In the connected world, the term bandwidth appears frequently during home Wi-Fi setups, video streaming, or virtual meetings like Zoom. But what does it really mean? Bandwidth refers to the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted over an internet connection in a given amount of time. Understanding this concept doesn’t require a technical background just a simple explanation.
What Does Bandwidth Mean?
Bandwidth refers to the highest volume of data that can be transmitted through an internet connection within a specific period. Think of it like a water pipe. Just like a broader pipe lets more water flow through it effortlessly, having a higher bandwidth allows a larger volume of data to move through your internet connection every second.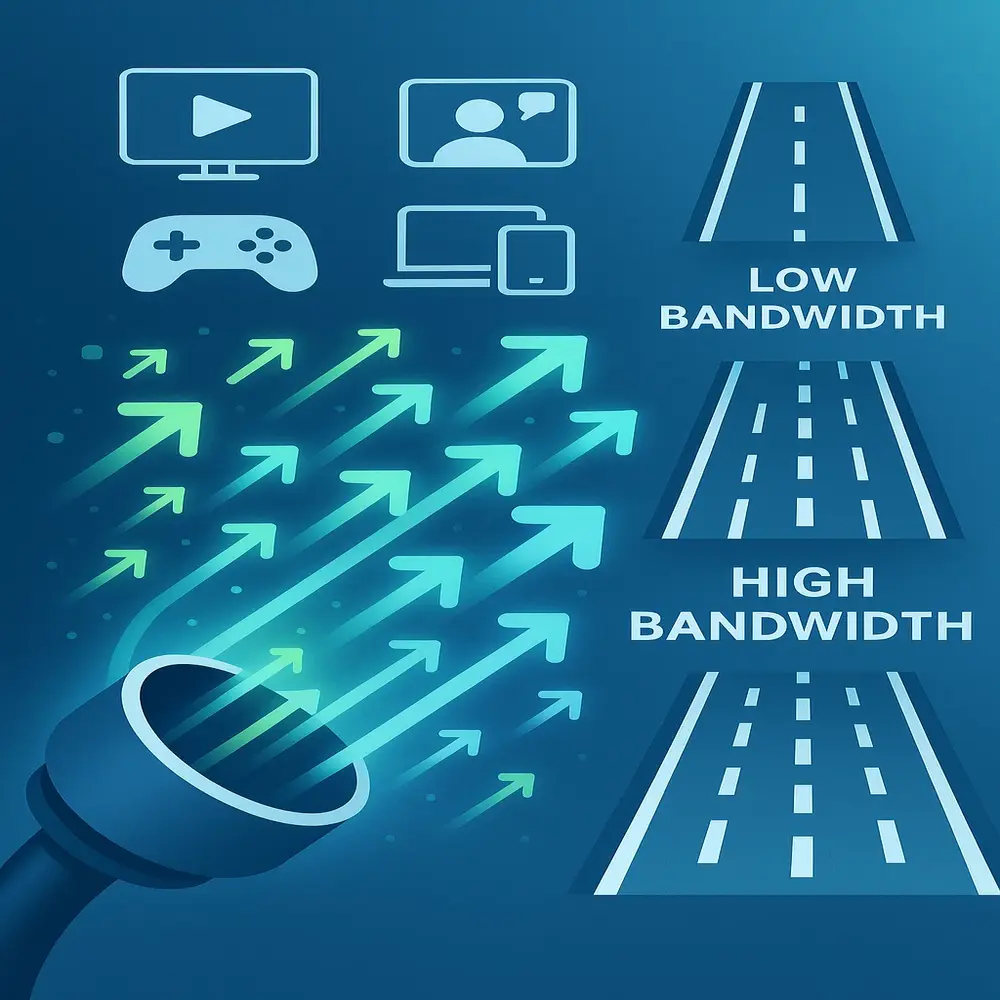
- It is usually measured in megabits per second (Mbps) or gigabits per second (Gbps).
- More bandwidth means faster data flow, not necessarily faster internet (we’ll explain that in a moment).
- It affects how quickly websites load, how smooth video streaming is, and how stable your video calls are.
So, bandwidth doesn’t mean how fast your internet is, but how much data it can carry at once.
Bandwidth vs. Internet Speed
Many people confuse bandwidth with internet speed. While they are closely related, they’re not the same thing.
- Bandwidth is the capacity of the connection (like the width of the road).
- Internet speed is how fast data travels on that connection (like how fast your car moves).
