We rely on computers and storage systems to keep our data safe, so knowing how that data is protected is more important than ever. One method many people and businesses use is called RAID 10. It might sound like a complicated tech term, but it’s just a smart way to keep your data fast and safe at the same time.
What Does RAID Mean?
RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks. Data is stored across multiple hard drives or SSDs to ensure it remains safe even if one of the drives stops working. RAID helps balance two main things:
- Speed: Making data read and write faster
- Redundancy: Keeping backup copies to avoid data loss
There are different levels of RAID, such as RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, and RAID 10. Each level has its way of storing and protecting data. Among these, RAID 10 is considered one of the best combinations of speed and safety.
What is RAID 10?
RAID 10 is a mix of RAID 1 (mirroring) and RAID 0 (striping). That’s why it’s often called a hybrid RAID.
- Mirroring (RAID 1) means that every piece of data is copied to another drive. This means that if one drive fails, an identical copy of the data is still available on another drive.
- Striping (RAID 0) means that data is split across two or more drives to make reading and writing faster.
RAID 10 combines both. First, it mirrors the data, and then it strips it across multiple mirrored pairs.
Example of How It Works?
Imagine you have four hard drives:
- Drive A and Drive B are a mirror pair
- Drive C and Drive D are another mirror pair
Then, the data is split (striped) across the two mirrored pairs. So:
- Half of the data goes to the A-B pair
- The other half goes to the C-D pair
If Drive A fails, Drive B still has your data. If Drive C fails, Drive D still holds the copy. This gives redundancy (data safety) and speed (faster access).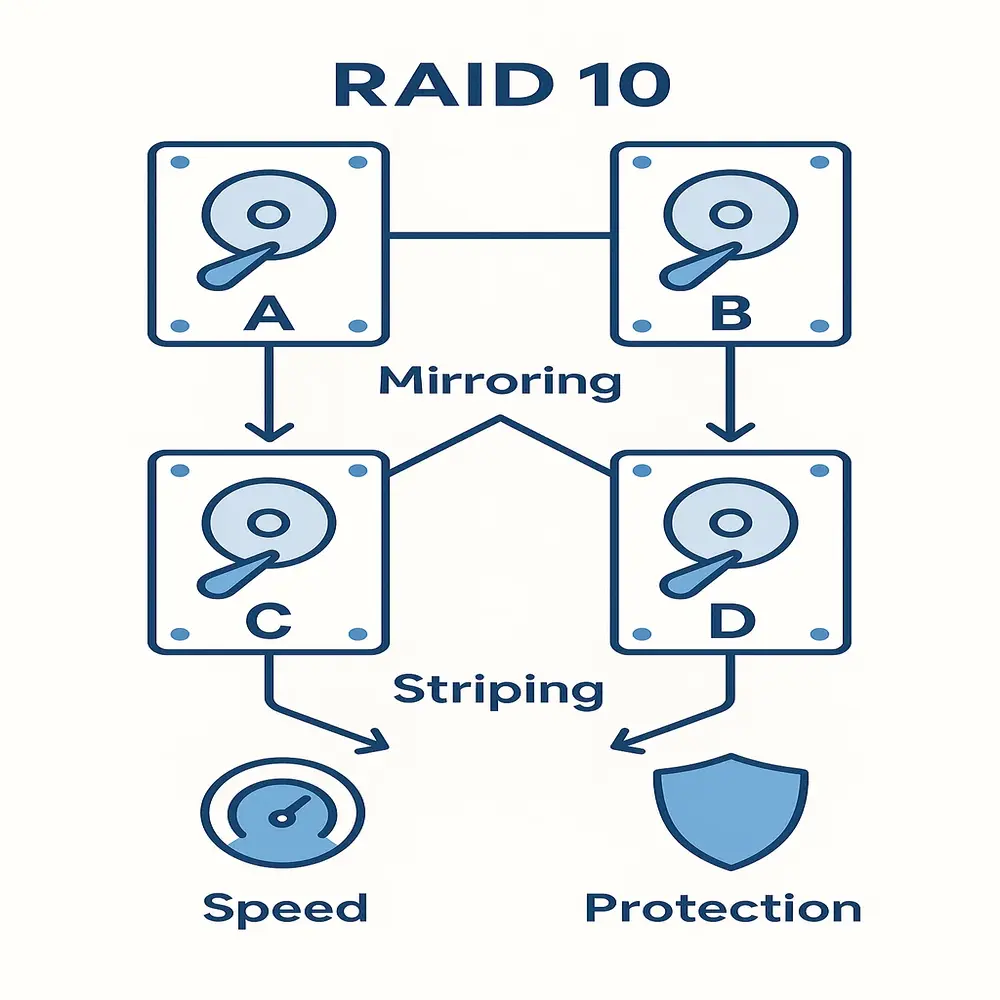
Why is RAID 10 Popular?
Many systems use RAID 10 to achieve both high performance and reliable data protection. It commonly supports:
- Business servers
- Database storage
- Gaming PC’s
- Video editing systems
- Cloud hosting services
Main Benefits of RAID 10
Here are the top reasons people choose RAID 10:
- High performance: Fast read and write speeds
- Strong data protection: Keeps working even if a drive fails
- Quick recovery: Rebuilding after a crash is faster than other RAID types
- Easy setup in modern systems: Supported by many hardware and software tools
How RAID 10 Protects Your Data?
It protects your data by creating multiple copies (mirroring). If one hard drive breaks, you still have a working copy on the other drive. This means your system stays running, and your data remains safe.
Also, because it uses striping, it spreads the workload across drives. So even while protecting data, it doesn’t slow things down.
