As everything becomes faster and more digital, the need to manage networks, services, and customers effectively has become increasingly important. This is where Operational Support Systems (OSS) come in. OSS is a term mainly used in the telecom and IT industries. These systems help companies run their operations smoothly and ensure services function without interruptions.
The Hidden Engine Powering Your Network
You can think of OSS as the behind-the-scenes brain that keeps the whole network running. While customers may only see their mobile phones, internet, or TV services working. OSS is doing the hard work in the background to make that happen.
Why Operational Support Systems Matter?
Every time you make a call, send a message, or use the internet, several technical processes happen in the background. These include:
- Checking if your device is allowed to connect
- Making sure the signal is strong
- Handling network congestion
- Monitoring if something goes wrong
OSS manages all these things and many more. It ensures that services are delivered, monitored, managed, and repaired when needed. Without it, telecom companies would not be able to run their business effectively.
Key Functions of OSS
Operational Support Systems consist of a variety of integrated tools and software applications. These systems collaborate to effectively oversee every operational layer of a telecom network. Here are the main functions of OSS:
1. Network Management
This involves overseeing, maintaining, and continuously monitoring network equipment such as routers, switches, base stations, and transmission towers. It ensures everything stays connected and any failures are quickly spotted.
2. Service Provisioning
When a user purchases a new SIM card or signs up for an internet package, the OSS system automatically initiates and configures the service for immediate use. It connects your request to the right part of the network so it can start working quickly.
3. Fault Management
If something goes wrong, OSS detects it immediately. It can raise alarms, log issues, and even try to fix small problems automatically. This coordination minimizes service disruptions and enhances overall network quality.
4. Performance Management
OSS tools constantly check how well the network is performing. They gather data like signal strength, speed, delays, and more. This helps engineers improve services based on real-time insights.
5. Inventory Management
Every device, cable, and software system used by a telecom company is tracked by OSS. This ensures that nothing is lost or duplicated and makes it easy to plan upgrades or changes.
Real-Life Example of OSS
Let’s say you ordered a new internet connection at your home. Here’s how OSS plays its part:
- The company enters your order into their system.
- OSS checks if there is an available port at your location.
- It calculates the optimal route to seamlessly connect the user’s device to the existing telecom infrastructure.
- It activates your internet service once the hardware is set up.
- After that, it keeps monitoring your connection 24/7.
If there’s a slow speed or any disconnection, OSS alerts the team and may even fix it automatically.
OSS vs BSS: What’s the Difference?
You might also hear about Business Support Systems (BSS) when talking about telecom companies. These two terms are closely related but have different jobs:
| OSS (Operational Support Systems) | BSS (Business Support Systems) |
| Manages network and service performance | Manages customer-facing activities |
| Deals with technical operations | Deals with billing, sales, and CRM |
| Keeps services running | Helps in customer care and payments |
In simple words, OSS is about the backend (technical stuff), and BSS is about the frontend (customer services).
