In today’s digital world, devices are getting smaller, faster, and more connected. From smartphones and laptops to networking gear and industrial machines, every device needs a way to connect to others or to share data quickly. That’s where the small form factor pluggable character, or SFP character, plays a key role. This small yet powerful component is changing the way devices talk to each other, especially in tight spaces and complex environments.
How Small Form Factor Plugable Characters Work?
The small form factor plugable character is a compact, hot-swappable interface used in electronic devices to plug in network modules or components like transceivers, storage devices, or sensors. In simple words, it allows a device to connect to another without taking much space, and you can easily plug or unplug it while the system is still on.
What Does “Small Form Factor Plugable Character” Mean?
Let’s break it down to understand it better:
- Small Form Factor: This refers to a highly compact size, designed to fit into tight spaces, such as laptops, networking devices, or embedded systems.
- Plugable: This part means you can plug it in or remove it without restarting or turning off the main device (hot-swappable).
- Character: In this context, “character” refers to a specific type of plug or port behavior that follows certain standards and performs a defined role in the communication process.
So, the small form factor plugable character refers to a small, easy-to-connect component that enables data transfer or connection between devices while following a certain functional character or pattern.
Why It Matters in Today’s Devices?
Devices today are expected to be thin, lightweight, energy-efficient, and powerful. Traditional bulky connectors or ports are not suitable for such modern designs. This is why engineers and designers prefer SFP characters. They save space while maintaining high-speed performance.
Key Benefits
- Compact size: Perfect for thin devices or stacked electronics.
- Hot-swappable: No need to turn off devices when plugging in or removing modules.
- Modular design: You can replace only the part you need without changing the entire device.
- Versatility: Supports different types of modules, optical, copper, and more.
- Cost-effective: Reduces waste and repair costs by allowing partial replacement.
Where Is It Used?
The small form factor plugable character is found in many industries and products. Let’s look at some common use cases:
1. Networking Equipment
This is one of the most popular areas. Routers, switches, and servers often use SFP ports to connect optical transceivers for fiber or copper connections.
2. Consumer Electronics
Laptops, mini-PCs, and even some game consoles may use small plugable characters for HDMI, USB-C, or display expansion.
3. Telecom Systems
Telecommunication base stations use them to upgrade bandwidth without replacing the whole system.
4. Data Centers
In large data centers, space and speed are critical. SFP characters allow dense networking layouts with high-speed modules and easy upgrades.
5. Embedded & IoT Devices
Tiny gadgets, medical tools, or industrial controllers often depend on plugable characters to add functionality without increasing size.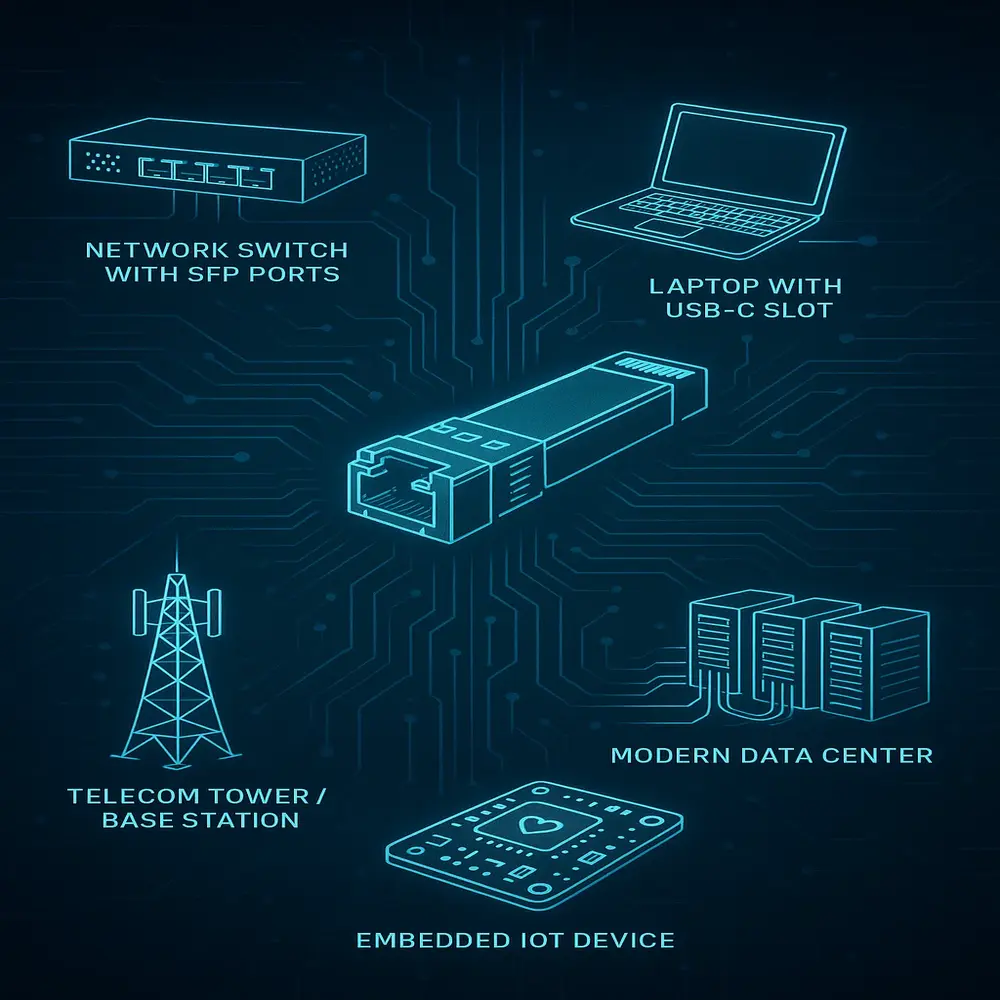
Different Types of Small Form Factor Plugable Characters
There is no single type of SFP character. Several types are used depending on the job they need to do. Below are some of the common ones:
- SFP (Small Form-factor Pluggable): The standard version, used mostly in networking.
- SFP+: A faster version that supports up to 10 Gbps of data transfer.