You can also picture it as a multi-lane highway the wider the road (higher bandwidth), the more vehicles (data) can travel at once without causing traffic or delays. But if cars are stuck in traffic (slow speed), even a wide road won’t help. That’s why both a strong connection and proper speed are important for a smooth online experience.
Why Bandwidth Matters in Daily Life?

Most people don’t notice it until something starts lagging or buffering. Here’s where a good internet connection becomes essential:
1. Streaming Videos
- Watching YouTube, Netflix, or any other streaming service requires a lot of bandwidth.
- High-definition (HD) or 4K videos consume even more.
- When it is low, it can cause interruptions like video buffering or reduced streaming quality.
2. Video Calls and Conferences
- Apps like Zoom, Google Meet, or Microsoft Teams need a solid connection to send and receive video and audio.
- Without enough bandwidth, video may freeze or become blurry, and audio may cut out.
3. Online Gaming
- Games often require both fast speeds and enough data capacity to run smoothly.
- It affects game updates, voice chats, and real-time player actions.
4. Multiple Devices at Home
- Phones, laptops, smart TVs, and even appliances like smart fridges use the internet.
- The more devices connected, the more bandwidth is shared.
- This is why the internet slows down when many devices are in use at the same time.
Download vs. Upload Bandwidth
Most internet plans mention two types of bandwidth:
- Download speed refers to the amount of data your device can receive from the internet within a certain time frame.
- Upload bandwidth is how much data you can send to the internet.
For most users:
- Downloading is more important (watching videos, loading pages, etc.).
- Uploading matters when you’re sending large emails, posting videos, or in video calls.
How Much Bandwidth Do You Need?
The amount of internet capacity you need usually depends on how you use the internet and how many devices or people are connected and actively sharing that connection. Here’s a basic guide:
| Activity | Recommended Bandwidth per device |
| Browsing, email | 1-5 Mbps |
| Video calls | 2-10 Mbps |
| HD streaming | 5-8 Mbps |
| 4K streaming | 15-25 Mbps |
| Online gaming | 3-6 Mbps |
| Large downloads | 20+ Mbps |
If you live with others and everyone uses devices at the same time, you’ll need to add up the needs to avoid slowdowns.
Common Problems Related to Bandwidth
Even with a high-speed plan, you might still face issues due to how it is used. Some common issues include:
- Network congestion: Too many users or devices at once.
- Wi-Fi interference: Wi-Fi performance can also be affected by interference from walls, electronic appliances, or poor router placement.
- ISP throttling: Some providers slow down speed after data limits are reached.
- Outdated equipment: Old routers or cables may not support higher speeds.
Tips to Improve Bandwidth Usage
Better managing your connection helps avoid strain and keeps things running smoothly.
- Limit unnecessary background apps.
- To improve your connection, consider upgrading your router to one that supports newer standards such as Wi-Fi 6.
- Use Ethernet cables for stable connections on PCs or smart TVs.
- Additionally, place your router in a central, open location to ensure better signal coverage across your space.
- Upgrade your plan if your usage has increased significantly.
How ISPs Provide Bandwidth?
Internet Service Providers (ISPs) offer different plans based on it. These plans decide how much data can flow to and from your home or office. When choosing a plan:
- Look at download and upload speeds.
- Check for data caps (limits on how much data you can use monthly).
- Compare plans for your area based on reviews and actual performance.
Shared Bandwidth in Offices or Public Places
In public Wi-Fi zones like cafes, airports, or schools, many users share the same connection. This is called shared bandwidth, and it can slow down speeds because everyone is drawing from the same “pool.”
In businesses and offices, having dedicated bandwidth is important to ensure a stable internet connection for multiple employees.
The Future of Bandwidth
As technology grows, our demand for strong internet keeps increasing. Here’s what we can expect:
- 5G networks are already boosting mobile internet bandwidth.
- Fiber-optic connections are replacing old copper wires to offer gigabit speeds.
- IoT (Internet of Things) means more connected devices in homes and offices, needing more bandwidth.
- Remote work and online learning trends are making high bandwidth more important than ever.
Final Thoughts
It might seem like a technical term, but it plays a big role in our everyday digital life. From watching Netflix without buffering to having clear video calls, it’s all about how much data your connection can handle at once. By understanding what it is, how it works, and how to manage it, you can make smarter choices when picking internet plans, setting up your Wi-Fi, or troubleshooting slow connections.