In our mobile-driven lives, phones are essential for calling, texting, browsing, banking, and social media. But how do they connect to networks and identify users? The answer lies in the tiny yet powerful SIM card Subscriber Identity Module that makes mobile communication possible by linking your phone to a network. This small chip is critical for every mobile device, from basic phones to the latest smartphones, ensuring connectivity and user identification.
What Is a Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) Card?
A Subscriber Identity Module card, or SIM card, is a small plastic chip with an embedded microcircuit. It’s usually inserted into your mobile phone and serves one major purpose: to identify and authenticate the subscriber (that’s you) to the mobile network.
When you buy a new phone or switch to a different carrier, the SIM card is what lets you make calls, send texts, and use mobile data. Without it, your phone can’t connect to the network to perform basic communication functions.
The SIM card stores important information such as:
- Your International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI)
- The mobile network’s authentication key
- Phone number linked to the network
- Text messages and contacts (in some phones)
- Carrier settings and preferences
In simple terms, the SIM tells your mobile network provider, “This is who I am, and this is the plan or services I’m allowed to use.”
How Does a SIM Card Work?
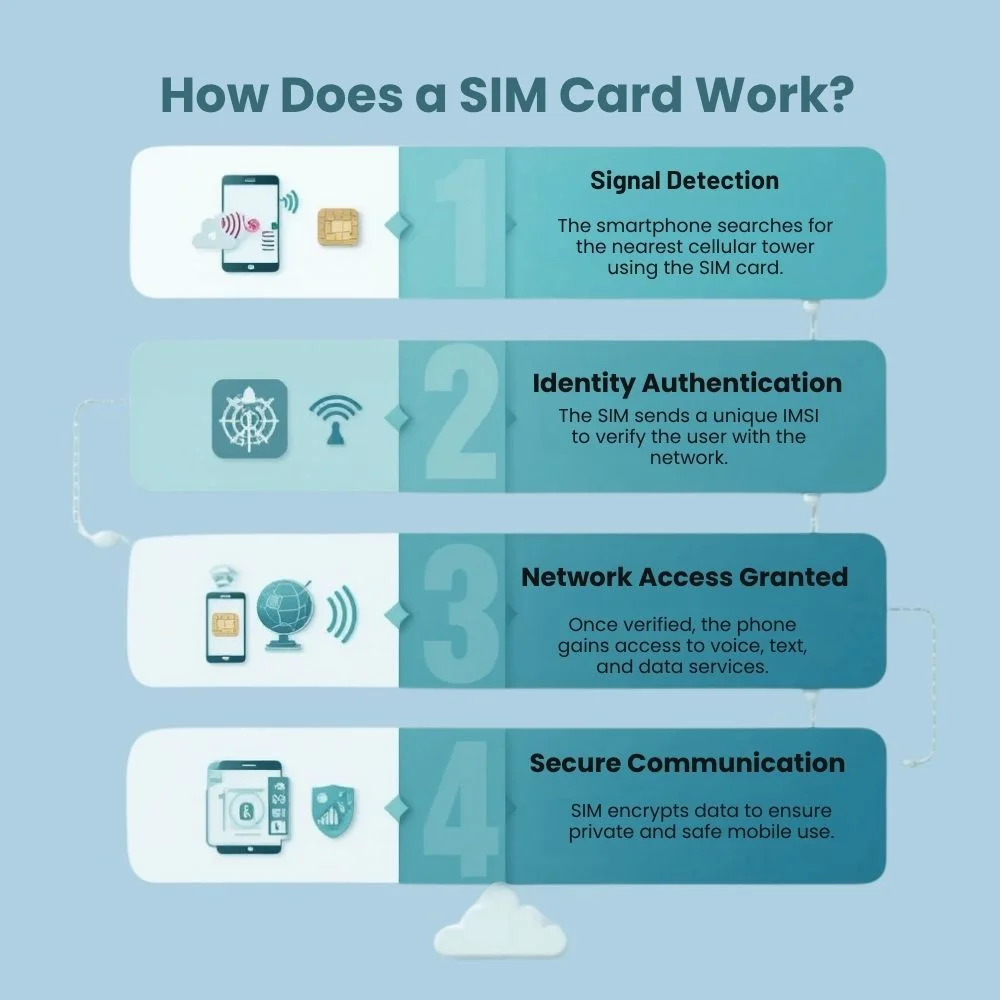
A SIM card works by securely storing your identity and allowing your phone to connect with your mobile network. The process starts when you insert the SIM into your device and power it on. Here’s how it works step-by-step:
- Network Detection: Your phone detects the nearest cell towers and reaches out to your mobile service provider.
