A tarbain, more commonly spelled as turbine, is a powerful yet simple machine used to turn natural forces into useful energy. You can think of it like a spinning fan, but instead of just moving air, it creates mechanical or electrical power. A tarbain uses flowing air, water, steam or gas to spin its blades. This spinning motion powers machines, generate electricity or even move vehicles.
You see turbines everywhere, even if you don’t notice them. From huge power plants to windmills in farms and the engine of a jet plane all use some form of a tarbain.
How Does a Tarbain Work?
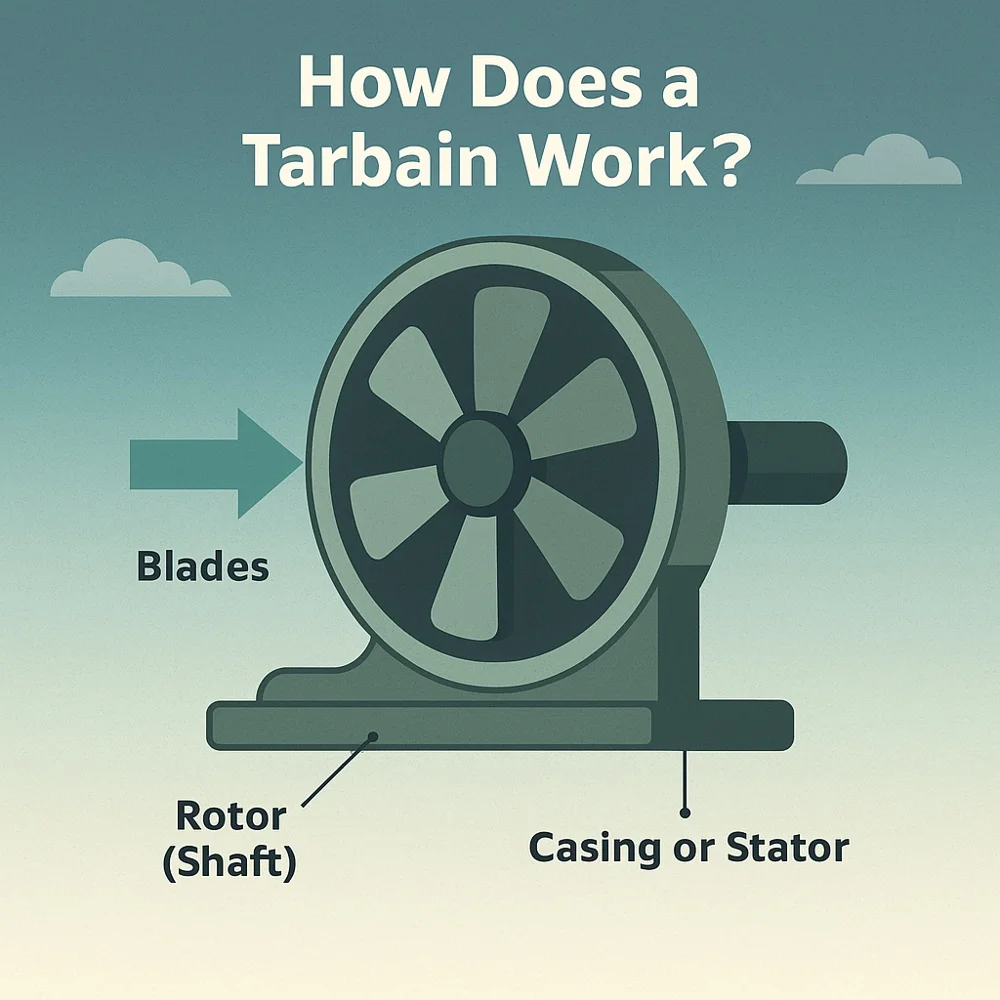
The working principle of a tarbain is quite simple. It involves three main parts:
- Blades: These are shaped to catch the force of moving fluid (like water or air).
- Rotor (or Shaft): The blades are attached to this central part. When the blades move, the rotor spins.
- Casing or Stator: This part holds everything in place and guides the fluid properly.
When the fluid (such as steam, air, or water) hits the blades, it causes them to spin. This spinning turns the rotor, which can be connected to a generator or other device to create energy. The force of nature is changed into useful power. That’s the real magic of a tarbain.
