When it comes to running a server, performance, speed, and data safety are extremely important. That’s where PowerEdge RAID Controllers (PERC) come into play. These controllers are specifically designed by Dell for their PowerEdge server line, enabling businesses to manage data storage more efficiently and securely.
Why Understanding PERC Matters?
If you’re managing a business server, building a data center, or simply curious about how storage works at a higher level, understanding PERC is a great step. Let’s break down what it is, what it does, and why it matters in everyday language.
What is a PowerEdge RAID Controller (PERC)?
The PowerEdge RAID Controller is Dell’s custom-made hardware RAID solution that comes with or is available for Dell PowerEdge servers. PERC helps servers read and write data to multiple hard drives in a smart way.
It keeps your data safe if one drive fails, speeds up how fast data is read and written, and helps organize everything behind the scenes.
There are many versions of PERC, such as: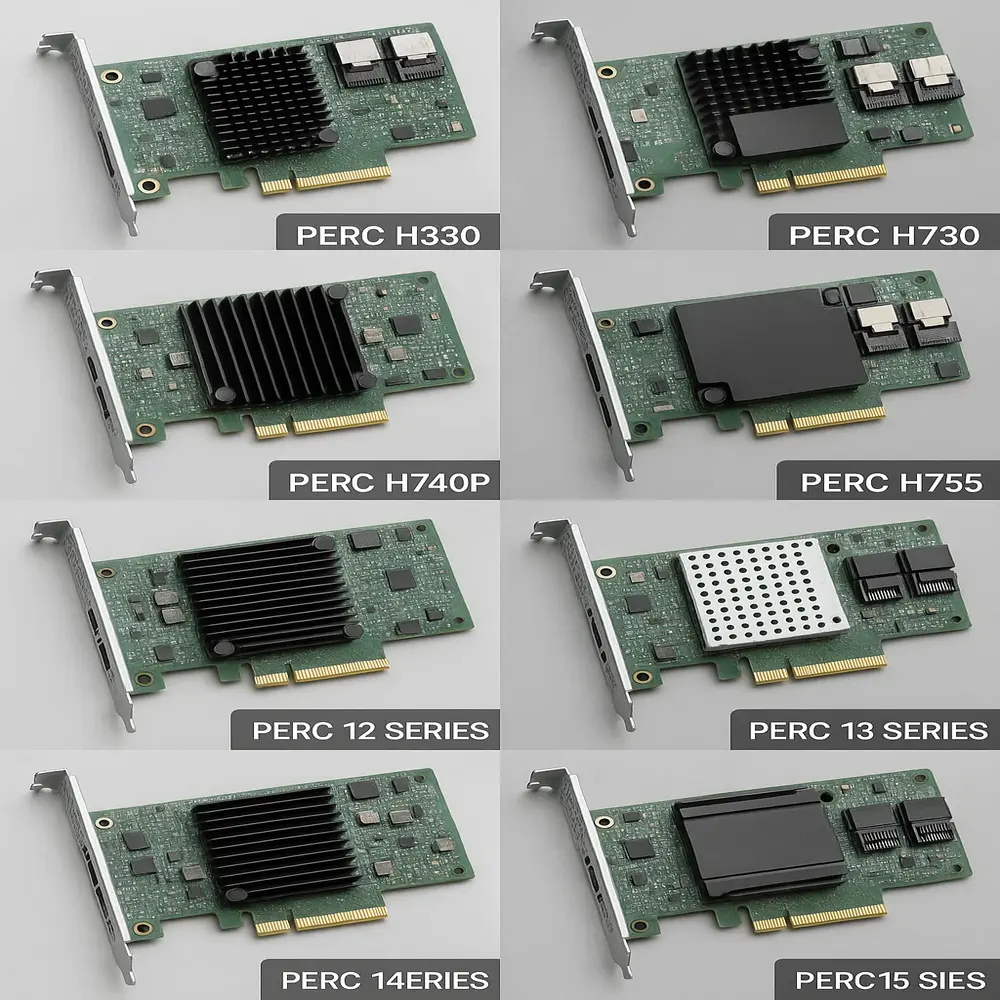
- PERC H330
- PERC H730
- PERC H740P
- PERC H755
- PERC 12, 13, 14, and 15 series
Each new generation brings better performance, more features, and improved reliability.
Why is a RAID Controller Important?
