A network controller card (commonly known as NIC) is the bridge that allows your computer, server or device to connect to a network, either wired or wireless. Although many computers come with built-in NICs, upgrading or choosing the right card can help improve your connection speed, reliability or add new features.
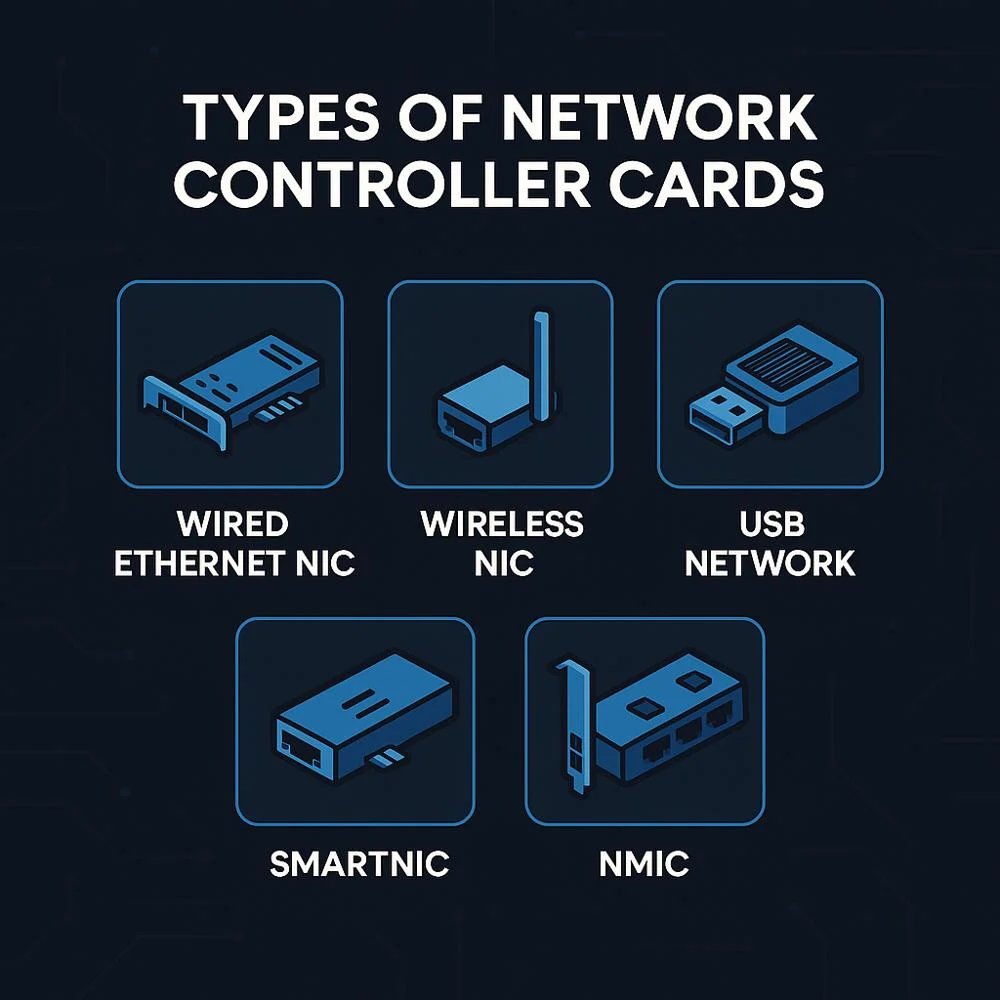
Types of Network Controller Cards
1.Wired Ethernet Cards (Copper & Fiber)
The most common type is the wired Ethernet NIC, which uses RJ‑45 connectors to plug into copper cables or fiber‑optic ports for high-speed data transmission. They come in speeds ranging from 1 Gbps to 100 Gbps or more
Why you’d pick one:
- Stable, fast connection for gaming, streaming, or data transfers.
- Less interference and better security compared to wireless.
- Ideal for desktops, servers and devices near network ports.
2.Wireless Network Interface Cards (WNICs)
These cards connect using Wi‑Fi, Bluetooth, or cellular (LTE/5G). They can be internal (PCIe, M.2) or external (USB dongles). Most laptops today ship with wireless NICs built-in
Why you’d pick one:
- Mobility & convenience no cables needed.
- Internal cards offer better performance; USB dongles are plug and play.
- Ideal for laptops, compact desktops or mobile setups.
3. USB Network Adapter
A USB network adapter is essentially a NIC in an external format either wired Ethernet or wireless, plugging into a USB port
Why you’d pick one:
- No need to open your PC, just plug it in.
- Ideal for laptops lacking Ethernet ports or desktops with damaged ports.
- Works across Windows, macOS and Linux without fuss.
4. SmartNICs (Intelligent Offload Cards)
SmartNICs are advanced cards that include their own processors, accelerators (ASIC or FPGA) and memory. They offload tasks like packet processing, security, encryption, load balancing and virtualization all from the server’s CPU
Why you’d pick one:
- For data centers, cloud providers or AI workloads where CPU resources are valuable.
- Improve performance, reduce latency, and enhance security at scale.
- Ideal for enterprise level networking and edge computing.
5. Network Monitoring Interface Cards (NMICs)
These are listen-only NICs used for capturing, filtering and monitoring network traffic. They have features like timestamping, packet capture engines and CPU offloading, commonly used in IDS, protocol analysis and lawful interception
Why you’d pick one?
- For network admins, security teams, or compliance officers.
- Helps with deep insights, real‑time logging, and troubleshooting.
