In today’s digital world, people use laptops, phones, and tablets to do their work from just about anywhere. But for companies, this flexibility also creates new challenges. How can businesses make sure their data stays safe when employees are working remotely or using personal devices? That’s where Microsoft Intune comes in.
Microsoft Intune for Managing Devices and Apps
Microsoft Intune is a cloud powered tool by Microsoft that enables businesses to oversee and secure employee devices and applications efficiently. Whether those devices are running Windows, macOS, Android, or iOS, Intune helps IT teams make sure everything is safe, secure, and working the way it should.
Intune and Microsoft Endpoint Manager: How They Work Together
It belongs to the Microsoft Endpoint Manager platform, which also features tools like Configuration Manager for comprehensive device management. You can think of Intune as a central tool that gives businesses control over how devices are used and ensures security policies are followed.
Why Companies Use Intune?
Companies today deal with a variety of devices: work laptops, personal smartphones, shared tablets and more. Managing all these manually would be almost impossible. Intune makes it easier by letting IT admins:
- Set up new devices remotely
- Install or block specific apps
- Enforce security rules (like password strength)
- Erase data from a device remotely if it gets lost or stolen.
- Verify if a device meets security standards before allowing access to company data
- Whether a company has ten employees or ten thousand, Intune scales to fit the need.
Key Capabilities of Microsoft Intune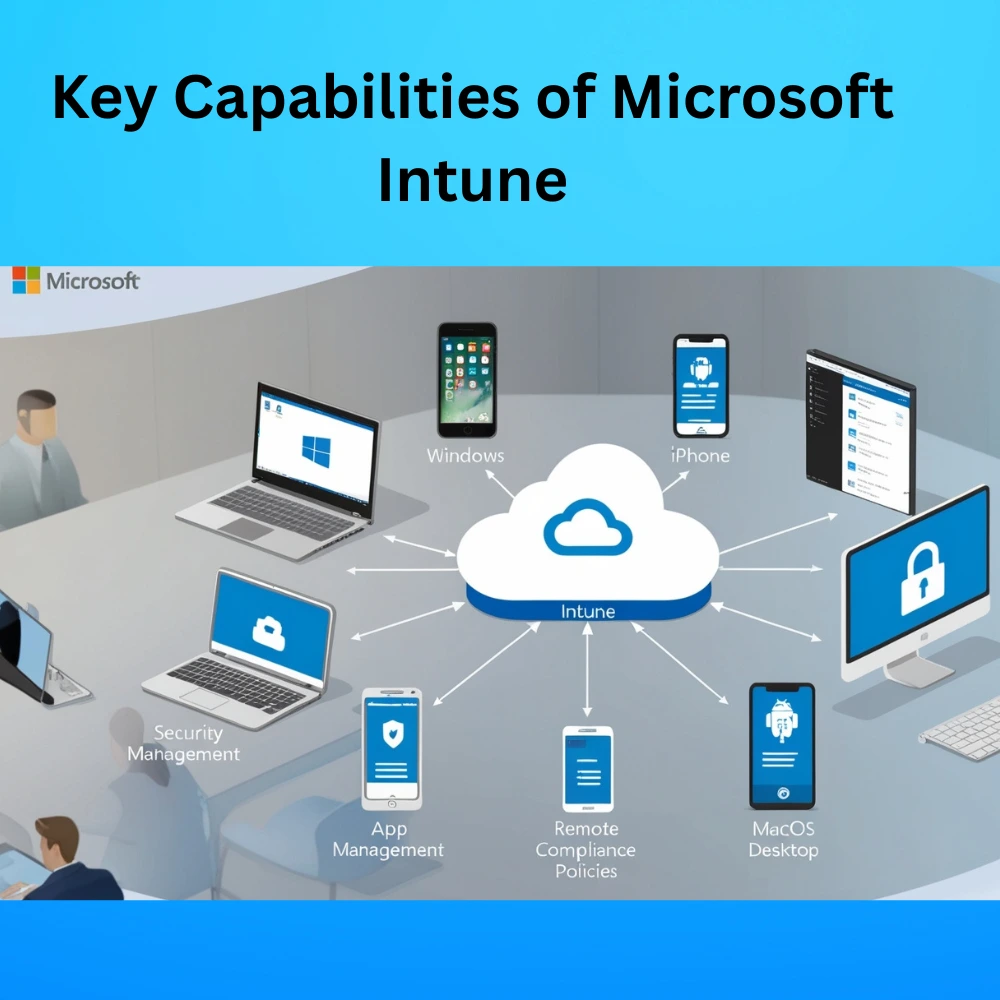
These capabilities form the core of Intune’s device and application management system. Whether you’re dealing with 10 devices or 10,000, these tools give you full visibility and control to protect your business and empower your workforce. Here’s a look at the major things Intune can do:
1. Mobile Device Management (MDM)
Mobile Device Management allows organizations to manage the entire device, whether it’s company-owned or personally owned (BYOD). Once a device is enrolled in Intune, IT administrators can enforce a range of security and configuration settings.
- Enforcing screen locks and encryption
- Restricting device features like Bluetooth, camera, or USB usage
- Blocking access to risky websites
- Deploying Wi-Fi and VPN settings automatically
- Detecting jailbroken or rooted devices
If an employee uses their phone to check work emails, the company can make sure the phone has a passcode and can remotely erase company data if the phone is lost.
