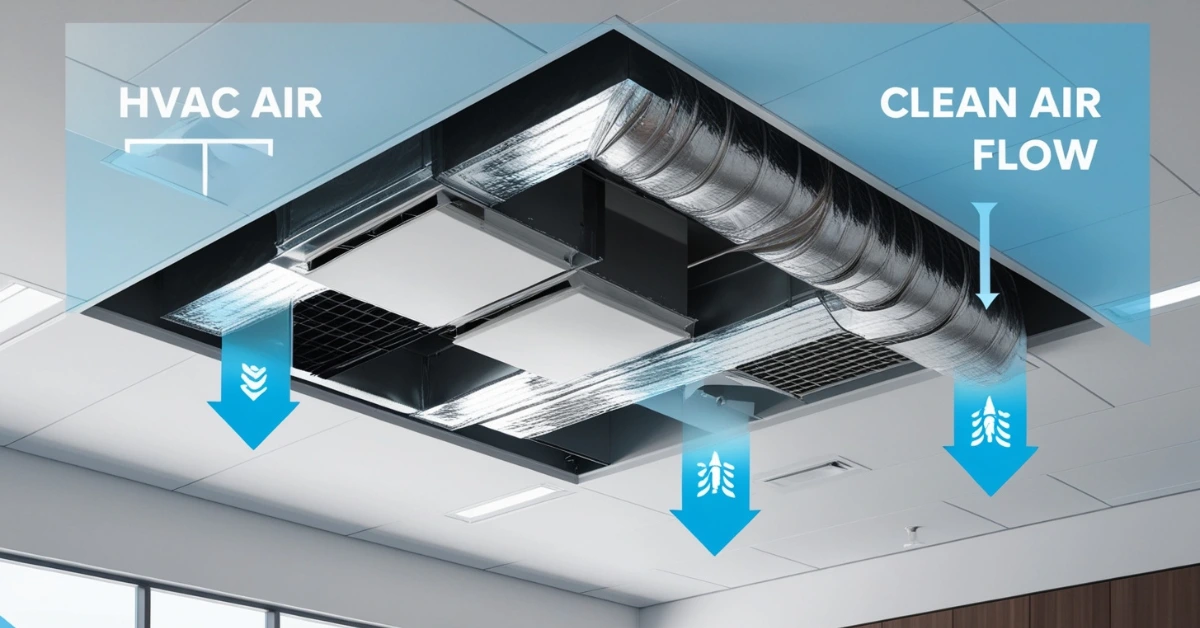
When we think of heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) we often focus on units, thermostats or vents. However, a key part of a building’s HVAC system that is often overlooked is the plenum ventilation system. Whether in homes, offices or large commercial spaces, plenum ventilation plays a crucial role in distributing air efficiently and maintaining indoor comfort.
What Is Plenum Ventilation?
Plenum ventilation refers to the method of using a plenum space, an open area above ceilings or beneath raised floors as a pathway for air circulation in a building’s HVAC system. Instead of relying solely on traditional ductwork to move air, plenum ventilation uses these larger, open spaces to distribute or collect air more efficiently.
This system works by either:
- Supplying air through a ceiling or floor plenum: where conditioned air from the HVAC unit is released into the plenum space and then directed into different rooms through diffusers or vents.
- Returning air by allowing used or warm air: to flow back through the plenum space to the HVAC unit for reconditioning.
Plenum ventilation is commonly used in:
- Office buildings
- Hospitals
- Schools
- Data centers
- Large commercial or industrial spaces
The main advantage of plenum ventilation is that it creates a centralized air pathway, which can simplify the layout of the HVAC system, improve airflow efficiency and reduce the need for extensive ductwork.
What Is a Plenum in HVAC Systems?
You can think of the plenum as the part of your HVAC system that helps move air in and out, much like how lungs support breathing in a body. It doesn’t condition the air itself but it plays a vital role in moving it efficiently and evenly throughout the space. In modern buildings, especially commercial setups, plenum ventilation offers several advantages over traditional duct only systems, which we’ll explore in detail below.
