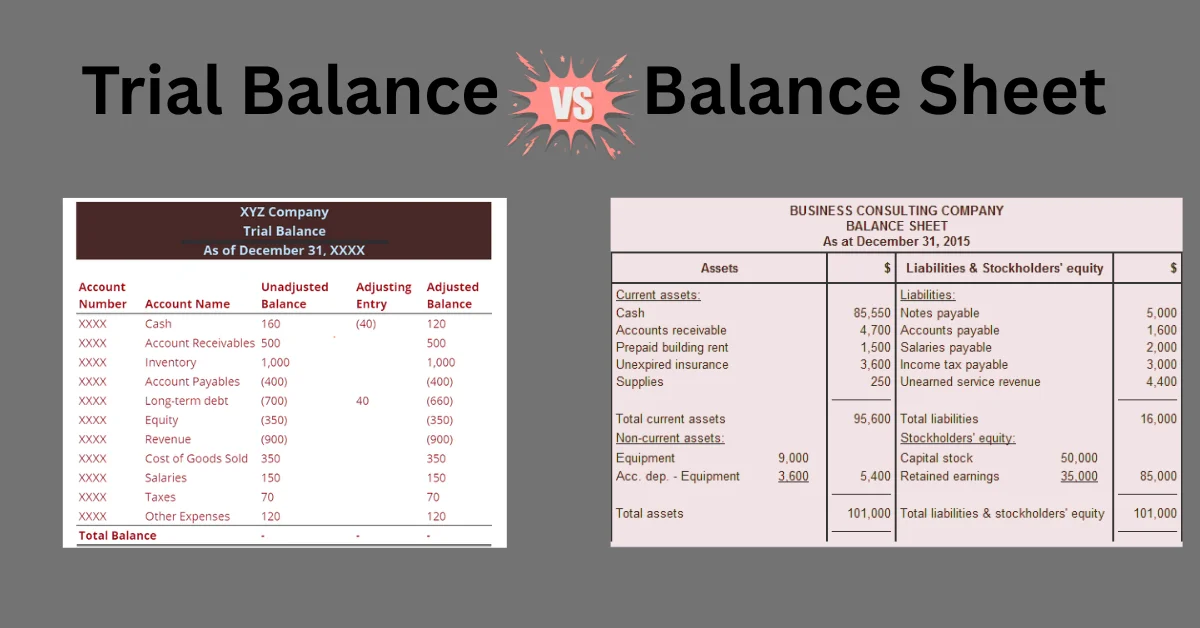
In the world of accounting, two terms often come up when reviewing financial records trial balance and balance sheet. While they may seem similar at first glance, they serve different purposes in financial reporting and analysis. Understanding both is crucial for business owners, accountants, and students alike.
What is a Trial Balance?
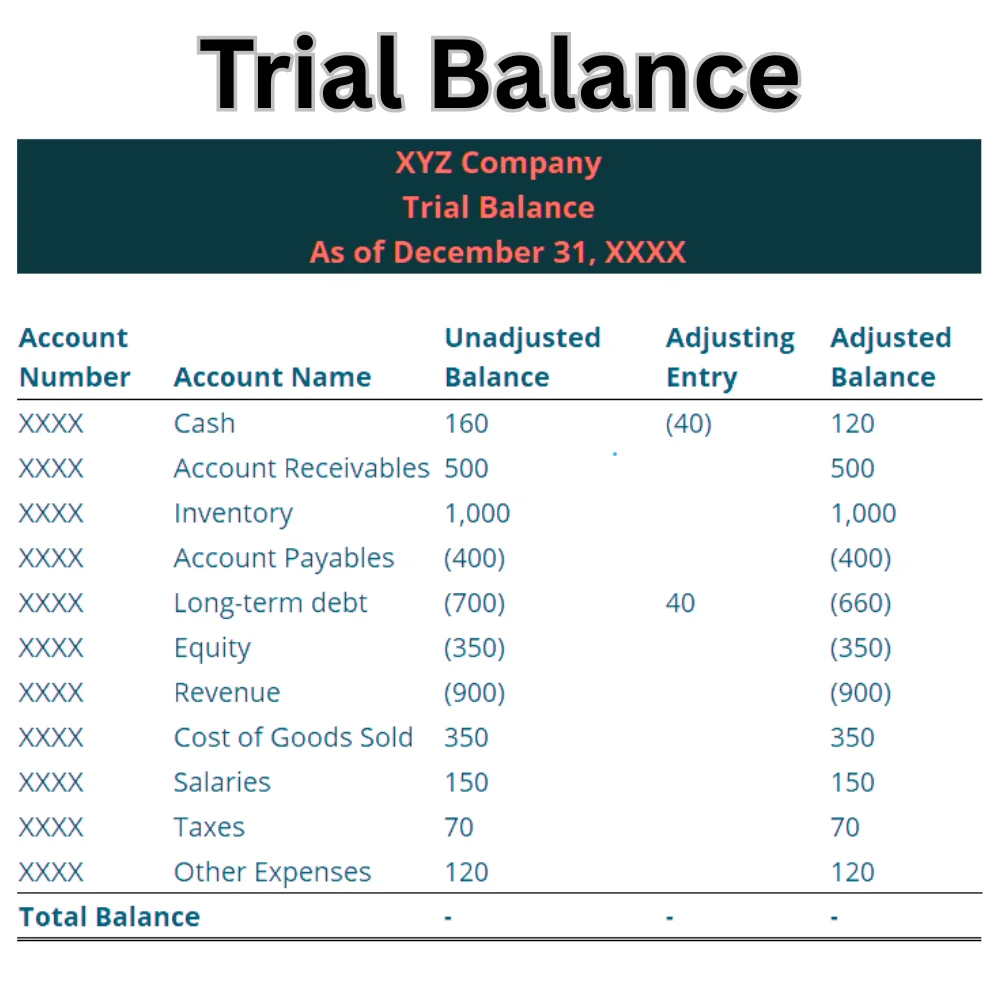
A trial balance is a report prepared to check the accuracy of a company’s bookkeeping records. Typically prepared at the conclusion of an accounting period, it presents the balances of all general ledger accounts, organized into two distinct columns: debits and credits.
The total of both columns should be equal. If not, it indicates that there may be an error in the recording of transactions. A trial balance does not show profitability or financial health, but it does ensure that the books are mathematically correct.