Here’s why using a RAID controller, especially PERC, is so useful:
- Data Protection: RAID helps keep data safe. If one drive fails, your data is still available from another.
- Improved Speed: RAID allows data to be spread out over many drives, so it can be accessed and saved faster.
- Simplified Management: PERC helps manage everything automatically, making the system easier to control.
- Better Uptime: Your server stays running even if one drive fails.
This is why businesses that can’t afford data loss or downtime always choose to use a RAID controller in their servers.
Features of PowerEdge RAID Controllers
Let’s explore what makes PERC stand out:
- Multiple RAID Levels: Compatible with RAID levels 0, 1, 5, 6, 10, 50, and 60 for versatile storage configurations. Each level offers different balances between speed and safety.
- Cache Memory: Some models have cache memory (like 1GB, 2GB, or more), which helps speed up data transfer.
- Battery Backup: Many models include a battery backup so data in memory won’t be lost if power goes out.
- Fast Interfaces: Works with SATA, SAS, and NVMe drives for high-speed storage.
- Web Management Tools: Comes with Dell OpenManage and other tools to easily view, set up, and monitor storage.
- Hot Swap Support: Allows you to remove and replace failed drives without turning off the server.
- Predictive Failure Alerts: Monitors hard drives and warns you if one may fail soon.
Different RAID Levels
PERC controllers support many RAID levels. Here’s what the common ones mean: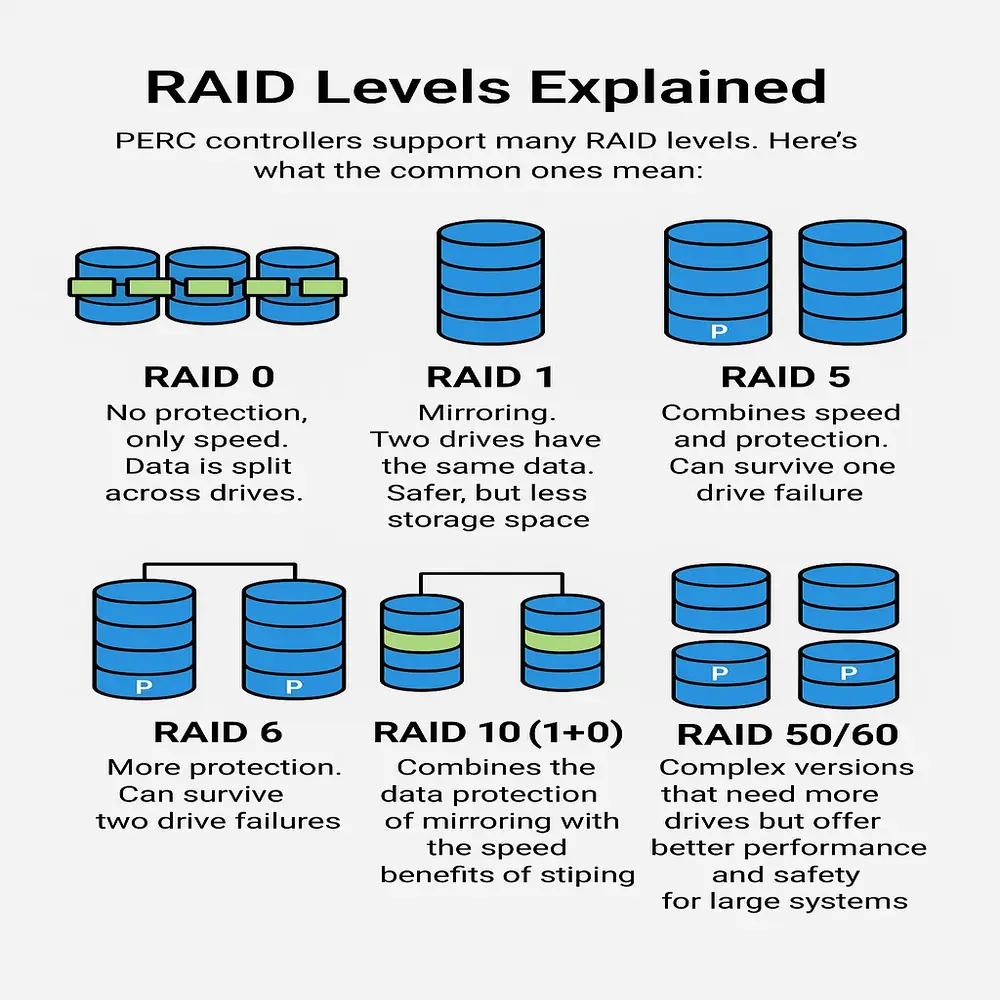
- RAID 0: No protection, only speed. Data is split across drives.