- Ideal for professional network monitoring and security environment
Choosing the Best Network Controller Card for Your Needs
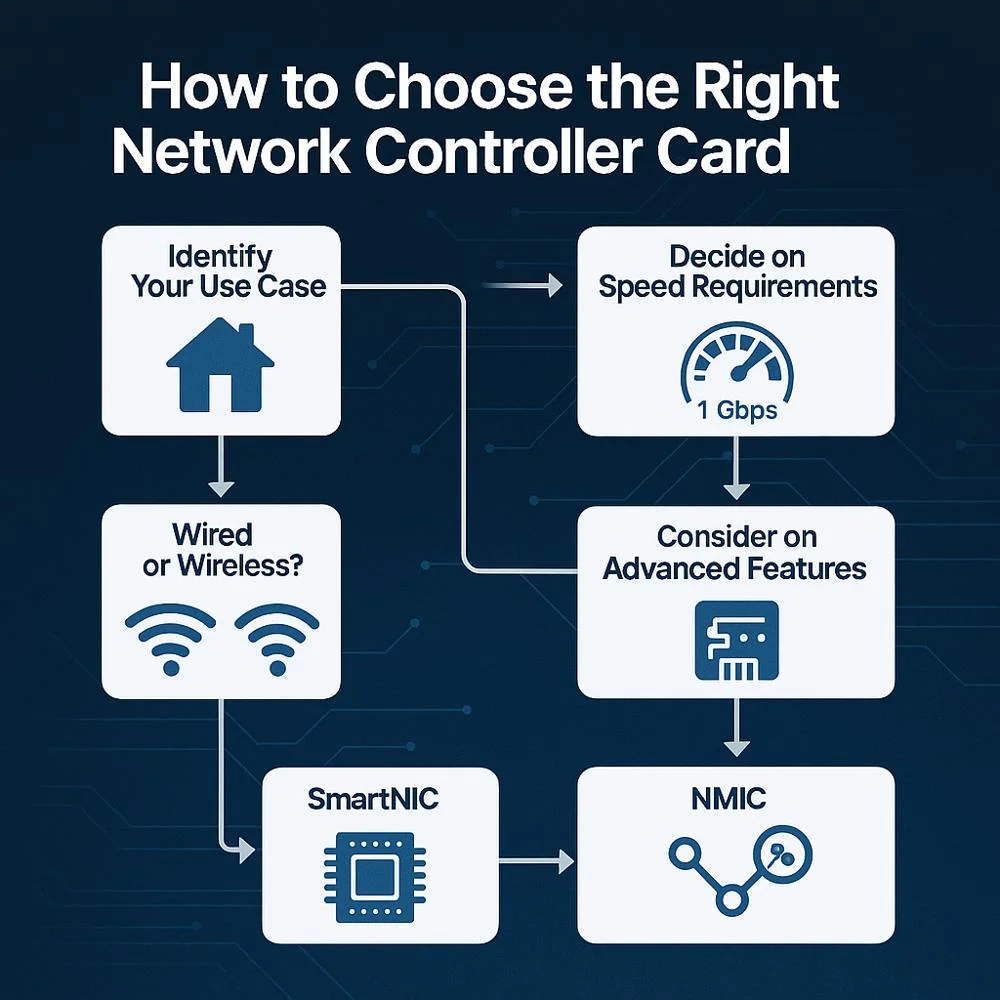
1. Identify Your Use Case
- General home/office use → wired Ethernet or basic WNIC
- Portability needed → USB adapter or internal WNIC
- High-performance/server infrastructure → SmartNIC or fiber Ethernet
- Security/monitoring → NMIC
2. Check Your Hardware Slots
- PCIe, PCI, M.2, USB: your motherboard or device must support the choice
3. Decide on Speed Requirements
- Basic: 1 Gbps ethernet
- Mid-range: 2.5 Gbps–10 Gbps
- High-end: 25 Gbps+ (for data center or server)
4. Wired or Wireless?
- Wired for reliability and low latency.
- Wireless for convenience and mobility.
5. Consider Advanced Features
- SmartNIC: ideal if you want encryption, security offload and CPU savings.
- NMIC: ideal if you need packet-level network analysis.
6. Budget and Complexity
- USB and wired NICs are affordable.
- SmartNICs and NMICs are expensive and may require expert configuration and maintenance
How Network Controller Cards Influence System Performance?
- A network controller card (NIC) plays a key role in how efficiently your system handles internet and network tasks.
- Using an outdated or low-performance NIC can result in slow connections, delayed downloads, or unstable online activity.
- In demanding situations, these issues can lead to frustration and reduced efficiency.
- Newer NICs are built to manage higher speeds, handle heavy data traffic, and support modern networking standards.
- Many advanced cards also reduce pressure on the main processor by managing certain network operations independently.
- This improves system performance, especially during multitasking or running resource-intensive applications.
- Upgrading your NIC doesn’t just improve network speed it can optimize overall system performance.
- It prepares your computer for future connectivity needs, such as faster internet plans or smarter networks.
- For smooth performance in work, entertainment, or cloud-based tasks, a reliable NIC makes a noticeable difference.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing a NIC
Choosing a network controller card might seem simple, but many users make mistakes that affect performance and compatibility. A common error is buying a card without checking if it matches your device’s available slots (PCIe, USB, M.2). Others focus only on speed and ignore whether their router or motherboard supports it.
Some users go for the cheapest option, only to face driver issues or frequent disconnects. To avoid frustration, make sure the card suits your system, usage and future network needs.
Final Thoughts
Whether you’re upgrading a home PC or building a server, the right network controller card depends on speed needs, connection type, budget and purpose. For most users, a simple wired or wireless NIC will do. If you’re managing enterprise-scale systems or handling security and monitoring, SmartNICs and NMICs are worth exploring.
Take a moment to check your device’s slots and pick the card type that matches both your hardware and goals. You’ll get better connectivity, performance and long-term value.