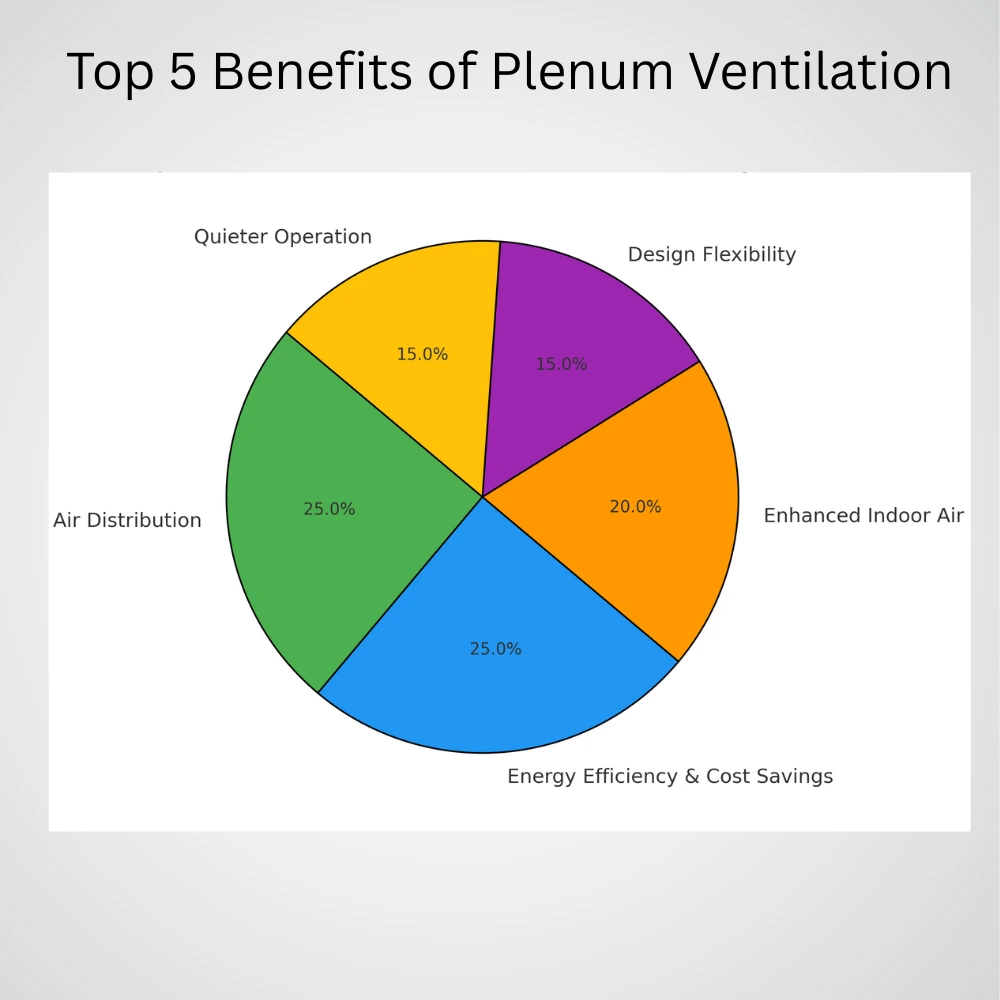
Top 5 Benefits of Plenum Ventilation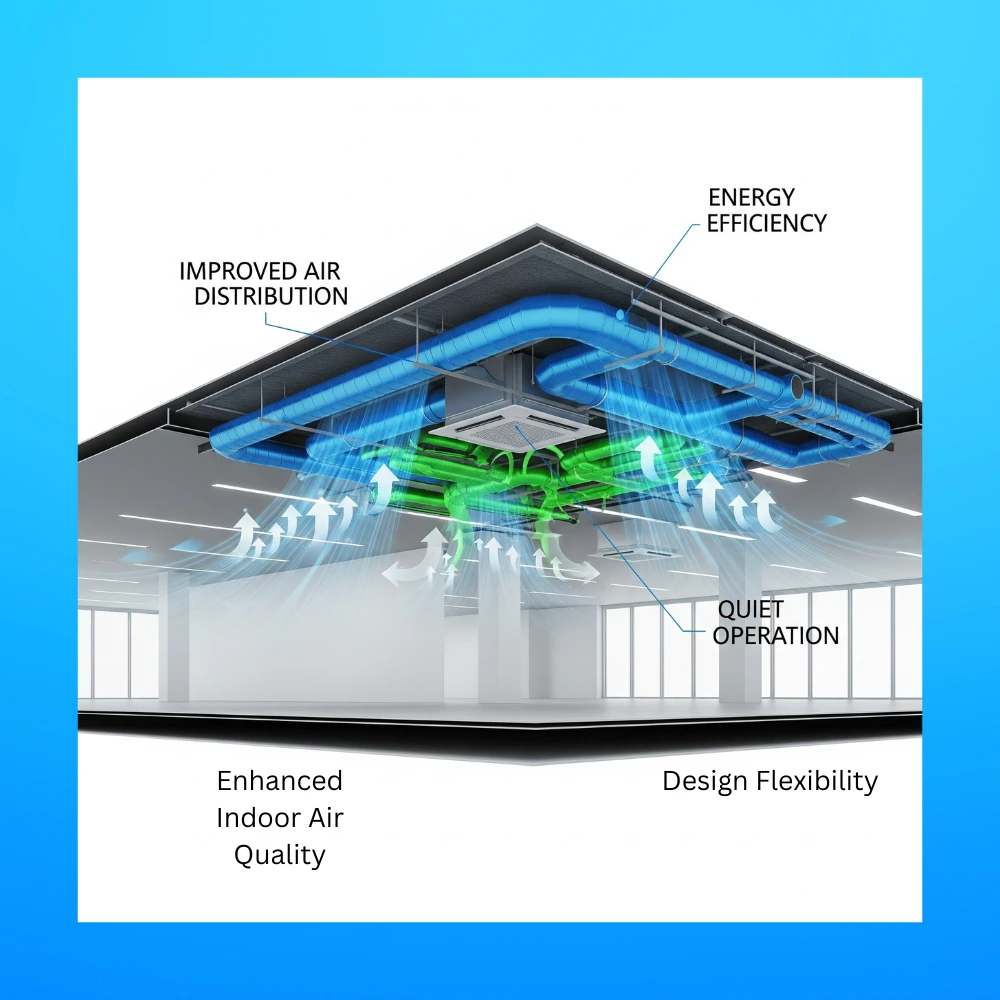
Below, we’ll explore the top five benefits of using plenum ventilation in modern HVAC systems.
