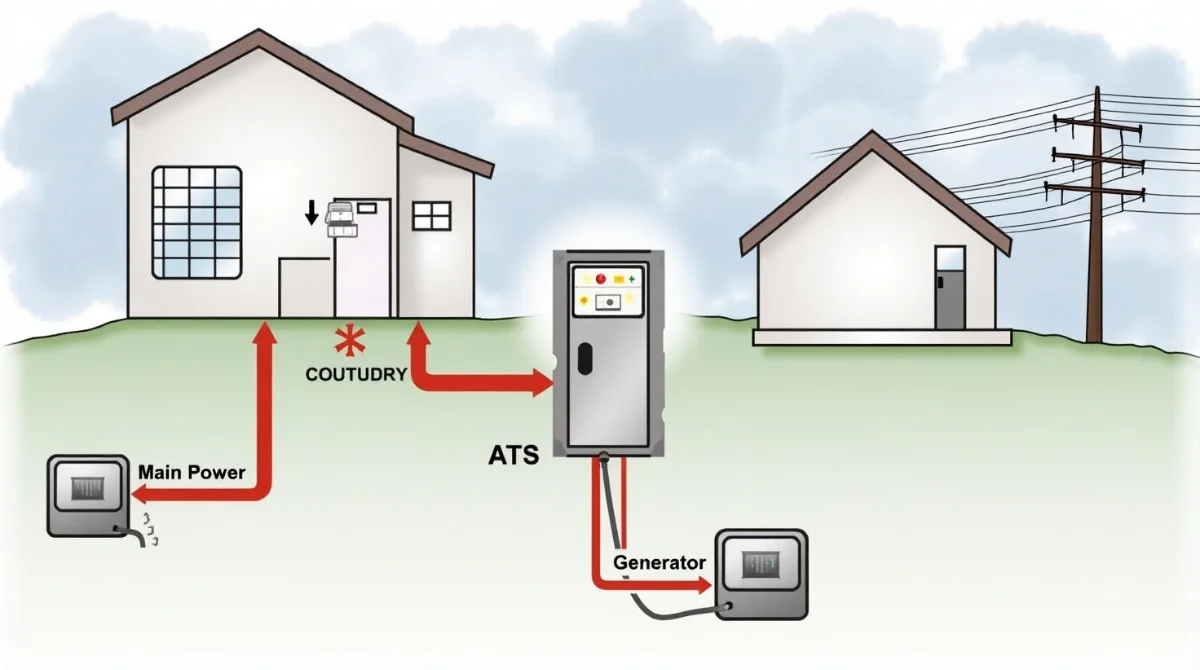
During a power outage, an Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) is a clever device that makes sure your house or place of business stays lit. Without requiring human involvement, it smoothly transitions your power supply from the primary utility to a backup generator or other source, maintaining your lights and appliances operational.
What Is an Automatic Transfer Switch?
During blackouts, a sophisticated gadget called an Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) controls your power supply automatically. It continuously checks the electricity coming from the utility provider, acting as a watchful sentinel. It instantly switches your power to a backup source, such a generator, if it detects an issue, such as a power outage, low voltage, or an odd frequency. The ATS seamlessly transitions everything back once the main power is stable and restored. In the event of a power outage, this helps avoid unexpected shutdowns, safeguards your equipment, and guarantees that your house or place of business keeps operating without requiring manual intervention.
Key Features of an Automatic Transfer Switch
For controlling backup power systems, an Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) has a number of crucial qualities that make it incredibly reliable and efficient. You should be aware of the following important features:
1. Automatic Switching
An ATS’s primary purpose is to automatically switch power sources during an outage without requiring human intervention. This ensures a steady power supply and quick response.
2. Real-Time Monitoring
Many ATS devices continuously monitor the power stability, frequency, and voltage of the main supply. This enables it to respond immediately in the event that something goes wrong.
3. Fast Transfer Time
An ATS is perfect for essential systems since, depending on the kind, it may transmit power in a matter of seconds or even instantaneously.
4. Manual Bypass Option
A manual bypass switch is a feature of certain ATS models that enables manual power transfers during emergencies or maintenance without causing your system to shut down.
5. Remote Monitoring
For big facilities or off-site administration, advanced models have integrated communication systems that enable remote monitoring and control via apps, software, or web dashboards.
6. Built-in Safety Features
In order to protect people and equipment, ATS devices have protections such overload protection, short-circuit protection, and back-feeding prevention.