Main Features of a Trial Balance
- It includes all ledger accounts with their balances.
- Divided into debit and credit columns.
- Helps identify mathematical errors in bookkeeping.
- Used to prepare final accounts like the income statement and balance sheet.
Example of a Trial Balance
| Account Name | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 5,000 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 2,000 | |
| Inventory | 3,000 | |
| Accounts Payable | 2,500 | |
| Sales Revenue | 7,500 | |
| Capital | 5,000 |
In this example, the total debit and credit sides both equal 10,000, which means the books are balanced.
What is a Balance Sheet?
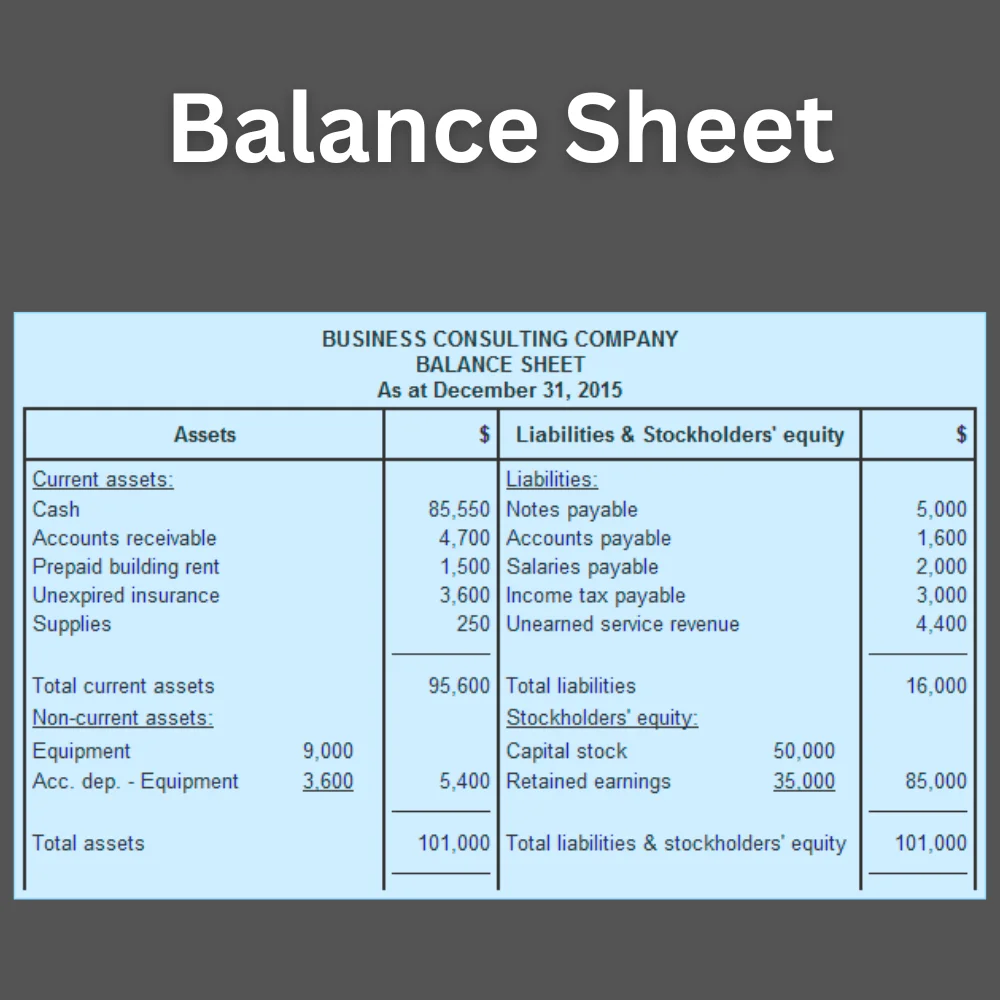
The balance sheet is a formal document that presents a snapshot of a company’s financial condition at a specific point in time. As part of the final accounts, it provides a concise overview of the business’s assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity.