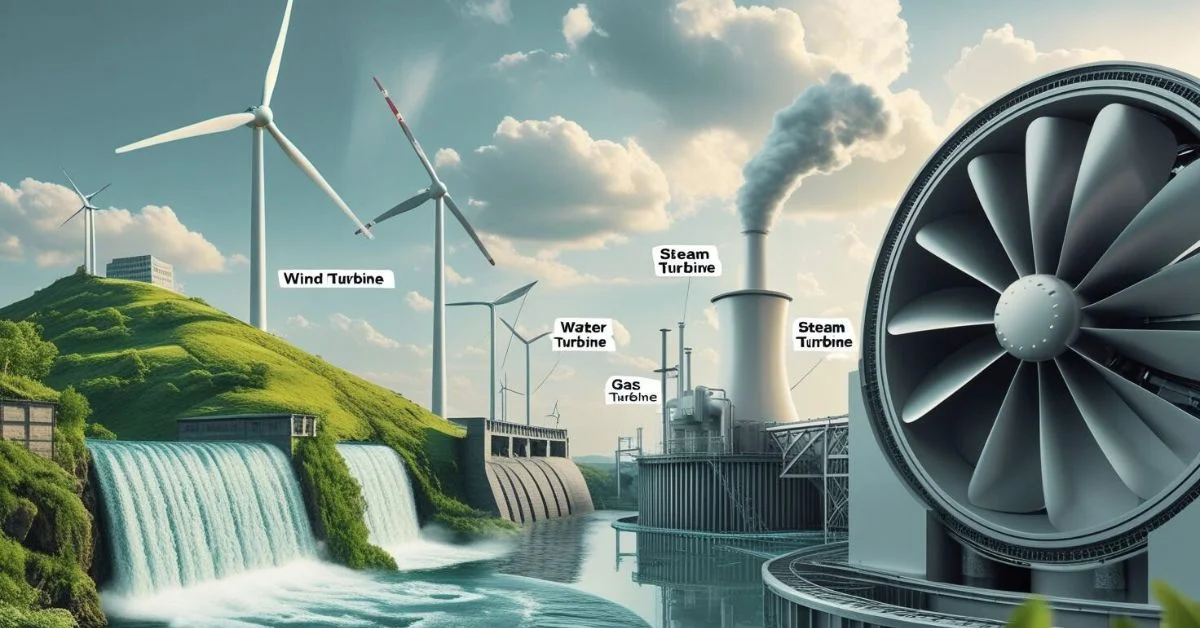
Types of Tarbains
There are several kinds of tarbains. Each one is designed for a different type of energy source or purpose.
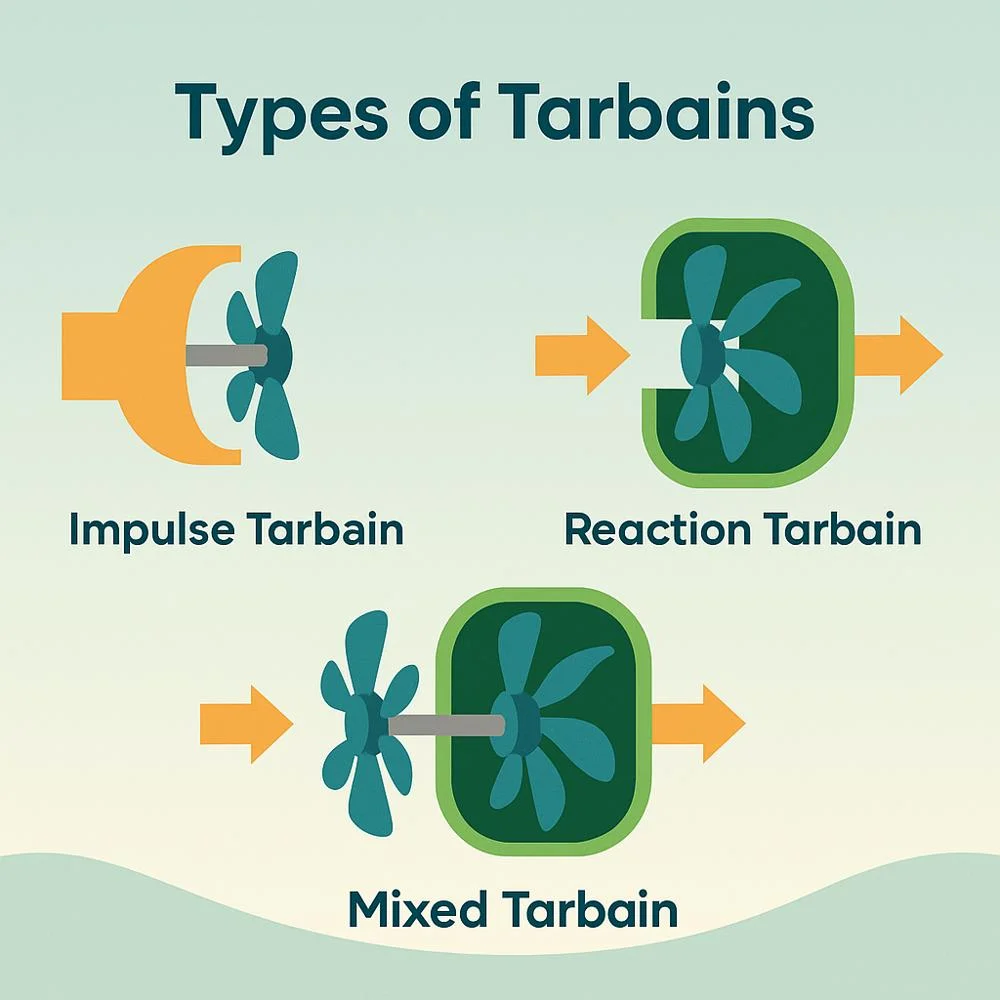
1. Impulse Tarbain
Uses high-speed fluid jets.
- The fluid strikes the blades and makes them spin.
- Ideal for high-pressure but low-flow conditions.
2. Reaction Tarbain
- Works by using both pressure and speed of the fluid.
- The blades are shaped so the fluid flows over them smoothly.
- Perfect for low-pressure but high-flow setups.
3. Mixed Tarbain
- Combines both impulse and reaction methods.
- Used for better performance and energy conversion.
Subtypes Based on Energy Source
- Steam Tarbains: Used in thermal power plants.
- Water Tarbains: Found in hydroelectric dams.
- Wind Tarbains: Common in wind farms.
- Jet engines and industrial plants use gas tarbains.”
Real-Life Uses of Tarbain
We use tarbains in more ways than most people realize. Here are a few real-life examples:
- Electricity Production: Most of the electricity we use daily is generated using steam or water tarbains in power plants.
- Wind Energy: Wind tarbains convert wind into clean energy.
- Jet Engines: Gas tarbains push airplanes through the sky.
- Factories: Many industries use tarbains to run big machines.
- Water Pumps: In some places, tarbains help push water through pipelines.
Why Are Tarbains Important?
The importance of tarbains in our world cannot be overstated. They play a major role in:
- Producing Clean Energy: Wind and water tarbains don’t pollute.
- Saving Fuel: Efficient gas tarbains use less fuel to make more power.
- Making Life Easier: Tarbains power tools and help in transport.