Components of a Modern OSS
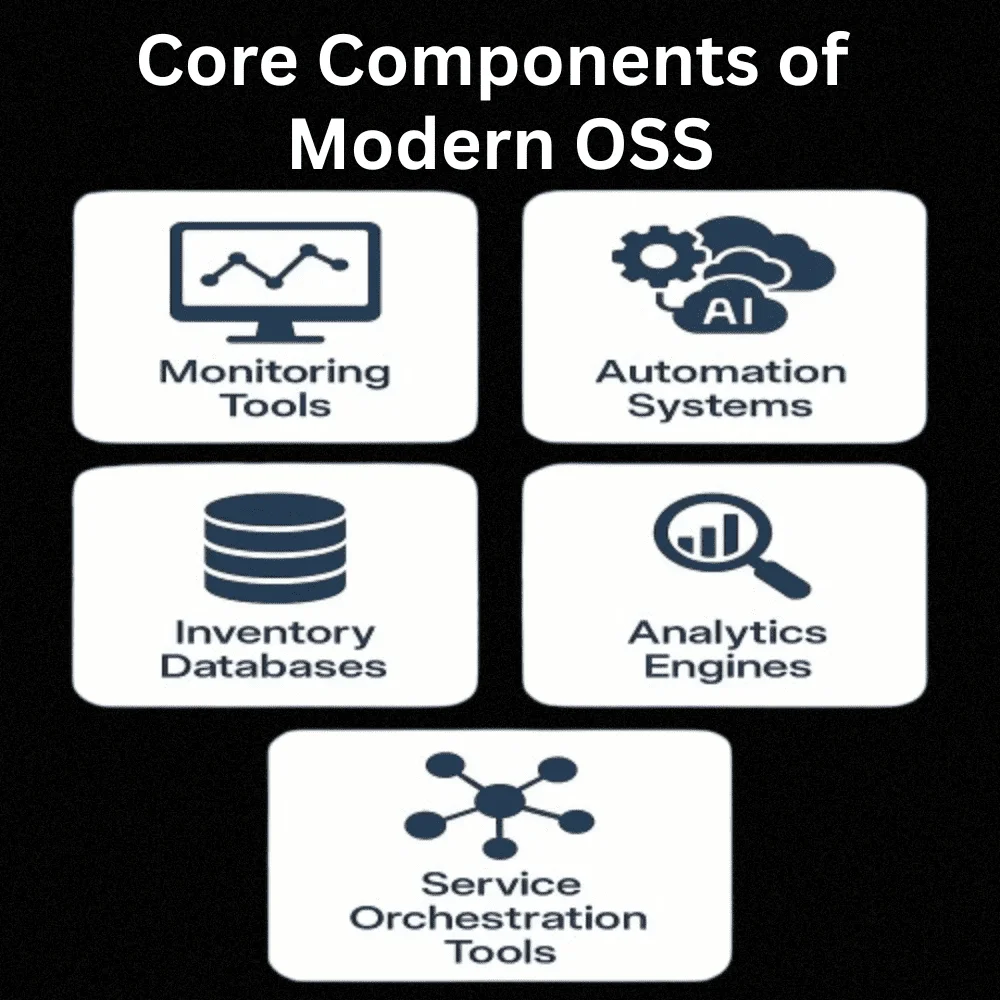
Today, OSS has become more advanced. Many tools are now cloud-based and use artificial intelligence to manage tasks. Let’s take a look at the core components that make up a modern OSS framework.
- Monitoring Tools: to watch the health of the network
- Automation Systems: to fix issues without human help
- Inventory Databases: to store hardware and software records
- Analytics Engines: to understand trends and improve performance
- Service Orchestration Tools: to combine different services and deliver them as one
How OSS Improves Customer Experience?
Most users don’t know OSS exists, but it plays a big role in their daily lives. Here’s how:
- Faster activation of new services
- Fewer service interruptions or dropouts
- Better signal and internet speeds
- Quicker resolution of problems
- Better handling of high traffic during peak times
Because OSS keeps things working quietly in the background, customers enjoy smoother and more reliable services.
Challenges Faced by Operational Support Systems
Like any system, OSS also faces some challenges:
- Complexity: One major challenge is complexity, as today’s networks are vast and consist of numerous interconnected systems and devices.