7. Compatibility
Modern ATS systems are adaptable to various energy settings since they can operate with a broad range of power sources, such as diesel generators, solar panel technology, and battery backups.
8. Compact and Durable Design
Many ATS models have waterproof and corrosion-resistant enclosures and are built to be strong and space-efficient, suitable for both indoor and outdoor use.
How Does an ATS Work?
Without requiring any operator assistance, an Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) uses a methodical procedure to help maintain a steady power supply during outages. To put it simply, here is how it operates:
- Monitoring: The main power line’s incoming electricity is constantly checked by the ATS. It checks that everything is normal by looking at things like voltage and frequency.
- Detection: It prepares to take action right away if it detects an issue, such as a power outage, an abrupt reduction in voltage, or any electrical abnormality.
- Activation: The generator or battery setup is then told to start up as the backup power source by the ATS. This guarantees that the restoration of power won’t be delayed.
- Transfer: After the backup system is reliably running, the ATS moves all electrical load from the primary power source to the backup source. To prevent any equipment from being harmed, this changeover is executed seamlessly.
- Reversion: The ATS turns off the generator and transfers everything back from the backup to the regular power source once the main power has stabilized.
The entire process usually only takes a few seconds, so your home, workplace, or factory can keep running normally. It protects appliances, prevents lost productivity, and offers comfort during unscheduled power outages.
Types of Automatic Transfer Switches

There are various varieties of Automatic Transfer Switches (ATS), each intended to address particular power requirements and consumption situations. Here is a simple summary of the most prevalent kinds:
- Open Transition ATS: The most fundamental kind. It briefly disconnects entirely before switching to the backup power when the main power goes off. For homes or other locations where a small pause won’t cause issues, this little interruption typically lasting only a second or two is acceptable.
- Closed Transition ATS: By let the primary power and backup power to operate together for a brief period of time during the switchover, this kind guarantees a seamless transition. For locations like hospitals or data centers, where even a single moment without power can result in major problems, it avoids any power outages at all.
- Delayed Transition ATS: has a slight delay between shutting off the main power and getting to the backup. This break can preserve delicate equipment by allowing any residual currents, or electrical energy, to drain out before the new source takes over.
- Bypass Isolation ATS: A manual bypass capability is included in this version. It enables technicians to maintain or fix the ATS without turning off the building’s electricity. In commercial or industrial situations where downtime is unacceptable, this is extremely helpful.
- Single Phase ATS: Designed to manage single-phase electricity, which is typical in residential settings, this ATS is ideal for houses or small enterprises. It is easy to use, reasonably priced, and effective for basic backup power requirements.
- Three Phase ATS: Made for larger establishments that require three-phase power for huge gear or equipment, such as factories, retail centers, or office buildings. During outages, this ATS makes sure the increased power demands are satisfied.
The size of your building, the sort of equipment you’re running, and how vital your power demands are will all influence which ATS type is best for you.
Benefits of Using an ATS
An Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) is a crucial component of any backup power system since it offers a number of practical advantages. Each benefit is explained in detail below:
- Uninterrupted electricity: Maintaining electricity even in the event of an outage is one of the main advantages of an ATS. The ATS rapidly transitions to a backup source, such as a generator, as soon as the primary power supply fails. This prevents delicate devices, such as computers, medical equipment, or security systems, from abruptly shutting down, which could result in data loss or harm.
- Safety: Back-feeding is avoided by ATS devices. Back-feeding, which occurs when electricity from a generator flows back into the main power lines, can damage your electrical equipment and pose a risk to utility workers attempting to restore power. This is automatically avoided by the ATS, protecting your property and employees.
- Convenience: When the electricity goes out, an ATS operates automatically, saving you from having to go outdoors or flip any switches. This is particularly useful in emergency situations or during storms. It handles everything for you, even switching to backup power and back again when regular service resumes.
- Efficiency: Even a brief power outage in a business or industrial context might result in major issues or monetary losses. By responding promptly and ensuring that electricity continues to flow, an ATS helps to minimize downtime and maintain uninterrupted operations.
- Versatility: ATS units are not limited to conventional fuel-powered generators; they can also be used with other types of backup power systems. You have more control over how you manage your power because they can also be connected to renewable energy sources like solar panels or battery storage systems.
In summary, an ATS protects people and equipment during unplanned power outages, maintains order, and offers peace of mind.