1. Improved Air Distribution
A major benefit of plenum ventilation is that it helps circulate air more evenly across all areas of a building. In traditional HVAC setups, air ducts carry conditioned air directly from the air handling unit (AHU) to vents in different rooms. However, this method can sometimes result in uneven air distribution, especially in larger or multi story buildings.
With plenum ventilation:
- The plenum serves as a central space where air is either collected or dispersed throughout the system.
- Air is spread more evenly through diffusers or floor vents.
- Temperature variations between rooms are minimized.
This ensures that all areas of the building receive the proper amount of heated or cooled air, leading to consistent indoor comfort. It also reduces the chances of hot or cold spots, which can be a common complaint in buildings with poor air distribution.
2. Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Energy efficiency is a top priority in modern building design, both for environmental and economic reasons. Plenum ventilation plays a key role in boosting the energy efficiency of an HVAC system. Since the plenum space reduces the reliance on long ductwork and complex routing, air can move more freely and with less resistance.
Here’s how plenum ventilation contributes to energy efficiency:
- Lower fan power consumption: Less resistance in the airflow path means fans don’t have to work as hard.
- Minimized leakage: Fewer ducts and connections reduce potential leak points.
- Balanced air pressure: Well designed plenums help regulate airflow more efficiently, minimizing energy waste.
Over time, these efficiencies translate into lower utility bills and operational costs. Building managers can also enjoy a reduced carbon footprint, aligning with sustainability goals and green building certifications.
3. Enhanced Indoor Air Quality 
Indoor air quality (IAQ) has become a growing concern, especially in workspaces and schools where people spend long hours indoors. Low indoor air quality may cause health problems like fatigue, asthma and allergic reactions. Plenum ventilation helps combat these problems by providing better air exchange and supporting advanced filtration methods.
Benefits to air quality include:
- Faster removal of contaminants: Plenum ventilation allows for faster cycling out of stale or polluted air.
- Integration with filtration systems: Air in the plenum can pass through HEPA or MERV-rated filters before reaching occupants.
- Moisture regulation: Certain plenums include humidity sensors and control features to help keep indoor moisture at healthy levels.
In spaces like hospitals, laboratories or schools, maintaining excellent air quality is not just a comfort issue. It’s a health and safety requirement. Plenum ventilation provides a reliable infrastructure for meeting these standards.
4. Design Flexibility and Space Utilization
Plenum ventilation systems offer significant flexibility when it comes to building design. Because air can travel through open plenum spaces rather than being confined strictly to ducts, architects and engineers have more freedom in how they lay out HVAC components.
Here are some ways plenum ventilation improves design flexibility:
- Reduced need for ductwork: Less space is required for routing ducts through ceilings or walls.
- Modular construction compatibility: Ideal for buildings with modular or raised floor systems, such as server rooms or modern office spaces.
- Adaptability to renovations: Plenums can often be modified or expanded more easily than ducted systems during remodels or upgrades.
This flexibility not only makes HVAC design easier but also allows for cleaner architectural aesthetics, as there are fewer visible vents and bulky components. It also means that future building changes or expansions can be handled with minimal disruption to the existing HVAC setup.
5. Quieter Operation
Noise can be a major issue in traditional HVAC systems, particularly in offices, classrooms or residential buildings. The sound of air whooshing through ducts, along with the mechanical noise from fans and blowers, can create a distracting environment.
Plenum ventilation can help reduce these noise levels:
- Larger air volume movement: Air can move more slowly through larger plenum spaces, reducing turbulence and noise.
- Less mechanical strain: With more efficient airflow, mechanical components like fans and motors operate at lower speeds and volumes.
- Strategic placement: HVAC components can be placed farther from occupied areas thanks to the centralized nature of plenums.
This quieter operation contributes to better concentration, comfort, and overall occupant satisfaction especially in places where a calm environment is important, such as libraries or hospitals.
Conbclusion
Plenum ventilation plays a key role in modern HVAC systems by providing better air distribution, improved energy efficiency, enhanced indoor air quality, increased design flexibility and quieter operation. While it may not be necessary for every building, it offers significant advantages in medium to large scale installations, especially in commercial or institutional settings.
Before implementing a plenum based ventilation system, it’s important to consult with HVAC professionals or engineers. The design and function of the plenum, whether it’s for return air, supply air or both must be carefully planned to maximize performance and comply with building codes.