Have you used a car key fob, watched satellite TV, or flown on a plane? Then you’ve likely used a transponder. It’s a small device that helps with communication, security, and navigation by receiving a signal and automatically sending a response. The word “transponder” combines transmit and respond exactly what it does.
What is a Transponder?
A transponder is a device that automatically receives a signal and sends back a specific response. Think of it like giving a set answer to a question. For example, when a satellite sends a signal, the transponder replies with the needed information. This keeps communication quick and clear. Technically, it receives a signal on one frequency, may change it, and sends it back. It’s used in systems like radio, aviation, satellites, and toll collection.
How Does a Transponder Work?
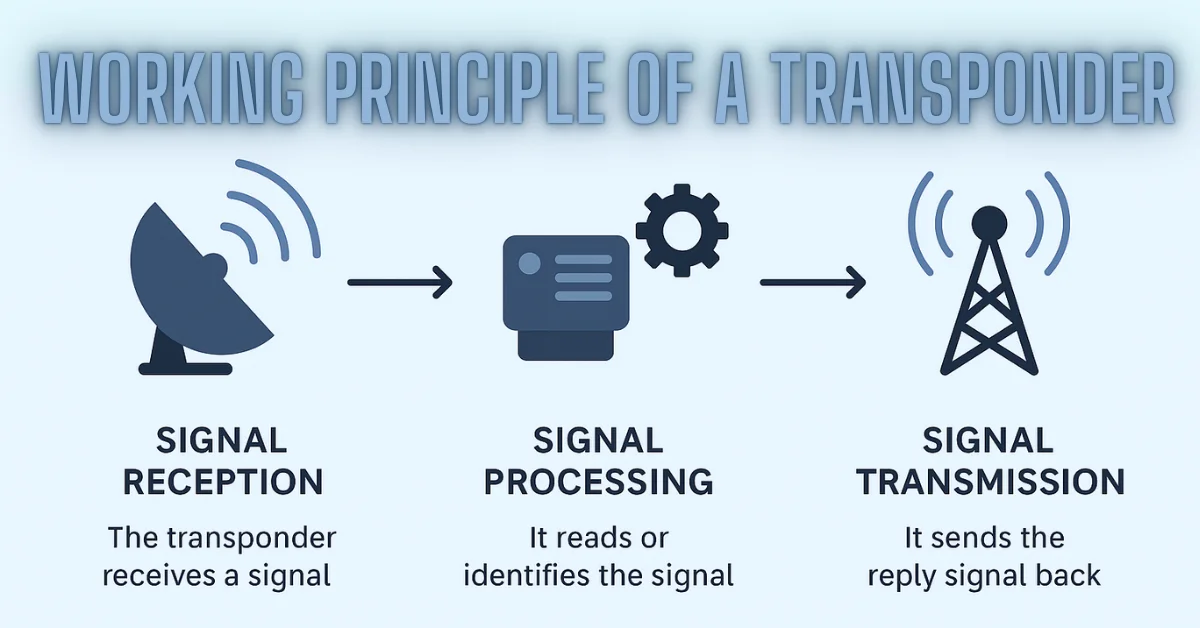
The basic working of a transponder can be explained in three simple steps:
- Signal Reception: The transponder receives a signal from a source like a radar, satellite, or radio tower.
- Signal Processing: It reads or identifies the signal and prepares a response.
- Signal Transmission: It sends the reply signal back, usually on a different frequency.
This all happens in a fraction of a second. In many systems, transponders are designed to work automatically without human control. They only respond when they get a trigger or signal.