Real-World Example
Let’s say you’re editing a video on a RAID 10 system. Stripping the video files across drives gives you fast access to them. If one of the drives fails during your work, the mirror copy kicks in automatically. The system preserves your data, allowing you to continue working smoothly.
Things to Keep in Mind
While RAID 10 is excellent, it’s not perfect. There are some important things to know:
- Uses more drives: It requires a minimum of four drives to function, which is more than some other RAID levels.
- Half storage available: If you use 4 TB (4 drives × 1 TB), only 2 TB is usable due to mirroring
- Not a backup: RAID 10 protects from hardware failure, but not from accidental deletion or viruses. You still need to back up your data separately
When Should You Use RAID 10?
RAID 10 is best when:
- You need both speed and safety
- You can afford at least four drives
- You run systems that can’t afford downtime
- It is especially useful when working with large files, such as videos or databases.
Here are some use-case examples:
- Video editors: Need fast data access and can’t afford to lose work
- Database managers: Require high-speed input/output and must keep data safe
- Gamers and streamers: Gamers and streamers benefit from faster load times and smoother game recording with it
- Web hosting services: Must serve many users while keeping websites live even during a failure
How to Set Up RAID 10?
Setting up RAID 10 depends on whether you’re using hardware RAID (a special RAID controller) or software RAID (through your operating system).
Basic Steps:
- Install four or more drives of the same size and speed
- Enter BIOS or RAID controller settings
- Choose RAID 10 as the configuration
- Follow the wizard or setup process
- After creating the RAID 10 volume, you should format it and install your operating system or necessary software.
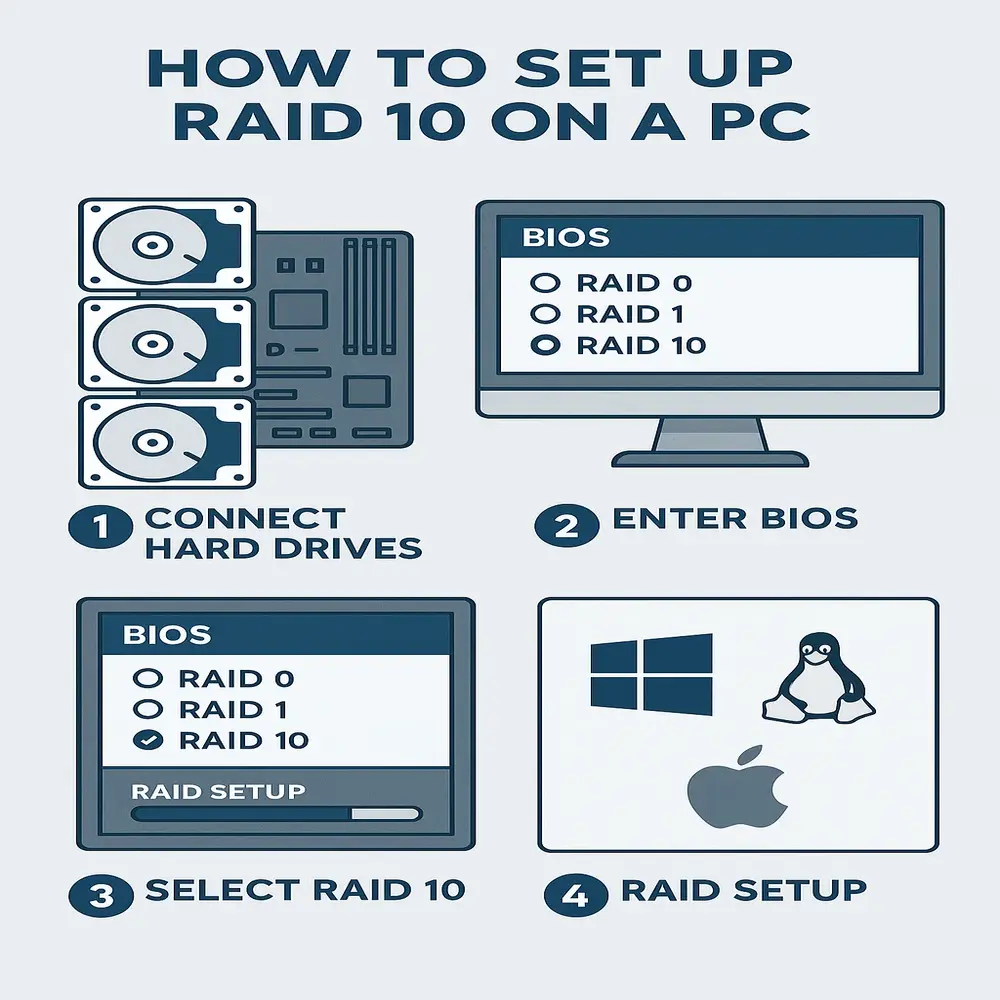
Windows, Linux, and macOS offer built-in tools to configure RAID, but hardware RAID provides better performance and greater control.
What Happens If a Drive Fails?
If a drive within a mirrored pair fails, the system continues operating using the remaining healthy drive. You will get a warning, and the system will run in degraded mode. You simply replace the failed drive, and the RAID system will rebuild the missing copy using the healthy drive.
Systems can still preserve data if multiple drives fail from different mirror pairs, but data loss will occur if both drives in the same mirror pair fail. That’s why RAID is not a full backup; it’s a part of your protection plan.
Final Thoughts
RAID 10 is a smart solution for anyone who wants fast and safe data storage.RAID 10 merges the speed advantages of RAID 0 with the data redundancy of RAID 1. You get the speed you need and the peace of mind knowing your data is safe if a drive fails. It’s perfect for businesses, professionals, or even serious gamers who want top performance without taking big risks.
Related Topic: What Is a PowerEdge RAID Controller?