- Authentication: The SIM transmits a unique identifier, known as the IMSI, to the mobile network to establish your identity.The network checks if the card is valid and if the services are active.
- Connection Established: Once authenticated, the network allows your device to connect. You can now make calls, send texts, or use mobile data.
- Secure Communication: The SIM card uses built-in security codes to make sure your communication is encrypted and private.
So even though the SIM card is tiny, it’s a smart little tool that handles your mobile identity, communication access, and network security.
Types of SIM Cards
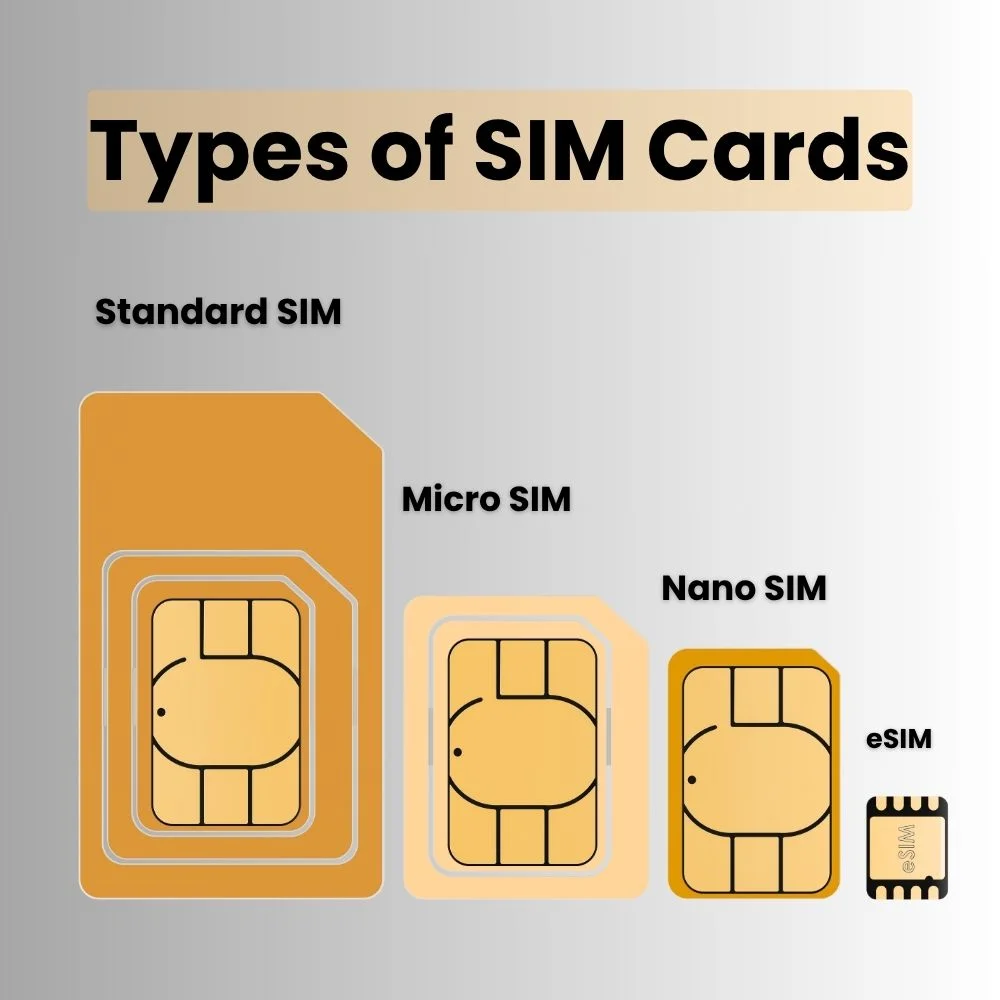
Over time, SIM cards have evolved in size and function. Here are the common types:
- Standard SIM: The original size, mostly used in older mobile phones.