2. Mobile Application Management (MAM)
Mobile Application Management is about protecting corporate data at the app level, without needing to control the full device. This is especially useful in BYOD environments where employees use personal phones or tablets.
With MAM, Intune can:
- Apply security policies directly to apps (like Outlook or Teams)
- Prevent copy/paste between business and personal apps
- Require app-level PINs or biometric authentication
- Remove only the organization’s data from the app while leaving personal content untouched.
An employee uses Outlook to access work email on their personal iPhone. Intune can prevent them from copying confidential email content into a personal Notes app.
3. Conditional Access
Conditional Access works with Azure Active Directory and acts as a gatekeeper. It checks the user and device against company rules before giving access to apps or data.
With Intune, access can be controlled by setting specific conditions, such as:
- Only allow access from compliant devices
- Block access if the device is jailbroken or out-of-date
- Require multi-factor authentication
- Limit access to certain apps when using public Wi-Fi
Example use case: An employee tries to open Microsoft Teams from an old Android phone that hasn’t installed the latest security patches. Access is denied until the phone is updated and meets compliance.
4. App Deployment
App Deployment with Intune allows companies to deliver apps to employees easily and quickly, without needing manual installs.
Intune supports
- Microsoft Store, iOS App Store, and Google Play apps
- Line of business (LOB) custom apps
- Win32 apps for Windows PCs
- Web apps and managed Google Play private apps
Apps can be installed automatically or made available in the Company Portal app, where users can install what they need.
A retail company pushes their point-of-sale (POS) app to all Android tablets used by sales staff in stores across the country automatically and remotely.
5. Remote Actions
When a device is lost, stolen or compromised, remote actions help secure company data instantly.
With just a few clicks in the Intune dashboard, admins can:
- Remotely secure a device by locking it to block any unauthorized use.
- Reset the password to secure the user’s account
- Wipe data either fully or selectively (only corporate data)
- Restart a device or issue a factory reset
- Track a device based on its most recent GPS location, if the feature is supported.
An employee misplaces their laptop during a business trip. The IT team immediately locks the device and wipes all business files before any data can be misused.
How Microsoft Intune Works?
Microsoft Intune connects to the cloud, which means companies don’t need to install any special servers or software. Everything is managed from a simple web-based dashboard.
Here’s how the process usually works:
- Enrollment: The user or IT admin enrolls the device in Intune. This lets the system manage it and apply rules.
- Policy Application: The IT admin creates rules, like requiring a PIN or blocking access to certain websites and pushes them to the device.
- Monitoring: Intune verifies whether the device is complying with the defined policies. If not, it alerts the admin or takes action (like blocking access).
- Ongoing Management: The system regularly checks in with devices and updates apps or settings as needed.
It’s smooth, automated, and efficient.
What Devices Can Be Managed?
Microsoft Intune supports all major platforms:
- Windows 10 and 11 PCs
- macOS devices
- iOS/iPadOS (iPhones and iPads)
- Android phones and tablets
- Linux (limited support)
No matter what device an employee uses, Intune offers a way to manage it.
Benefits of Using Intune
There are many reasons businesses choose Microsoft Intune. Here are some of the top benefits:
- Better Security: Keeps business data safe by enforcing rules and wiping lost devices.
- More Control: IT teams have control over what apps and settings are allowed.
- Easy Management: All devices can be handled from one place, saving time.
- Supports BYOD (Bring Your Own Device): Employees can use personal phones while still keeping work data secure.
- Cloud-Based: No need to install servers—everything runs from the cloud.
- Integration with Microsoft 365 and Azure AD: It works perfectly with other Microsoft tools already in use.
Common Use Cases
To make it easier to understand, here are a few examples of how companies use Intune:
- Healthcare organizations use it to keep patient data secure on doctors’ mobile devices.
- Schools and universities manage student laptops and tablets with pre-installed apps and safety settings.
- Sales teams use it to access client data securely from their phones while traveling.
- Remote teams are able to stay productive and connected without risking data leaks.
Learning Microsoft Intune
If you’re new to Intune, Microsoft offers plenty of training materials. These include:
- Beginner tutorials
- Practice labs
- Learning paths in Microsoft Learn Certification options, such as the Microsoft Certified: Endpoint Administrator Associate, are also available.
You don’t need to be an IT expert to get started, especially with the help of guided lessons.
Real Life Tips for Admins
Admins who manage Intune often share some helpful advice:
- Start small: Test Intune on a few devices before rolling it out company-wide.
- Use groups wisely: Assign settings to groups based on roles (like HR, Sales, or IT) for easier control.
- Monitor regularly: Keep an eye on compliance and troubleshoot any issues early.
- Learn the logs: Understanding Intune’s logs helps fix problems quickly.
- Stay updated: Microsoft adds new features regularly, so it’s good to check for updates each month.
Final Thoughts
Microsoft Intune is a powerful tool that helps businesses stay secure, productive, and flexible in the modern digital world. It protects company data, helps manage devices and apps, and gives employees the freedom to work from anywhere it safely.
Even if you’re not a tech expert, the idea is simple: Intune keeps your work devices and data under control, no matter where your team works or what devices they use.
Whether you’re a small business owner, IT manager, or just someone curious about modern workplace tools, understanding Intune is a great step toward smarter and safer device management.