In today’s digital age, transferring data quickly and efficiently is more important than ever. Whether you’re moving photos, videos, or large documents, the speed at which this happens can make a big difference. This is where USB 3.0 comes into play. Often referred to as “SuperSpeed USB,” USB 3.0 offers significant improvements over its predecessors. Let’s explore what USB 3.0 is, how it functions, and why it’s a valuable upgrade for everyday tech use.
What is USB 3.0?
USB 3.0 is the third major version of the Universal Serial Bus (USB) standard, introduced in November 2008. It was designed to provide faster data transfer rates, improved power efficiency, and better overall performance compared to earlier versions like USB 2.0. With USB 3.0, users can experience data transfer speeds of up to 5 gigabits per second (Gbps), which is about ten times faster than USB 2.0’s 480 megabits per second (Mbps).
Key Features
1. Faster Data Transfer Speeds
One of the most significant advantages of USB 3.0 is its increased data transfer speed. This means that large files, such as high-definition videos or extensive photo libraries, can be transferred in a fraction of the time it would take with USB 2.0. For example, transferring a 1GB movie file might take around 40 seconds with USB 2.0, but only about 4 seconds with USB 3.0.
2. Improved Power Efficiency
USB 3.0 not only transfers data faster but also manages power more efficiently. It provides more power to connected devices, allowing for quicker charging and better support for power-hungry peripherals. Additionally, USB 3.0 introduces new power management features that reduce power consumption when devices are idle.
3. Backward Compatibility
A crucial feature of USB 3.0 is its backward compatibility with USB 2.0. This means that USB 3.0 ports and devices can work with USB 2.0 counterparts. However, when a USB 3.0 device is connected to a USB 2.0 port, the data transfer speed will default to the slower USB 2.0 rate.
4. Enhanced Connector Design
USB 3.0 connectors are designed with additional pins to support higher data transfer rates. These connectors are typically distinguished by a blue color inside the port, making it easier to identify them.
Understanding the Technical Aspects
Let’s break down each of these technical aspects of USB 3.0 in a simple way:
1. Data Transfer Mechanism: Dual-Bus Architecture
USB 3.0 uses something called a dual-bus architecture, which means it has two channels for data. One channel sends data, while the other receives it at the same time. This is called full-duplex communication.
Think of it like having two lanes on a highway: while one car is going in one direction (sending data), another car is going in the opposite direction (receiving data). This helps USB 3.0 transfer data much faster and more efficiently than older versions, like USB 2.0, which can only send or receive data one way at a time (half-duplex).
2. Encoding Scheme: 8b/10b Encoding
USB 3.0 uses an encoding system called 8b/10b encoding. This is a method where every 8 bits of actual data (1 byte) are sent as 10 bits. This extra 2 bits are not data themselves but are used for error checking and to make sure the data isn’t corrupted during transmission.
To put it simply, when you send 8 pieces of information, USB 3.0 sends them with extra “guard” bits, ensuring the information arrives correctly without interference. This is similar to adding extra letters or numbers to a message to check if it has been delivered correctly, so you can catch any mistakes.
3. Power Delivery: 900mA vs. 500mA
Another improvement of USB 3.0 over USB 2.0 is its ability to deliver more power. USB 3.0 can supply up to 900 milliamps (mA) of current to devices, while USB 2.0 can only deliver 500mA.
This increased power allows USB 3.0 to charge devices faster and provide better support for power-hungry gadgets. For example, newer external hard drives, smartphones, or even some high-performance peripherals need more power to function properly, and USB 3.0 can handle that more efficiently..
Practical Benefits in Everyday Use
Let’s explore how the benefits of USB 3.0 apply to everyday use in simple terms:
1. Quicker File Transfers
One of the biggest advantages of USB 3.0 is the ability to transfer files much faster.Whether you’re backing up important documents, transferring large video files, or syncing data between devices, USB 3.0 dramatically reduces the time it takes to do these tasks.For example, if you’re copying a large file like a movie or a whole folder of photos, USB 3.0 can do this in a fraction of the time compared to older versions like USB 2.0. This is especially helpful for people who regularly work with big files, like photographers, video editors, or anyone who needs to move large data quickly.
2. Enhanced Peripheral Performance
USB 3.0 provides a significant boost in performance for devices like external hard drives, flash drives, and even high-resolution webcams.Because it supports higher data transfer speeds, these devices can perform tasks more efficiently.For example, an external hard drive connected via USB 3.0 will read and write data faster, allowing you to access your files or save new ones without lag or delays.Webcams connected to USB 3.0 also benefit from better performance, making video calls or live streaming smoother and less prone to interruptions.
3. Improved Charging Capabilities
Another great benefit of USB 3.0 is its ability to charge devices faster.Because USB 3.0 can deliver more power (up to 900mA compared to USB 2.0’s 500mA), it can charge smartphones, tablets, and other portable gadgets at a quicker rate.This is especially useful when you’re in a rush and need to charge your device quickly, or when you’re using power-hungry accessories like external hard drives that need a stable power supply.For instance, if you’re in a hurry and need your phone to charge faster, USB 3.0 ensures it gets the power it needs more efficiently than older USB versions.