- Integration Issues: OSS must work with older tools and newer ones at the same time
- Security Risks: Any problem in OSS could impact many services
- High Costs: Building and maintaining OSS tools require investment
- Real-time Demands: Customers want problems fixed instantly, putting pressure on OSS to work faster
The Future of Operational Support Systems
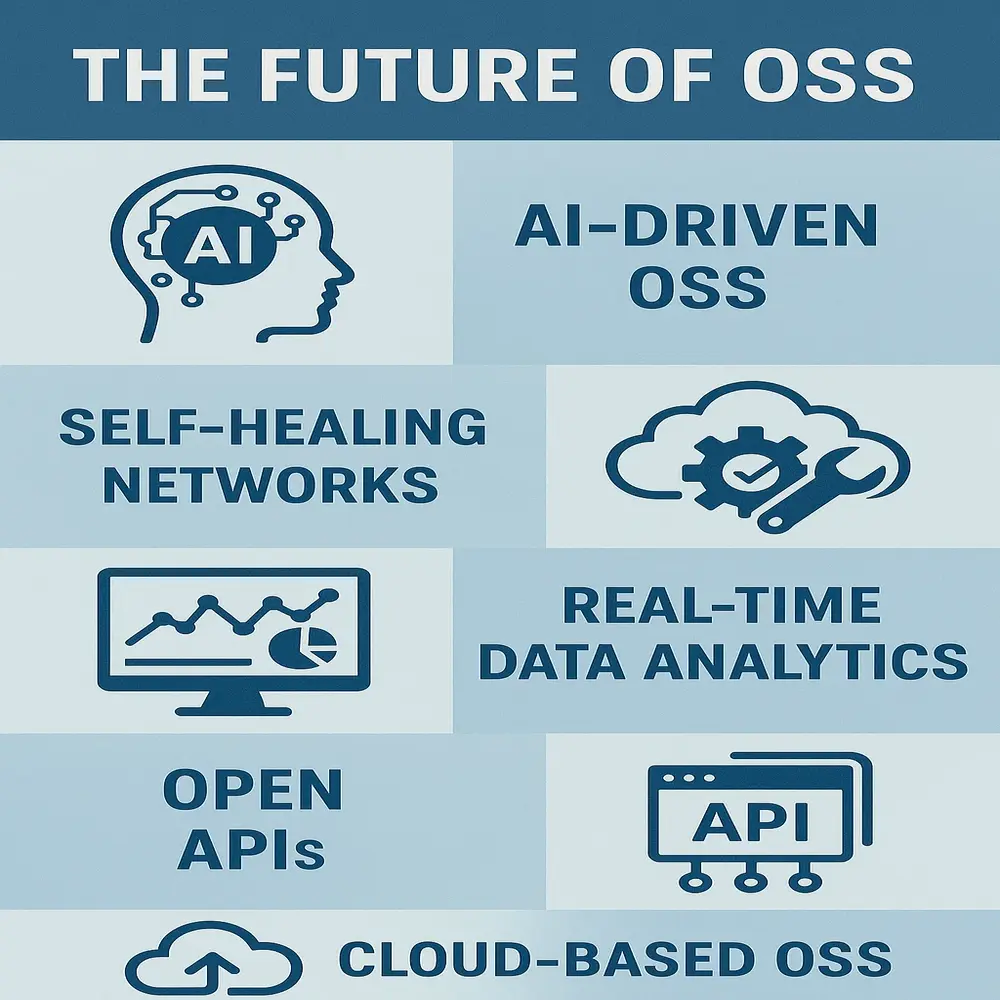
The future of OSS looks exciting. With the rise of 5G, Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud computing, OSS will continue to grow smarter and more powerful. Here are some trends to watch:
- AI-driven OSS: AI-powered OSS platforms are capable of learning from data patterns and continuously enhancing their performance over time.
- Self-healing Networks: Fixing issues without human help
- Real-time Data Analytics: For instant decision-making
- Open APIs: Making it easy to connect OSS with other software
- Cloud-based OSS: Reducing hardware costs and increasing speed
As networks become increasingly complex, OSS will become even more crucial in managing and delivering reliable, fast, and intelligent services to users.
Conclusion
Operational Support Systems (OSS) are the hidden backbone of modern telecom and IT services. They manage everything from phone calls to stable internet connections. For telecom companies, a strong OSS setup is a key business asset improving service, cutting costs, and boosting competitiveness. For those pursuing careers in telecom, IT, or network engineering, understanding OSS provides a strong technical edge.