- Micro SIM: A smaller version that became popular with earlier smartphones.
- Nano SIM: The smallest and most widely used today in modern smartphones.
- Embedded SIM (eSIM): A digital version built directly into the device no physical card is needed. Settings can be changed through software.
Each version works the same way it simply depends on the size and how your device uses it.
Why Is a SIM Card Important?
SIM cards do much more than just allow phone calls. They are essential for many everyday mobile tasks:
- Network Access: Without a SIM, your phone can’t connect to the cellular network for calling, texting, or using data.
- Phone Number Identity: Your phone number is usually linked directly to your SIM card.
- Roaming Services: SIM cards help you stay connected when traveling by allowing your phone to use networks in other countries.
- Switching Devices Easily: You can move your SIM card from one device to another and keep your number and carrier services.
- Carrier Settings: Some settings like network preferences or internet configurations are stored on the SIM.
Can a SIM Card Store Data?
Yes, but only a small amount. SIM cards are not meant to store files like music or videos. However, they can save:
- Up to 250 contacts (in older phones)
- Text messages
- Carrier-specific settings
Modern smartphones mostly save contacts and messages in cloud services or internal storage, but in basic phones, the SIM can still act as a mini storage device.
How to Insert and Remove a SIM Card?
Depending on your phone model, inserting or removing a SIM card can be slightly different. Here’s a general guide:
- Turn off your phone before removing or inserting the SIM.
- Use the SIM ejector tool (or a paperclip) to open the SIM tray.
- Place the SIM card into the tray with the gold chip facing down.
- Carefully slide the tray back into the phone.
- Power on the device and allow it a moment to establish a network connection.
Be sure to handle your SIM card with care, and refrain from touching the gold-plated contacts to prevent damage
What Happens if You Remove Your SIM Card?
When the SIM card is removed from your phone, certain network-dependent functions become unavailable
- Your phone will lose access to the network.
- You won’t be able to make calls, send texts, or use mobile data.
- You may still use the phone over Wi-Fi (for browsing, apps, etc.).
- Any data stored on the SIM (contacts/messages) will no longer be visible.
Removing a SIM card does not delete anything from your phone, but it temporarily disconnects you from mobile services.
Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) Cards and Mobile Security
SIM cards play a key role in mobile security. Here’s how:
- PIN Protection: You can set a PIN to prevent unauthorized use of the SIM card.
- Encryption: SIM cards help encrypt your communication so others can’t intercept your calls or messages.
- Carrier Control: Carriers can block a lost or stolen SIM to prevent misuse.
In case your phone is lost or stolen, contacting your mobile provider to disable your SIM card is a smart security step.
Is It Possible to Operate a Mobile Phone Without a SIM Card?
Yes, but with limitations. A phone without a SIM card:
- Can connect to Wi-Fi and use internet-based apps like WhatsApp or Skype.
- Cannot make regular calls or send traditional texts.
- Can still be used as a minicomputer, camera, or music player.
This is common with kids’ devices or backup phones used only on Wi-Fi.
Final Thoughts
The SIM card is a tiny chip with big responsibilities. It identifies your device, enables mobile communication, stores data, and ensures security. With evolving tech like eSIMs and 5G, SIM cards are getting smarter but remain essential. Knowing how they work helps you stay connected and protected.