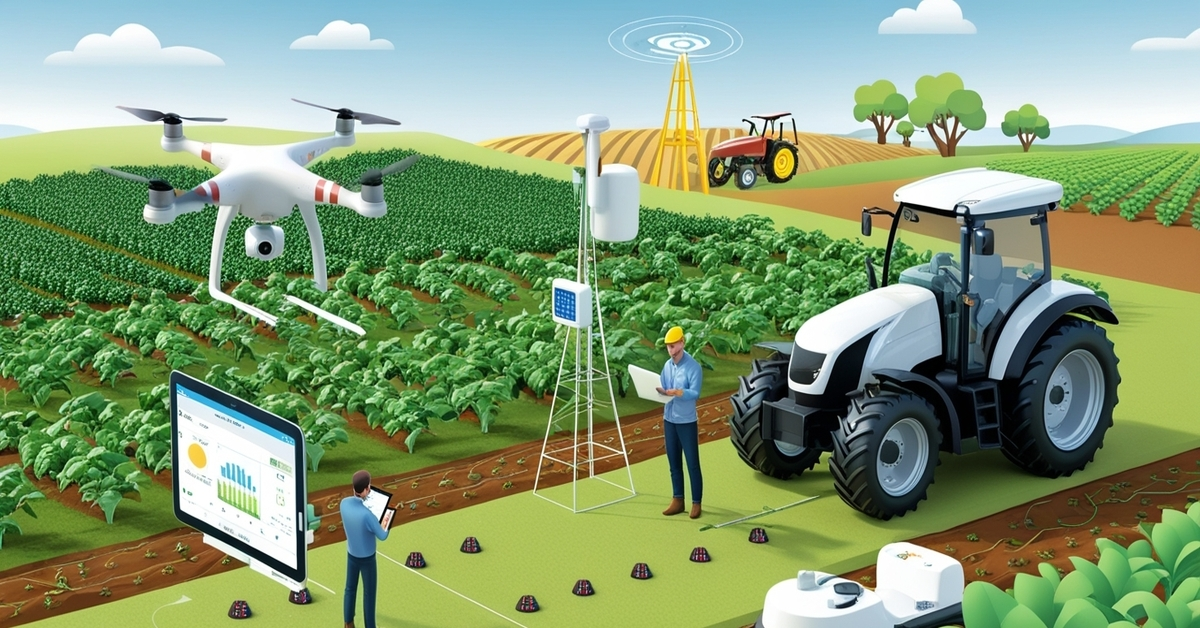
Throughout history, agriculture has played a vital role in sustaining human life and civilization. But today, it’s going through a big change. Thanks to the Internet of Things (IoT), agriculture is becoming smarter. This new way of farming is called smart agriculture, and it uses connected devices to grow food more efficiently. By adding sensors, drones, data tools, and smart machines, farmers can make better decisions, save money, and increase food production.
Understanding IoT in Farming
The Internet of Things, or IoT, describes a system where intelligent devices are linked through the internet, allowing them to gather and exchange information automatically, without direct human control. In farming, IoT means putting sensors, cameras, or smart tools in fields, greenhouses, and even tractors.
For example:
- A sensor in the soil can tell if plants need water.
- A drone can scan crops and send images showing unhealthy plants.
- A weather station on a farm can report local conditions in real time.
This live data helps farmers respond quickly and accurately to what their crops or animals need. This is why smart agriculture is becoming a game changer.