- QSFP (Quad SFP): Combines four lanes for higher speed (40 Gbps or more).
- M.2 and NVMe slots: Used in storage modules for laptops and PCs.
- Mini DisplayPort or USB-C: Acts as a plugable character for displays or charging.
Each of these types serves a unique purpose but follows the same general idea: small, swappable, and smart.
How does it improve connectivity?
The whole point of using the small form factor plugable character is to make devices smarter and easier to connect. Here’s how it improves daily tech life:
- Simplifies Upgrades: Instead of changing the whole motherboard or circuit, you can swap just one module.
- Increases Speed: Modern plugable modules support fast data and internet speeds.
- Improves Portability: Smaller ports allow thinner and lighter gadgets.
- Boosts Flexibility: One device can support many functions just by changing plug-in modules.
Challenges and Solutions
While small form factor plugable characters are great, they come with some challenges too:
Challenges
- Fragility: Smaller size may mean more delicate connectors.
- Compatibility: Not all modules fit all ports.
- Cost: Some high-speed modules can be expensive.
Solutions
- Standardization: Industry standards like SFP, USB-C, or M.2 help with compatibility.
- Protective casing: Most characters come with shields to avoid damage.
- Hot-swap handling: Devices are designed to detect and manage hot-swaps safely.
What the Future Holds?
As we move into a world of AI, 5G, and ultra-compact computing, the demand for smart connectivity is rising. That means the small form factor plugable character will become even more important.
We’re already seeing new developments like:
- Optical plugable characters for ultra-fast data.
- AI-ready modules that can be plugged into edge devices.
- Energy-efficient designs for use in green computing.
Soon, almost every connected device from your fridge to your drone might rely on this tiny but powerful connector.
What Makes the SFP Important?
The small form factor pluggable character may not be something you hear about every day, but it’s working quietly behind the scenes to keep your devices connected, smart, and ready for the future. It’s compact, easy to use, and essential for today’s fast-paced technology.
Technical Working of a Small Form Factor Plugable Character
The small form factor plugable character works on a modular interface standard, often developed by industry groups like the SFF Committee or IEEE. These standards define:
- Pin layout for power, signal, and data lanes
- Communication protocols (like PCIe, USB, or optical transmission)
- Thermal and electrical tolerances
Once connected, the character uses plug-and-play detection via BIOS/firmware. Many modules also support auto-negotiation, which allows devices to identify compatible speeds and configurations automatically.
Size Comparison with Traditional Connectors
| Connector Type | Approx Size | Hot Swappable? | Use Case |
| RJ45 | Large | No | Ethernet |
| USB-A | Medium | Yes | PC Accessories |
| SFF Plugable | Tiny | Yes | Fiber, Storage, Embedded boards |
Highlight that the small form factor pluggable character saves space and still does the job of these traditional ports, often better and faster.
Conclusion
The small form factor pluggable character is more than just a tiny connector; it’s a big leap in how modern devices communicate. Its compact size, hot-swappable nature, and modular design make it a key player in networking, computing, and embedded systems. As technology continues to shrink while performance demands grow, these plugable characters will remain at the heart of flexible and future-ready connectivity solutions.