Common Uses
Transponders are used in many devices and systems you see or use every day. Let’s explore some of the most common uses of transponders:
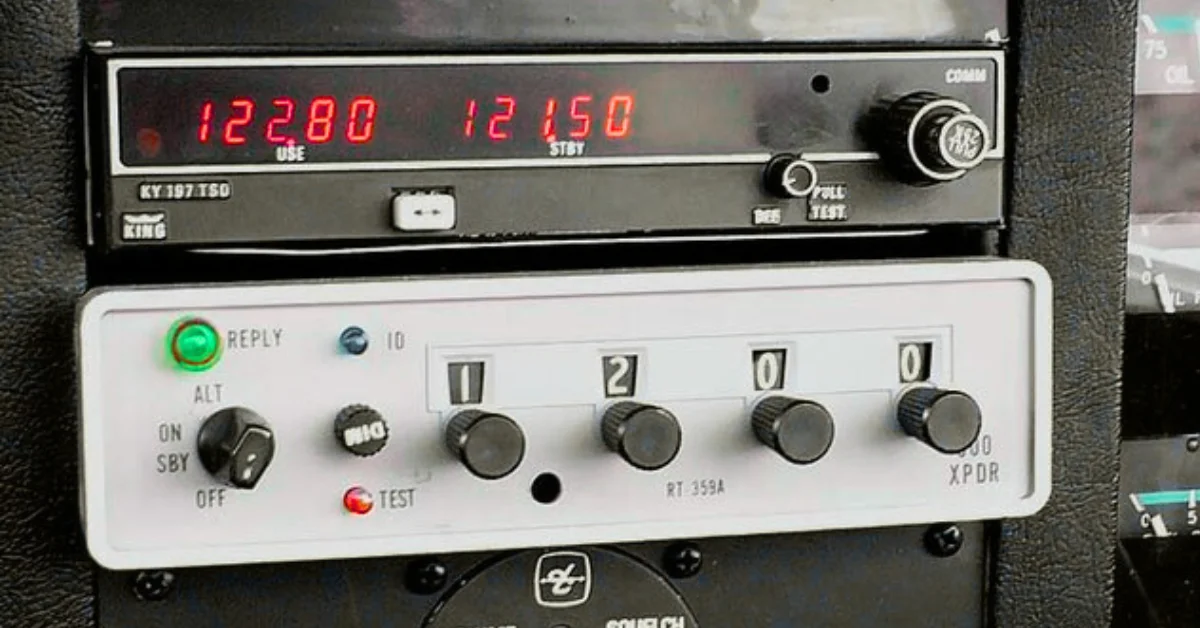
1. Aviation (Aircraft Transponders)
In airplanes, transponders are used to help air traffic controllers identify aircraft. Each plane has a unique code, and when radar sends out a signal, the transponder replies with the aircraft’s ID and altitude.
- Helps avoid collisions in the air
- Used for airspace control and monitoring
- Required for most commercial flights
2. Satellites
Communication satellites use transponders to receive signals from Earth, amplify them, and send them back to a different location on Earth. This allows people to make international phone calls, use GPS, and watch satellite TV.
- Handles thousands of calls or data transmissions at once
- Works silently in space for years
- Core part of satellite communication
3. Automobiles (Key Fobs and Anti-Theft)
Most modern cars use transponders in their keys. When you insert or bring your key near the ignition, the car reads the signal from the key’s chip. If the signal is right, the engine starts. If not, the car stays off.
- Prevents car theft
- Adds an extra layer of security
- Used in smart keyless entry systems
4. RFID and Toll Collection
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags are a form of transponder used in toll booths. When a car with a tag passes the scanner, the tag sends a signal with information like car ID or account balance, and the toll is automatically charged.
- Fast and automatic toll payments
- Saves time and reduces traffic
- Also used in warehouse tracking and supply chain
5. Maritime and Space
Ships and space vehicles also use transponders to send location and status information to control centers. In marine use, this helps avoid ship collisions, and in space, it helps monitor satellites and space probes.