Key Features of Smart Agriculture
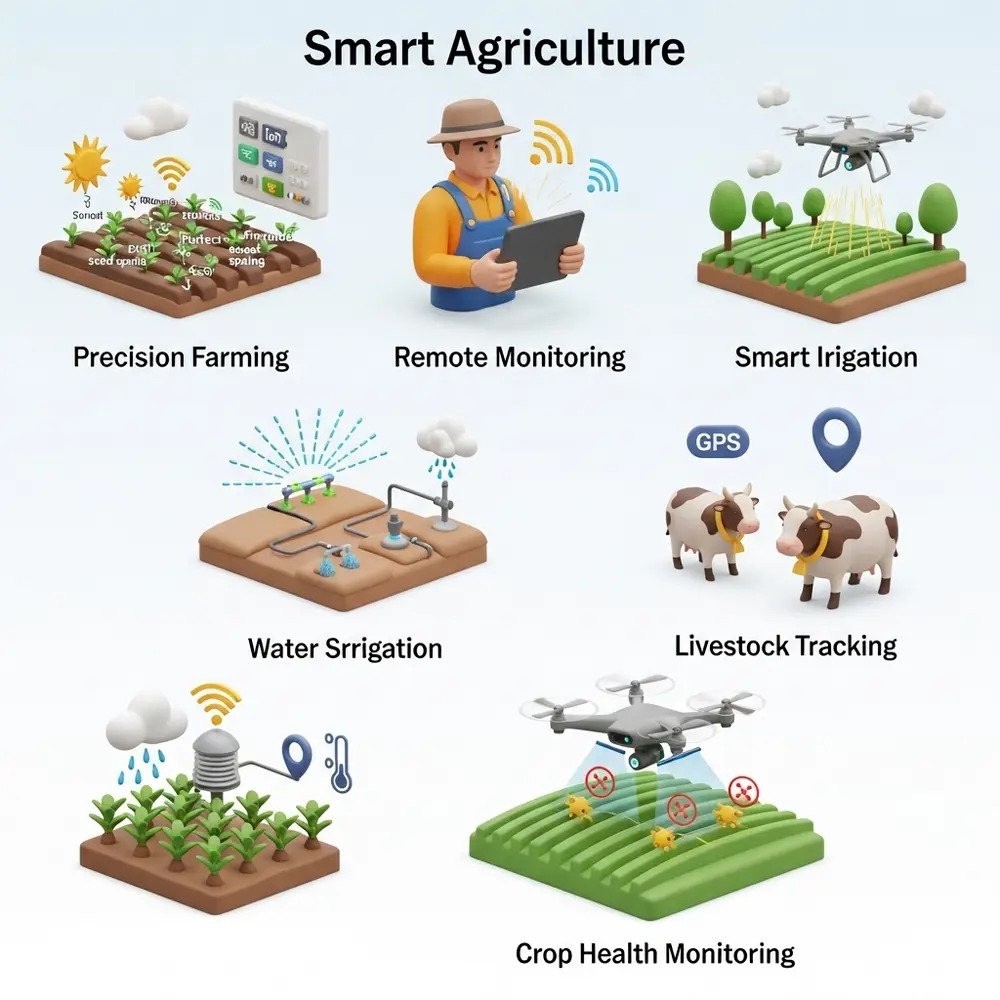
Here are the top features that make smart farming using IoT so powerful:
1. Precision Farming
Precision agriculture focuses on delivering the correct resources like water, fertilizer, or pesticides to specific parts of a field, exactly when and where they’re needed
IoT tools can:
- Measure soil quality and moisture
- Track sunlight and temperature
- Help plant seeds with perfect spacing
With this data, farmers can water only the areas that need it, use fewer fertilizers, and plant crops with better timing. This saves water, cuts costs, and boosts yields.
2. Remote Monitoring
One of the biggest benefits of IoT in agriculture is remote monitoring. Farmers no longer have to walk through every field every day. Instead, they can check their smartphone or computer to see live data from sensors, cameras, or drones. This is especially useful for large farms or farms in harsh climates. Farmers can stay informed and react quickly, even from miles away.
3. Smart Irrigation Systems
Water is one of the most important parts of farming, but also one of the most wasted. IoT based smart irrigation uses real time data to water crops only when needed.
Systems can:
- Detect soil dryness
- Check weather forecasts
- Turn water pumps on or off automatically
- This leads to healthier crops and big savings on water bills.
4. Livestock Tracking
IoT doesn’t just help plants. It helps animals too. Smart collars and ear tags can track cows, sheep, or goats in real time.
These tools report:
- Location of animals
- Body temperature
- Eating patterns
Farmers get alerts if an animal is sick or lost. This improves animal health, reduces losses, and saves time.
5. Crop Health Monitoring
Drones with cameras and sensors can fly over fields and detect problems that are hard to see from the ground. They use special cameras to spot.
- Pest attacks
- Nutrient shortages
- Fungal infections
This lets farmers treat issues early before they spread, leading to better harvests.
Benefits of IoT in Agriculture
Using IoT in farming offers many advantages that go beyond just saving time. Here’s why smart agriculture technology is growing fast:
- Increased Productivity: Farmers can grow more food with fewer resources.
- Lower Costs: Smart tools help reduce waste of water, fertilizer, and labor.
- Sustainable Practices: IoT promotes eco-friendly farming with less harm to soil and water.
- Real-Time Decisions: Instant data helps farmers make faster, smarter choices.
- Reduced Risk: Early detection of crop or animal issues prevents bigger problems.
Real World Examples
Smart agriculture is no longer a concept of the future; it’s actively transforming farms across the world today. Here are some real-life examples:
- India: Farmers in dry regions use smart irrigation systems to manage water better.
- Netherlands: One of the world’s top food exporters, it uses greenhouses with sensors to grow crops year round.
- USA: Large farms use autonomous tractors and drones for planting, spraying, and inspecting crops.
These stories show how IoT in agriculture is helping both small and big farms thrive.
Key Technologies Powering Smart Agriculture
Let’s take a closer look at the actual technologies that make smart farming possible:
- Sensors: Soil moisture, pH level, weather, light, and motion sensors are placed in fields.