Applications of ATS
Automatic Transfer Switches (ATS) are utilized in a variety of settings where maintaining power is crucial. Here is a brief description of their applications in different contexts:
1. Residential
An ATS keeps families safe and comfortable in their homes when there is a power outage. When the main power goes off, the ATS automatically activates the backup generator in a home. This eliminates the need for someone to go outdoors and manually turn on lights, freezers, heaters, or medical equipment. Storms and other extreme weather conditions make it very useful.
2. Commercial
Even a brief power outage can cause operational disruptions, impair customer service, and result in financial loss for enterprises. An ATS assists by guaranteeing that the power supply never stops. For instance, stores, banks, and eateries can maintain the functionality of their equipment, lights, and systems.
3. Healthcare
Power must always be available at clinics, hospitals, and other healthcare facilities. Electricity is necessary for devices like ventilators, monitors, and surgical instruments. Here, a power loss might be fatal. In order to save patients and employees, ATS devices make sure that the backup power starts up immediately.
4. Data Centers
Large volumes of digital data are managed and stored in data centers. Even a brief power outage might result in data loss or corruption. ATS devices ensure uninterrupted operation of networking tools, servers, and cooling systems.
5. Industrial
Downtime can halt production, postpone delivery dates, and result in significant financial losses in factories and major manufacturing facilities. By lowering the chance of expensive disruptions, ATS systems assist in maintaining a consistent power supply so that equipment and production lines continue to operate.
Installation and Maintenance of ATS
An Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) installation is not a straightforward do-it-yourself project. To ensure that it complies with local electrical codes and is secure for your residence or place of business, it must be completed by a certified electrician. Additionally, an expert will make sure that the ATS is properly connected to your backup power source, such as a generator or battery system, as well as your primary power source.
To maintain the ATS operating dependably after installation, frequent maintenance is necessary. The main duties involved are as follows:
- Visual Inspections: Check the ATS on a regular basis for physical damage, loose wires, corrosion, and wear. Larger issues later on can be avoided by identifying problems early.
- Testing: To see how the ATS reacts, it’s crucial to periodically mimic a power outage. This test makes that your backup system is operating correctly and that power switches seamlessly. (Source: PNNL)
- Cleaning: Dust and debris may accumulate within the ATS over time. Cleaning it keeps the internal components operating effectively and helps avoid overheating.
- Software Updates: Digital controllers and software are included with certain contemporary ATS machines. You may acquire the newest features, security patches, and performance boosts by keeping the firmware or software updated.
Choosing the Right ATS
Selecting the appropriate ATS is as crucial as correctly installing it. To ensure that it meets your unique power requirements, you must take into account a number of factors:
- Load Requirements: Determine the overall power load that the ATS is expected to handle first. This covers everything that must continue to run in the event of a power outage, such as computers, lighting, appliances, and industrial machinery. Verify that the ATS can manage that load without being overloaded.
- Power Source Type: Verify that the ATS is compatible with both your primary and backup power sources. For instance, your ATS needs to support the sort of generator you’re using, such as a gas-powered generator or a solar backup.
- Transfer Time: The transfer speeds of various ATS units vary. You’ll want a unit with a faster or smoother transmission time if you’re using sensitive equipment, such as data servers or medical devices. In the case of needs, a small delay can be acceptable.
- Features: Depending on your arrangement, you may want additional features like remote monitoring (which allows you to check your ATS from a computer or phone), a manual bypass (which allows you to function without the ATS while maintenance is being done), or real-time indicators and alerts that let you know how the system is doing.
Making the correct decisions during installation and upkeep guarantees that your ATS will function effectively when you need it most, maintaining your devices’ safety, your power stability, and the uninterrupted functioning of your daily life or business.
Conclusion
One essential component for preserving a consistent and dependable power supply is an Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS). In order to minimize interruptions during outages, it makes sure that power automatically shifts from the primary source to a backup. An ATS provides piece of mind by reacting swiftly and safely to any power outage, whether it is utilized in homes for comfort or in vital settings like hospitals, data centers, or factories. It is a wise investment because of its capacity to safeguard delicate equipment, minimize downtime, and offer ease. When installed correctly and maintained on a regular basis, an ATS can greatly increase energy reliability. Whether you’re powering a huge industrial plant or a tiny home, selecting the appropriate type based on your needs guarantees seamless operation.