Power outages are a common issue in many places, especially during the summer or in areas with unstable electricity supply. Whether you’re working from home, running a small office or simply want to stay comfortable during a blackout, having a power backup system is essential. When it comes to power backup, two commonly used devices are the UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) and the inverter.
What is a UPS?
UPS, or Uninterruptible Power Supply, is a device that provides instant power backup when electricity goes out. The key benefit of a UPS is that it switches to battery power immediately, without any delay.
This instant switch ensures that sensitive electronic devices like:
- Computers
- Internet routers
- Security cameras
- Medical equipment
- Networking devices
stay running without a glitch. A UPS also protects these devices from power surges; voltage drops or short circuits, making it a great option for protecting your data and equipment.
How it Works?
A UPS has a built-in battery. When electricity is flowing normally, the battery stays charged. If the power supply cuts off, the UPS switches instantly to its battery, supplying power without interruption.
What is an Inverter?
An inverter is another power backup system, but it works differently. Instead of giving instant power, it takes a few seconds (usually 2 to 5 seconds) to turn on when power goes out. That’s because an inverter converts stored DC (Direct Current) from a battery into AC (Alternating Current) used by your appliances.
Inverters are commonly used in homes to run:
- Lights and ceiling fans
- Televisions
- Air coolers
- Mobile chargers
- Some kitchen appliances
In simple terms, an inverter acts as your home’s power reserve. When the main power fails, the inverter kicks in and runs basic appliances for hours, depending on the battery size.
Key Differences Between UPS and Inverter
To help you choose wisely, let’s break down the main differences in simple points.
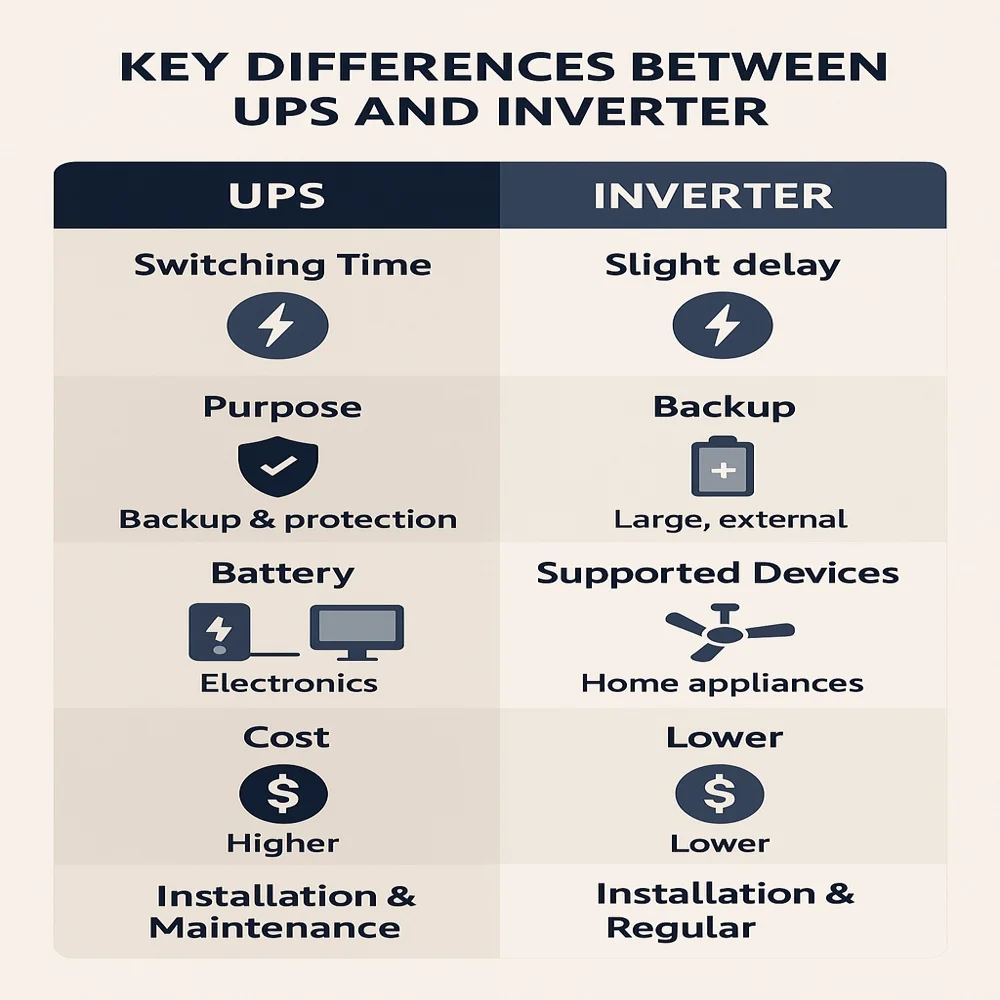
1. Switching Time
- UPS: Instant (0 milliseconds). No disruption.
