When it comes to electronics and power devices, two terms you’ll often hear are IGBT and MOSFET. If you’re new to these components, it can feel confusing to figure out which one is better for your project. Both IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) and MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor) are used to control electrical power, but they work differently and have their own strengths and weaknesses. In this guide, we’ll break down what they are, how they work, and where each one is best used so you can understand them clearly.
What is a MOSFET?

A MOSFET is a type of transistor that is commonly used in electronic circuits to control or amplify electrical signals efficiently. It acts like a switch or amplifier and controls the flow of electricity using an electric field. A MOSFET has three main parts: the gate, drain, and source. When you apply a voltage to the gate, it enables current to flow between the drain and the source terminals.
MOSFETs are very popular because they can switch on and off very quickly. They are used in applications that need fast switching and operate at high frequencies, like computer motherboards, power supplies, and motor controllers.
What is an IGBT?
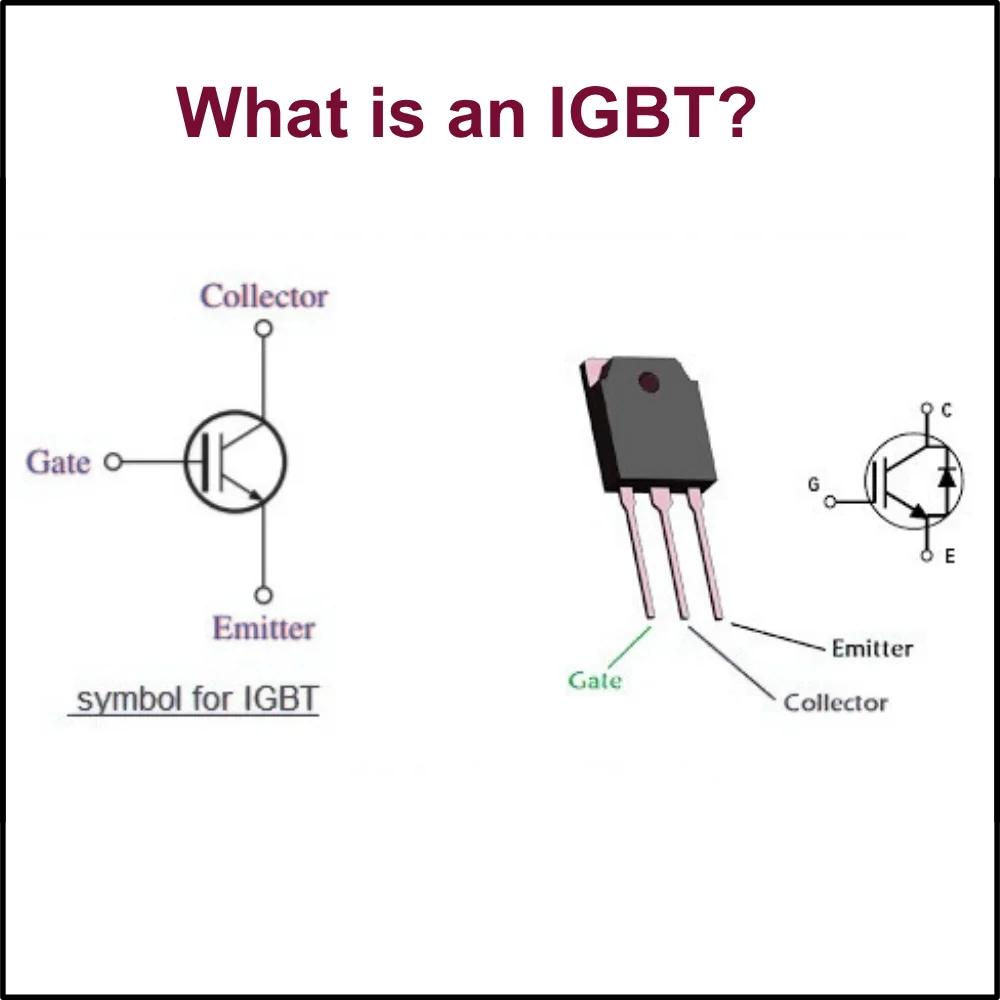
IGBT stands for Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor. It combines the simple control features of a MOSFET with the high current and voltage handling abilities of a bipolar transistor, making it a hybrid device. Like MOSFETs, IGBTs also have three terminals: gate, collector, and emitter.
IGBTs are widely used in applications where high voltage and high current are needed, such as in electric cars, trains, industrial motor drives, and power inverters. They are designed to handle more power than MOSFETs and are excellent for slow to medium switching frequencies.
