SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) is a computer-based system used to monitor and control industrial processes in real time from a central location. It’s essential in industries like power, water, and manufacturing, helping operators track performance, detect issues, and automate operations for smooth, efficient functioning.
Why is Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) Important?
SCADA systems are important because they help:
- Monitor everything in real time
- Control equipment from a distance
- Collect and store data for later analysis
- Send alerts when something goes wrong
- Make operations more efficient and safer
Without SCADA, large operations like power grids, manufacturing plants, and oil pipelines would be much harder and riskier to manage.
Where is (SCADA) Used?
SCADA systems are used in many industries. Some common examples include:
- Electric power plants to manage electricity flow
- Water and wastewater facilities use SCADA systems to oversee the treatment of clean water and the management of sewage operations efficiently
- SCADA systems are used in oil and gas pipelines to monitor flow rates, pressure levels, and ensure safe, continuous operations
- Factories to control robots, machines, and assembly lines
- Transportation systems such as railways, traffic lights, or airports
- Food and beverage industries for process control and safety
Basically, anywhere something needs to be monitored and controlled remotely, SCADA can be useful.
How Does SCADA Work?
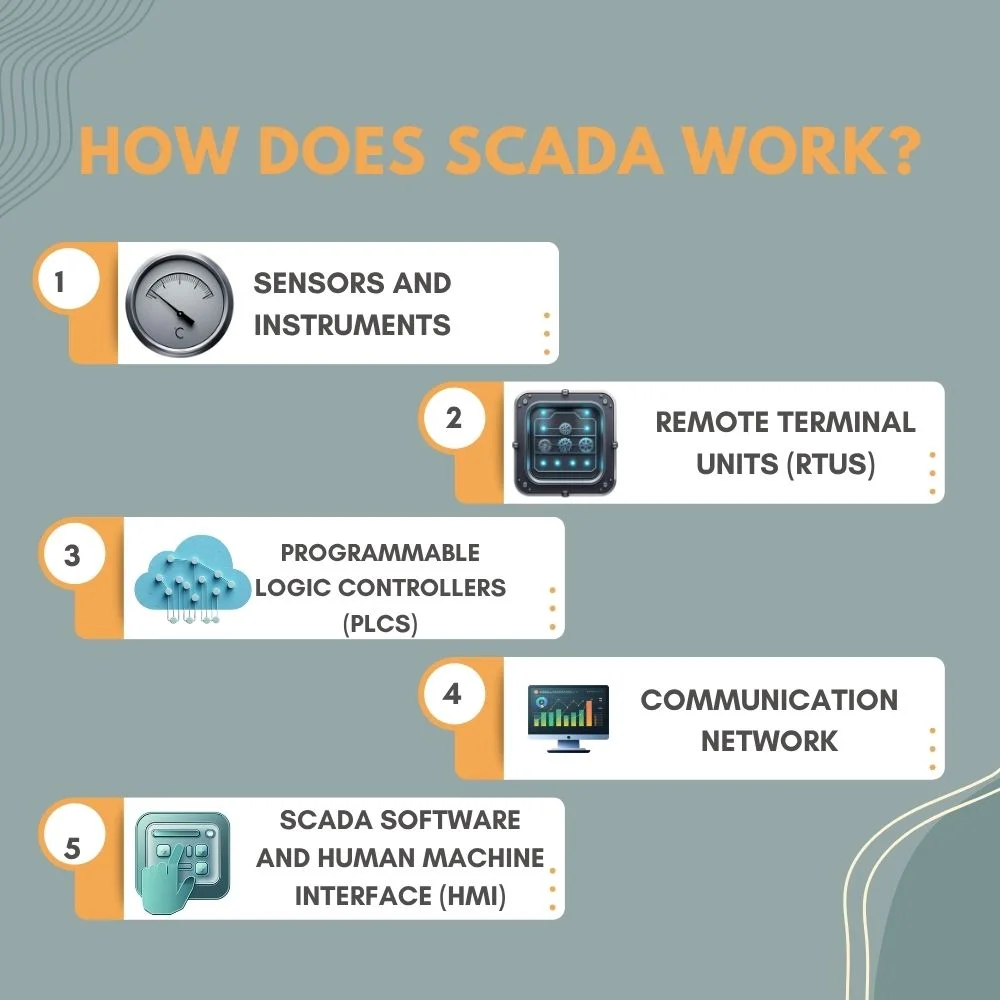
A SCADA system works by collecting data, processing it, and sending commands. Here’s a simplified explanation of the main parts of a SCADA system:
1. Sensors and Instruments
These are the devices that collect data. They measure things like temperature, pressure, flow, speed, and more. Think of them as the “eyes and ears” of the system.