- Improves safety at sea and in space
- Sends data back to Earth during missions
- Used by NASA and international space agencies
Types of Transponders
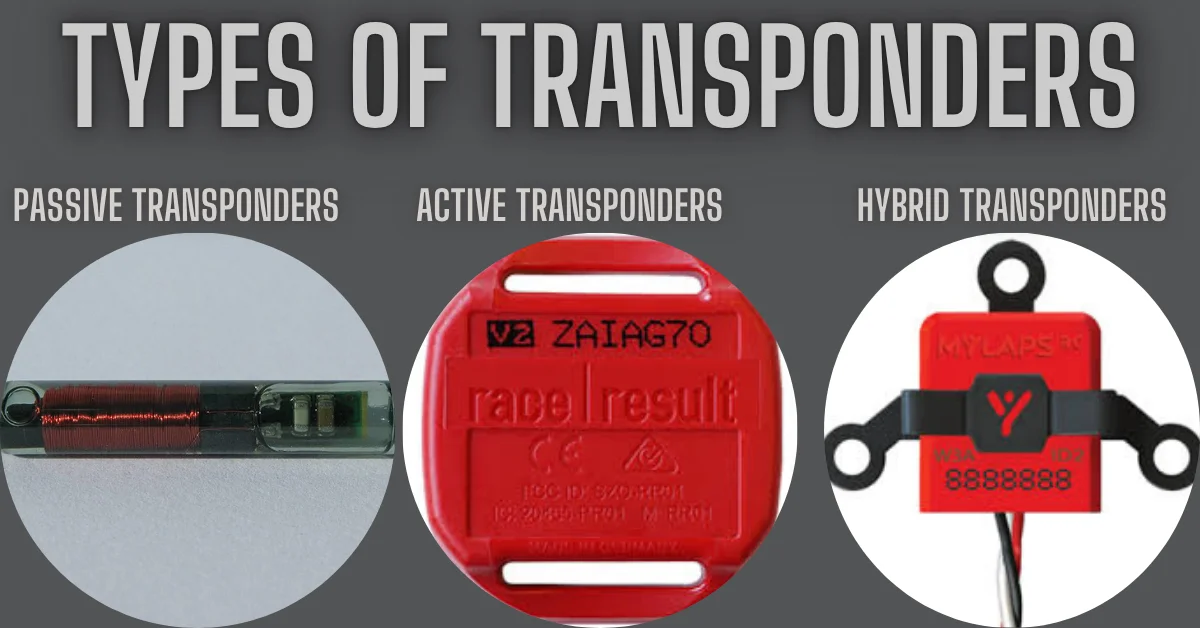
There are different types of transponders, depending on where and how they are used:
- Passive Transponders: These don’t have their own power source. They rely on the signal they receive to power themselves and respond. RFID tags in stores or libraries are often passive.
- Active Transponders: These have their own battery or power source. They can send stronger signals and work over longer distances. These are used in aircraft and space applications.
- Hybrid Transponders: A mix of both active and passive features. These are used in complex systems where both low power and long range are needed.
Why Are Transponders Important?
Transponders are quiet workers. They do their job without much notice but play a critical role in:
- Safety: In aviation, maritime, and cars, transponders help avoid accidents.
- Security: Car transponders and RFID access cards help prevent unauthorized use.
- Convenience: Toll systems, keyless entry, and satellite TV are faster and easier because of transponders.
- Communication: Without satellite transponders, long-distance communication would be hard or slow.
Limitations of Transponders
While transponders are very helpful, they do have a few limitations:
- Range Limitations: Passive transponders don’t work well over long distances.
- Signal Interference: Too many signals in one area can cause confusion or lost responses.
- Power Supply Issues: Active transponders need battery replacements over time.
- Privacy Concerns: In RFID systems, unprotected data could be accessed without permission.
Future Outlook
As technology grows, transponders will continue to improve. We may see smarter versions with more features like internet connection, longer battery life, and AI-based responses. Transponders might soon play a role in smart cities, automated driving, advanced medical devices, and even drone delivery systems.
Some futuristic uses of transponders might include:
- Self-driving cars communicating with each other
- Smart hospitals tracking patients and equipment
- Agriculture drones using transponders for precise navigation
Conclusion
Transponders are tiny but powerful tools that help systems work automatically and safely. From car keys to planes and satellites, they quietly support communication, tracking, and security. As technology grows, they’ll play an even bigger role in smart systems, making life easier and more connected.