- Drones: Provide aerial views and thermal images of crop health.
- GPS & GIS: Help with mapping land and planning planting patterns.
- Automation Systems: Turn on sprinklers or machines without manual control.
- AI & Machine Learning: Analyze large data sets to give insights or detect patterns.
All these work together in a connected farm ecosystem, powered by cloud services and mobile apps.
Challenges in Adopting IoT in Farming
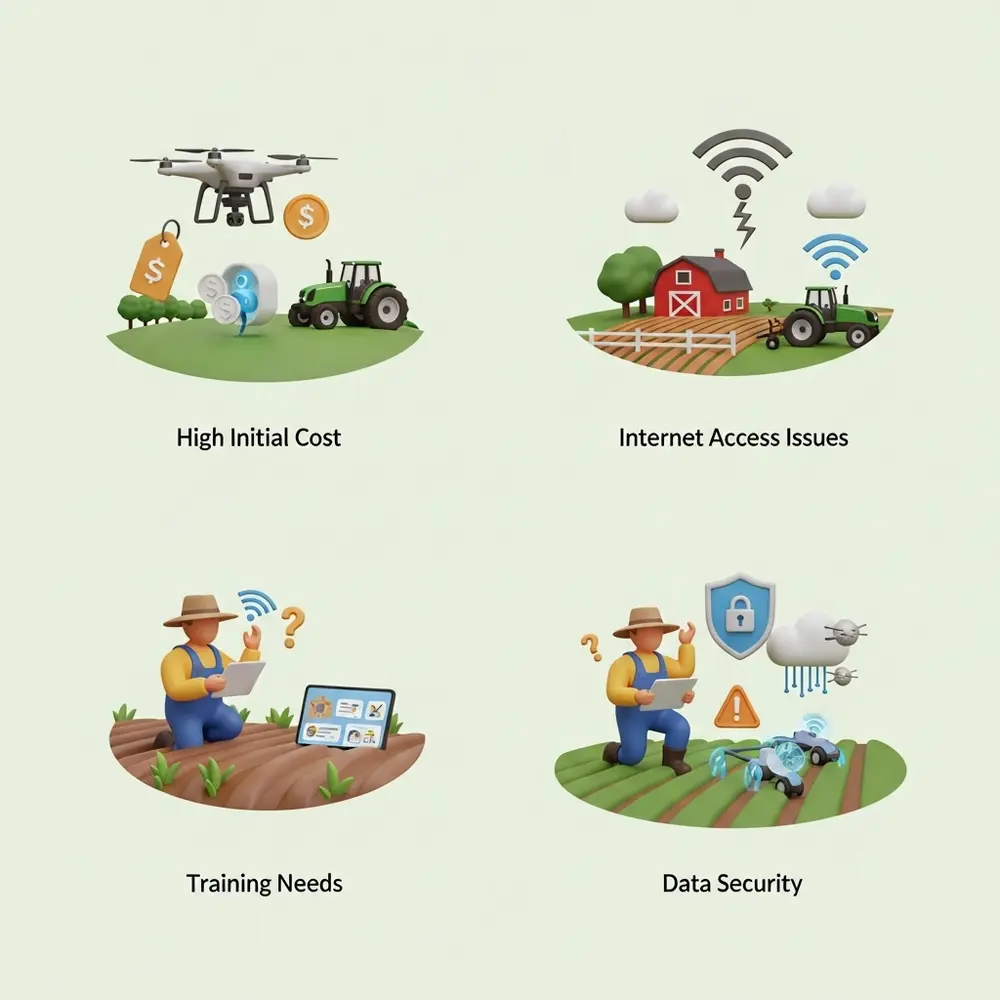
Despite all the benefits, smart agriculture faces some challenges too:
- High Initial Cost: Buying sensors, drones, or smart tractors can be expensive.
- Internet Access Issues: Rural areas often have poor connectivity.
- Training Needs: Farmers must learn to use new tech tools.
- Data Security: Protecting farm data from cyber threats is important.
Still, as technology becomes cheaper and internet access improves, more farmers are jumping in.
The Future of Smart Farming
Looking ahead, IoT in agriculture will only grow stronger. In the next few years, we’ll see:
- Smarter AI tools giving better crop advice
- More robots in planting and harvesting
- Better climate tools to adapt to changing weather
- Blockchain systems to trace food from farm to table
Smart farming will help feed a growing global population in a sustainable way.
Final Thoughts
Smart agriculture is not just about using gadgets. It’s about making farming smarter, faster, and more efficient. With IoT, farmers now have tools that were once only imagined. They can make better choices, grow more food, and protect the planet at the same time. Whether it’s monitoring soil, saving water, or spotting a sick cow, the power of connected technology is reshaping farming right now. As more farmers adopt this smart approach, we can expect better food systems for everyone.