- Supporting Modern Life: Every part of modern infrastructure, from lights to trains, depends on energy made by tarbains.
Challenges in Using Tarbains
Even though tarbains are very helpful, they come with a few problems too:
- Wear and Tear: The spinning parts face friction and heat, so they need maintenance.
- Noise and Vibration: Wind tarbains can make noise and affect local wildlife.
- Cost of Installation: Building a tarbain system needs money and planning.
- Environmental Impact: Dams for water tarbains can change natural rivers.
The Future of Tarbains
As a result, tarbains are becoming more advanced every year. Engineers and scientists are working on new ideas to make them more useful and eco-friendlier:
- Smarter Designs: New blade shapes improve efficiency.
- Better Materials: Heat-resistant metals and ceramics last longer.
- AI and Sensors: Used for better control and early repairs.
- Hybrid Energy Systems: Tarbains are now combined with solar and battery systems.
Tarbains will continue to grow in importance as we move toward greener energy.
Everyday Meaning of Tarbain
The word “tarbain” is commonly used in Hindi and Urdu to refer to turbines. Whether you’re talking about a windmill or a power plant generator, the term “tarbain” fits all. It’s a local word that helps people better understand complex technology in their own language.
Conclusion
A turbine is a machine that turns natural movement like wind, water, steam, or gas into energy. Found in power plants, airplanes, and factories, turbines help produce electricity and reduce pollution. There are three main types: impulse, reaction, and mixed. As clean energy becomes more important, engineers are making turbines smarter and more efficient, making them a key part of our energy future.