- RAID 1: Mirroring. Two drives have the same data. Safer, but less storage space.
- RAID 5: Combines speed and protection. Can survive one drive failure.
- RAID 6: More protection. Can survive two drive failures.
- RAID 10 (1+0): RAID 10 (1+0) combines the data protection of mirroring with the speed benefits of striping, delivering both performance and redundancy in one setup.
- RAID 50/60: Complex versions that need more drives but offer better performance and safety for large systems.
PERC Use Cases
You’ll find PERC RAID controllers in many professional setups, such as:
- Web Hosting Servers
- Database Servers
- Virtualization Platforms
- File Sharing Servers
- Backup and Archive Systems
In short, anywhere you need your data to be fast and safe, PERC has a role to play.
How to Configure a PowerEdge RAID Controller?
Setting up a PERC is usually done during server setup. Dell provides an easy BIOS-level tool called CTRL-R Configuration Utility, where you can:
- Choose your RAID level
- Add or remove drives
- Create virtual disks
- Format and initialize drives
For more advanced settings, you can use Dell OpenManage or Lifecycle Controller through a web interface.
PERC Models Comparison
Below is a quick overview comparing several widely used PERC models:
| Model | Cache Memory | Interface | RAID Support | Best For |
| PERC H330 | None | SATA/SAS | Basic RAID | Entry-level servers |
| PERC H730P | Up to 2GB | SATA/SAS | Full RAID | General enterprise environments |
| PERC H740P | Up to 8GB | SATA/SAS | Full RAID | High-performance workloads |
| PERC H755 | PCIe Gen4 | NVMe/SAS | Advanced | Cutting-edge performance servers |
Each model supports different workloads, so choosing the right one depends on your server’s purpose.
Choosing the Right PERC Controller
Before buying or upgrading, ask yourself:
- How important is data safety?
- Do I need high performance or basic storage?
- How many drives will I use?
- Will I expand storage later?
- Do I need NVMe or SAS drive support?
Answering these will help you choose the best PERC model for your needs.
Troubleshooting with PERC: Common Issues and Fixes
Even with smart technology, things can go wrong. Here are some common issues you might face with PowerEdge RAID Controllers and how to fix them:
- Virtual Disk Degraded: One or more drives failed or disconnected.
- Controller Not Detected: This usually happens after firmware updates or reseating. Reseating the controller or flashing firmware again helps.
- Foreign Configuration Detected: This means the drives have RAID metadata from another system. The configuration can be reviewed and either imported or cleared through the RAID controller’s BIOS interface.
- Battery/Cache Warnings: The battery may need replacement, or the cache module may not be seated properly.
The Dell support site provides regular updates, and using Lifecycle Controller helps keep all components in sync.
How to Perform a RAID Rebuild with PERC?
A RAID rebuild is the process of restoring redundancy after a drive failure. PERC handles this automatically, but here’s what typically happens:
- You receive an alert that a drive has failed.
- If hot-swap is supported, the failed drive can be replaced with a new one without shutting down the system.
- PERC automatically starts the rebuild using the new disk.
During this time, the array may run slightly slower but remains fully functional.
Rebuild times vary depending on the RAID level, drive size, and server workload, but typically, a 1TB drive might take 2–5 hours.
PowerEdge RAID Controller in Virtual Environments
In virtualized setups (like VMware, Hyper-V, or Proxmox), PERC plays a big role by offering:
- High Input/Output Operations Per Second (IOPS): Crucial for running multiple VMs smoothly.
- Thin provisioning support: Efficient storage allocation.
- Pass-through mode (also known as HBA mode): Allows the underlying hypervisor to manage disk operations directly, making it ideal for software-defined storage environments.
Admins can configure PERC in RAID mode or HBA mode depending on the virtual environment’s requirements.
Final Thoughts
PowerEdge RAID Controllers (PERC) are vital for secure and efficient server performance, minimizing downtime and data loss. Whether for a small business or enterprise data center, choosing the right PERC improves reliability and speed. Dell’s evolving PERC models ensure top-tier compatibility with PowerEdge servers. Just remember pair your RAID setup with regular backups and monitoring for full data protection.