The balance sheet follows the accounting equation:
Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity
This equation must always be balanced. The balance sheet helps investors, creditors, and owners understand how healthy a company’s finances are and how efficiently it is managing its resources.
Main Features of a Balance Sheet
- Shows assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Prepared at the end of a financial year or accounting period.
- Reflects the company’s net worth.
- Helps in financial planning and decision-making.
Example of a Balance Sheet
ABC Company Balance Sheet as of 31st May 2025
Assets
- Cash: $5,000
- Accounts Receivable: $2,000
- Inventory: $3,000
Total Assets: $10,000
Liabilities
- Accounts Payable: $2,500
Owner’s Equity
- Capital: $7,500
- Total Liabilities and Equity: $10,000
As illustrated above, the total value of assets matches the combined total of liabilities and equity, confirming the accuracy of the balance sheet.
Key Differences Between Trial Balance and Balance Sheet
Now that we understand both, let’s look at their major differences:
1. Purpose
- Trial Balance: Checks the mathematical accuracy of ledger balances.
- Balance Sheet: Provides a snapshot of the company’s financial status.
2. Content
- Trial Balance: Includes all ledger accounts, including income and expenses.
- Balance Sheet: Includes only real and personal accounts like assets, liabilities, and equity.
3. Time of Preparation
- Trial Balance: Usually prepared before the financial statements.
- Balance Sheet: Prepared after final accounts and adjustments.
4. Structure
- Trial Balance: Two columns debit and credit.
- Balance Sheet: Three sections assets, liabilities, and equity.
5. Legal Requirement
- Trial Balance: Not mandatory by law.
- Balance Sheet: Legally required for companies under various financial regulations.
Why Are They Both Important?
Both trial balance and balance sheet play an important role in financial reporting.
Trial Balance ensures that all entries are correctly made in the books. If there is an error, it can be spotted and corrected before preparing the final accounts.
Balance Sheet helps stakeholders like investors, banks, and the management team understand the company’s worth and make informed decisions.
Without a trial balance, the financial statements could be built on incorrect data. Without a balance sheet, a business wouldn’t be able to show its financial health to the outside world.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Here are a few mistakes people make while dealing with these reports:
- Assuming both are the same: Remember, one is a draft, the other is a formal report.
- Ignoring trial balance errors: Even small errors can affect the balance sheet.
- Misclassifying accounts: Placing an income item in the balance sheet will give incorrect results.
- Not updating balances: Always ensure updated figures are used when creating the balance sheet.
How Trial Balance Leads to the Balance Sheet?
The trial balance is the first step in preparing the balance sheet. Once the trial balance confirms the books are accurate, the next steps include:
- Adjusting Entries: For depreciation, accrued expenses, prepaid incomes, etc.
- Income Statement: Prepared using income and expense accounts.
- Balance Sheet: Using asset, liability, and equity accounts.
In short, the trial balance sets the foundation for the preparation of the final financial reports.
Final Thoughts
While the trial balance and balance sheet both deal with financial figures, they serve completely different purposes. The trial balance is like a rough draft useful for internal checks and balance. On the other hand, the balance sheet is a polished and formal document that shows a company’s strength and stability to the outside world.
A clear understanding of both enables business owners to make informed decisions, prevent errors, and maintain transparency in their financial operations. Whether you’re an accounting student or a small business owner, knowing how and why these tools are used is a big step toward mastering your financial knowledge.
If you’re just starting, remember: Trial balance is where accuracy begins, and the balance sheet is where your business story is told.
Related Topic: Post Closing Trial Balance in Accounting Guide