmetrical) | Delivers lower upload speeds |
| Latency | Typically under 20 ms | 10–50 ms (can drop to 1 ms on mmWave) |
| Stability | Highly stable | Variable depending on tower distance, walls |
When comparing Fiber Internet vs 5G in terms of speed, fiber usually provides symmetrical high-speed connections, while 5G speeds may fluctuate depending on coverage and network congestion.
Verdict on speed:
Fiber provides more consistent and higher speeds across the board, while 5G can deliver fast speeds but with more fluctuation.
Reliability & Stability
A high-speed internet connection is useless if it keeps dropping out.
Fiber Internet:
- Not affected by rain, buildings, or interference
- Uses underground cables for uninterrupted service
- Delivers consistent performance 24/7
5G Internet:
- Can be affected by weather, walls, and physical obstacles
- High-band 5G, also known as mmWave, often faces challenges with indoor coverage and has limited range over longer distances.
- Network performance on 5G may decrease during peak usage times or in densely populated locations.
Verdict on reliability:
Fiber is the winner for uninterrupted, stable internet, especially for business, school, or mission-critical tasks.
Latency: The Invisible Speed Factor
Latency measures the time it takes for data to travel from your device to the server and back.
- Fiber: Usually has latency under 20 milliseconds, which makes it great for real-time interactions like gaming and Zoom calls.
- 5G: Can reach ultra-low latency of 1 ms in perfect lab conditions, but real-world latency is often around 30–50 ms.
Verdict on latency:
Fiber offers consistently lower latency, which matters most for competitive gamers, streamers, and remote workers.
Installation & Availability
Fiber Internet:
- Requires professional installation
- Cables need to be buried, and it can take days or weeks
- Not available in all rural or underserved areas
5G Internet:
- Easy, plug-and-play setup
- Just needs a 5G modem/router
- Available in many urban and suburban areas, expanding fast
Verdict on setup:
If you need internet quickly, 5G is more accessible. But fiber is a better long-term investment if it’s available in your area.
Cost Comparison
Pricing varies by provider and location, but here’s a general comparison:
Fiber Internet:
- Plans usually range from $40 to $100+ per month
- Often includes unlimited data
- Installation fees may apply
5G Internet:
- Plans range from $50 to $80 per month
- May include equipment or be bundled with mobile plans
- Some plans have data caps or speed throttling
Verdict on cost:
Both are similarly priced, but fiber often delivers better value thanks to faster, more stable service and no data limits.
Use Cases: Which One Suits You Best?
Choose Fiber Internet if:
- You work or study from home
- You stream 4K or 8K video
- You play online games
- You upload large files frequently
- You want the most stable, lag-free connection
Choose 5G Internet if:
- You move frequently or rent
- You don’t have access to fiber
- You want a portable or temporary setup
- You want a backup connection to your main internet
Security and Privacy
Both fiber and 5G can be secure if you follow good practices.
- Fiber: Being wired, it’s less prone to interception.
- 5G: Slightly more exposed due to its wireless nature, but still secure with encryption and a strong password.
Verdict on security:
Both are safe when configured properly, but fiber offers an edge in terms of reduced exposure to wireless threats.
Environmental Impact
- Fiber is more energy-efficient during operation.
- 5G requires more energy due to many small towers, especially in dense urban areas.
Verdict on eco-friendliness:
In terms of energy efficiency and environmental impact, fiber remains the more sustainable option over time.
The Future: Will 5G Replace Fiber?
Not likely. Both technologies are advancing rapidly but serve different needs. Many 5G towers are powered by fiber backbones, meaning the two work together behind the scenes. As technology grows, you may even use both fiber for your home and 5G on the go.
Final Thoughts
Choosing between Fiber and 5G depends on your location, budget, and usage needs. Fiber offers stable, high-speed internet with long-term value, ideal for homes and businesses. 5G provides quick setup and mobility, great for areas without fiber access. Together, fiber and 5G are driving the evolution of internet connectivity as we move through 2025 and beyond.