2. Remote Terminal Units (RTUs)
These are small computers located near the equipment. They gather the information from sensors and send it to the central system. RTUs are also capable of receiving commands and directly operating connected machinery or equipment
3. Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs)
PLCs are similar to RTUs but often used in more complex or local automation tasks. They can make quick decisions based on logic rules and handle repetitive tasks like turning motors on or off.
4. Communication Network
All the collected data has to be sent somewhere. The communication network links RTUs, PLCs, and sensors to the central computer using cables, radio signals, or even satellite connections.
5. SCADA Software and Human Machine Interface (HMI)
This is the brain of the system. The software collects data from the field, displays it on a computer screen, and allows humans to see what’s happening. The HMI is what operators use to monitor data, get alerts, and send control commands. It’s usually shown as dashboards, graphs, buttons, and warning signs.
What Can You Do with SCADA?
Once the SCADA system is set up, you can do many things without physically going to each machine or location. Some of the common tasks include:
- Viewing real-time data like temperature or flow rate
- Changing settings such as opening a valve or turning off a motor
- Setting alarms to alert you when something goes wrong
- Generating reports for inspections or performance analysis
- Logging data for future planning or legal compliance
This makes SCADA a valuable tool for managers, engineers, and technicians alike.
Real-World Example
Imagine a water company that supplies drinking water to a city. Using SCADA, the operators can sit in an office and see how much water is being pumped from wells, the water pressure in pipes, and whether the filters and pumps are working correctly. If something fails, like a pump overheating, the system will sound an alarm, and the operator can turn it off remotely or call a technician.
Without SCADA, someone would have to drive to each pump, check meters by hand, and call others by phone a slow and inefficient process.
Benefits of (SCADA)
SCADA systems provide many benefits for companies and workers:
- Saves time by allowing remote control and monitoring
- Improves safety with early warnings and alarms
- Reduces cost by avoiding breakdowns and downtime
- Increases efficiency by automating routine tasks
- Supports decision making through data collection and analysis
By using SCADA, businesses can work smarter, respond faster to problems, and maintain better control over their operations.
SCADA and Cybersecurity
One important topic when discussing SCADA is security. Since these systems control critical infrastructure, they can be targets for cyberattacks. That’s why many modern SCADA systems are built with strong cybersecurity measures like:
- Password protection
- Encrypted communication
- Firewalls and antivirus tools
- User access control
- Regular software updates
Operators and IT teams need to work together to keep the system secure from outside threats.
Future of SCADA
As technology grows, SCADA is also changing. New trends include:
- Cloud-based SCADA that allows access from anywhere with an internet connection
- Mobile apps for real-time alerts and monitoring on smartphones
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) for smarter data analysis and predictions
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) where more devices are connected and smarter decisions can be made automatically
These innovations are making SCADA even more powerful, flexible, and useful in industries that never used it before.
Conclusion
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) is more than just a system it’s an intelligent solution for monitoring and managing critical operations from one central interface. It’s used in many industries to make operations more reliable, safe, and cost-effective. From water plants and energy stations to factories and transportation systems, SCADA plays a big role in modern infrastructure.