- Inverter: Slight delay (2–5 seconds). Can cause a brief pause or restart in devices.
This is why UPS is the better choice for devices like computers or modems that need constant power.
2. Purpose
- UPS: Meant for both power backup and protection from voltage issues.
- Inverter: Focuses only on providing backup power.
If your devices are sensitive to power changes, UPS offers added safety.
3. Battery Type and Capacity
- UPS: Has a small, internal battery. Good for short-term backup (15–30 minutes).
- Inverter: Uses large, external batteries. Can run multiple appliances for several hours.
Inverters are designed to handle long outages, while UPS is for short-duration support.
4. Devices It Supports
- UPS: Ideal for electronics like PCs, routers, medical equipment.
- Inverters: work well for running everyday household items such as ceiling fans, light bulbs and televisions.
5. Cost
- UPS: More expensive per watt. Limited capacity.
- Inverter: More cost-effective for long back up and running multiple appliances.
6. Installation and Maintenance
- UPS: Plug-and-play. Minimal maintenance.
- Inverter: Needs professional installation and regular battery maintenance (especially if using tubular or lead-acid batteries).
Advantages and Disadvantages
Let’s look at the pros and cons of both systems to help you understand them better.

1. UPS
Pros
- Provides instant power without delay
- Protects devices from voltage fluctuations
- Keeps internet and computers safe during outages
- Easy to install and use
Cons
- Short backup time
- Expensive for larger capacity
- Not meant for powering heavy appliances
2. Inverter
Pros
- Runs appliances for hours
- Affordable for large backup needs
- Can power multiple rooms
- Ideal for homes with long outages
Cons
- 2–5 second switching delay
- No surge or voltage protection
- Requires maintenance and battery care
When Should You Choose a UPS?
Choose a UPS if
- You use a desktop computer for work or business
- You have a home office and can’t afford a sudden shutdown
- You run sensitive equipment (like medical devices)
- Internet connectivity is essential for your daily tasks
- You want both backup and protection for your electronics
Even a small UPS can save your files from being lost during power cuts or protect your expensive electronics from damage.
When Should You Choose an Inverter?
Choose an inverter if
- If you often experience long and repeated electricity outages in your area.
- You want to run lights, fans and a few other appliances for hours
- You need a cost-effective and long-lasting power solution
- You don’t need instant switching
- You’re looking to back up multiple rooms or a full small home
Inverters are perfect for regular household use and provide quiet, efficient backup during outages.
Can You Use Both?
Yes! Many people use both a UPS and an inverter, especially if they have a home office or run a small business.
Here’s a common setup:
- UPS for computers, routers and network systems
- An inverter is a reliable choice for powering household essentials like lights, fans and basic appliances.
This gives you full protection, smooth operation and long backup in one setup.
Types of Inverters to Know
If you decide to go with an inverter, you should know there are different types:
- Square wave inverters: Cheapest but not suitable for sensitive devices
- Modified sine wave inverters are an affordable option that works with many homes’ devices
- pure sine wave inverters provide cleaner, more stable power similar to what you get from the main electricity supply. Ideal for all devices but more expensive
Choose based on your budget and the types of devices you’ll power.
Safety and Maintenance Tips
Whether you choose a UPS or inverter, proper care helps it last longer and perform better.
Here are a few tips:
- Don’t overload the system beyond its capacity
- Keep the device in a dry, ventilated area
- Check battery health every few months
- If using tubular batteries, top up water when needed
- Use branded batteries and quality wires for safety
- Hire a certified technician for installation
Final Thoughts
Both UPS and inverters solve the same problem power outages, but in different ways.
- A UPS is best if you need immediate power and want to protect sensitive devices.
- An inverter is best if you want to run your home appliances for hours during long blackouts.
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer. It depends on how often you face power issues, what kind of devices you use and how much you’re willing to invest.
If your budget allows, using both systems gives you the best balance of safety, convenience and long backup.
Related Topic: Snowbreak Locate Uninterruptible Power Supply: Reliable Power