Key Differences Between MOSFET and IGBT
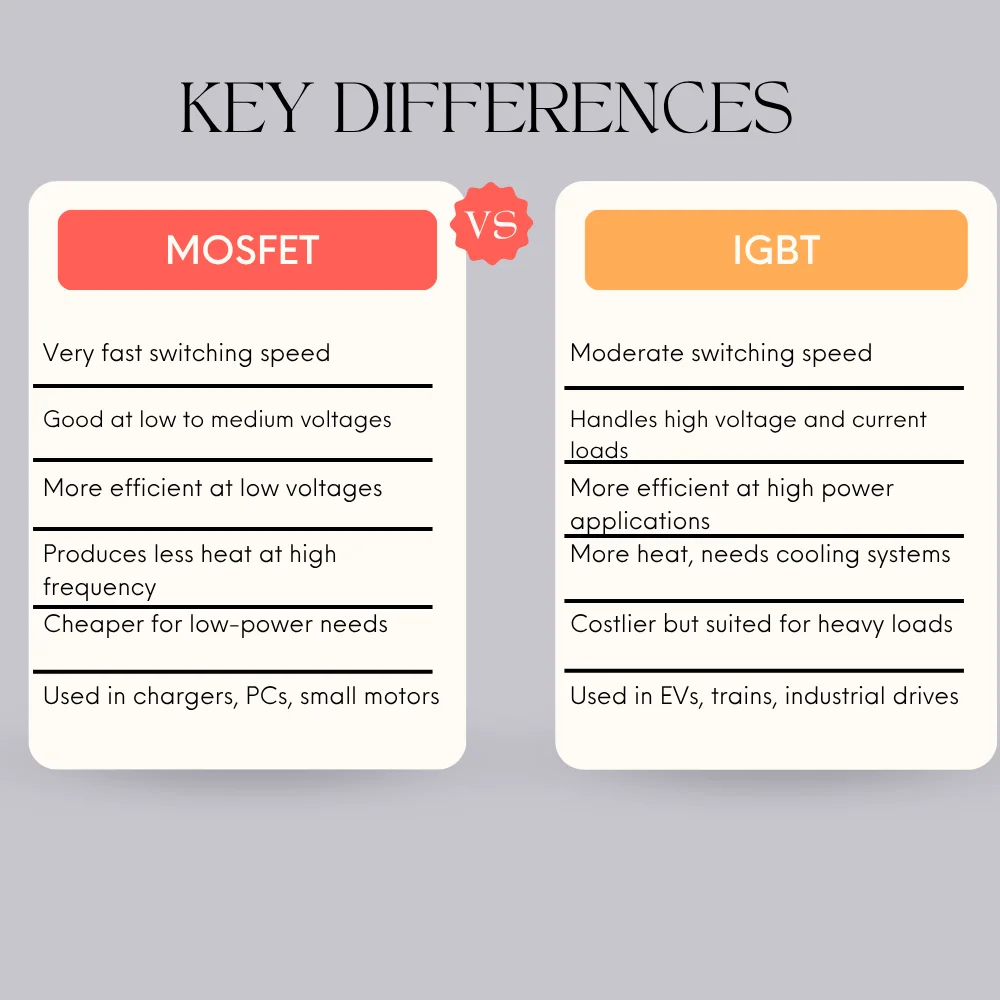
To help you understand the main differences more clearly, here’s a breakdown:
- Switching Speed: MOSFETs are faster. They can turn on and off very rapidly, which makes them perfect for applications that require high-frequency switching.
- Voltage and Current: IGBTs can handle higher voltages and currents, which is why they are chosen for heavy-duty applications.
- Efficiency at Different Loads: At lower voltages, MOSFETs are more efficient. At higher voltages, IGBTs perform better.
- Cost: MOSFETs are generally cheaper when used in low-voltage applications, while IGBTs tend to cost more but offer better performance in high-power situations.
- Heat Dissipation: MOSFETs produce less heat during fast switching. IGBTs may generate more heat and often require cooling systems.
Applications of MOSFET
MOSFETs are used in many everyday electronic devices. You might not even realize it, but they are almost everywhere. Here are a few common uses:
- DC-DC converters: Used in laptops and mobile chargers to manage voltage.
- Motor controllers: Ideal for controlling small motors in fans or robotics.
- Switching power supplies: Found in almost all modern electronic gadgets.
- Audio amplifiers: Help boost sound signals cleanly and efficiently.
- LED drivers: Control the brightness and power of LED lights.
Because they can handle fast and frequent switching, MOSFETs are perfect when size and speed are more important than extremely high voltage or heavy loads.
Applications of IGBT
IGBTs shine when it comes to handling bigger loads and higher voltages. Here are some places you’ll find them:
- Electric and hybrid vehicles: Used to control the power from the battery to the motor.
- Industrial motor drives: Run large machines in factories smoothly.
- Renewable energy systems: Help manage energy flow in solar and wind power systems.
- Railway traction systems: Provide power control in trains.
- Induction heating: Used in industrial processes to heat metals efficiently.
While they aren’t as fast as MOSFETs, they can handle a lot more power without breaking down, which makes them the perfect choice for heavy-duty tasks.
Advantages and Disadvantages
MOSFET Advantages
- High switching speed
- Lower on-state resistance
- Efficient at low voltages
- Less heat generation at high frequencies
MOSFET Disadvantages
- Limited voltage handling
- Not ideal for very large power loads
IGBT Advantages
- High voltage and current capacity
- Good efficiency for large loads
- Easy to control with low input power
IGBT Disadvantages
- Slower switching speed
- Generates more heat at high frequencies
- Needs additional cooling systems in some cases
How to Choose Between IGBT and MOSFET?
Choosing between a MOSFET and an IGBT depends on your needs. If you need to switch a circuit on and off very quickly and are dealing with lower voltages, a MOSFET is usually the best choice. It’s more efficient, generates less heat, and is more cost-effective.
If your project involves higher voltages and you need to handle large currents, an IGBT is the better option. Even though it may switch slower and cost more, it can manage large power loads reliably.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between IGBT and MOSFET can help you pick the right component for your electronic designs. By focusing on voltage, current, speed, and efficiency, you can make sure your project runs safely and effectively.
Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced engineer, knowing when to use each of these powerful devices can make all the difference in your results.