Identifying USB 3.0 Ports and Devices
Recognizing USB 3.0 ports and devices is easy once you know what to look for:
- Color Coding: USB 3.0 ports are often marked by a blue color inside the port. This blue coloring helps distinguish USB 3.0 ports from USB 2.0 ports, which are typically black or white inside. So, when you’re plugging in a device, if you see a blue port, it’s most likely a USB 3.0 port. This simple visual cue makes it easy to spot USB 3.0.
- Labeling: Another way to identify USB 3.0 is by looking for the “SS” logo, which stands for “SuperSpeed.” This logo indicates that the device or port supports USB 3.0, and it’s usually found near the port or on the device itself. The “SS” symbol helps confirm that you’re dealing with a high-speed connection, distinguishing it from older USB versions.
Compatibility Considerations
USB 3.0 is designed to be backward compatible, meaning you can use a USB 3.0 device with an older USB 2.0 port. However, there is a catch: to get the maximum performance, both the device and the port need to be USB 3.0.
- USB 3.0 Device with USB 2.0 Port: If you connect a USB 3.0 device to a USB 2.0 port, you’ll still be able to use it, but it will operate at USB 2.0 speeds. That means you won’t get the faster data transfer rates that USB 3.0 offers.
- USB 3.0 Device with USB 3.0 Port: To take full advantage of USB 3.0’s faster speeds, both the device (like a hard drive or flash drive) and the port (on your computer or laptop) need to support USB 3.0. If both parts are USB 3.0 compatible, you’ll get the fastest data transfer speeds.
The Evolution Beyond USB 3.0
Since the introduction of USB 3.0, the technology has continued to evolve with newer versions:
- USB 3.1: Introduced improvements in data transfer speed (up to 10 Gbps) and introduced the USB Type-C connector, which is reversible and more compact.
- USB 3.2: Brought further enhancements to data speeds, offering up to 20 Gbps on supported devices and cables.
- USB4: The latest version of USB technology, which offers data transfer speeds up to 40 Gbps, improved performance for Thunderbolt devices, and better compatibility with other devices like displays.
Even though these newer versions offer even faster speeds and more advanced features, USB 3.0 remains widely used because it provides more than enough speed and power for most everyday applications. It’s reliable, works with a wide range of devices, and is still a very popular choice for transferring data and charging devices.
Types of USB 3.0 Connectors
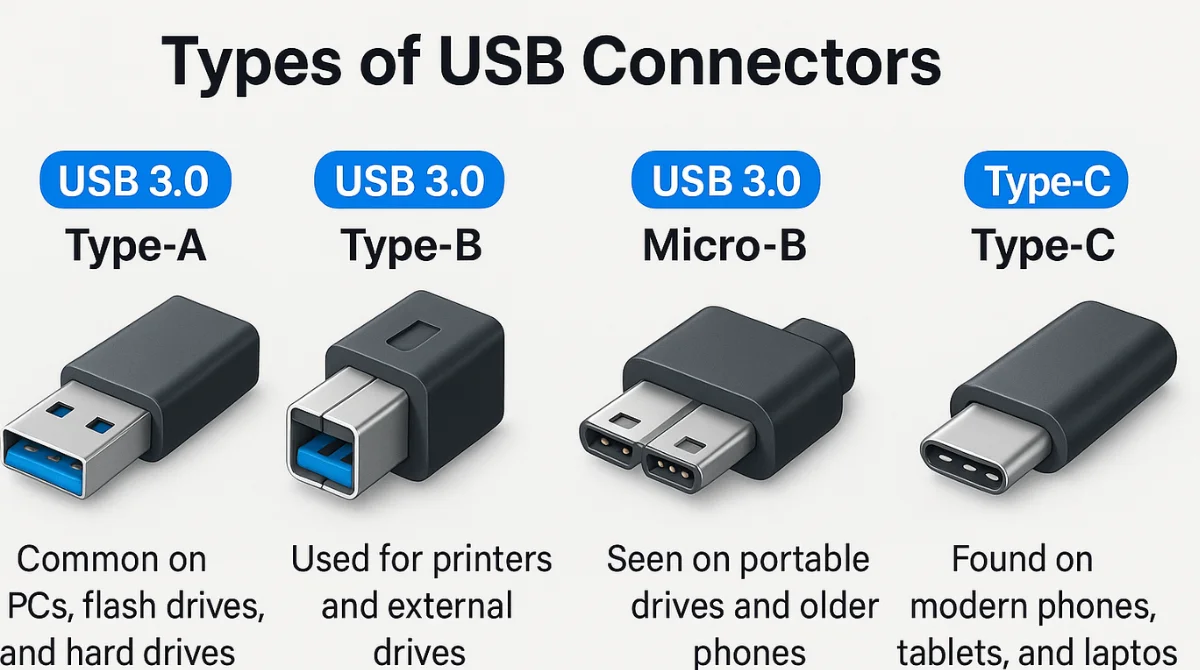
USB 3.0 comes in different connector types, which are used depending on the device. Understanding these types helps you know which cable or port to use for your gadgets.
1. USB 3.0 Type-A
This is the most common USB connector, shaped like a flat rectangle. It’s usually found on computers, laptops, TVs, game consoles, and other larger devices.
- Where you see it: Desktop PCs, flash drives, keyboards, and external hard drives
- Tip: It looks just like a regular USB plug but often has a blue plastic insert to show it’s USB 3.0.
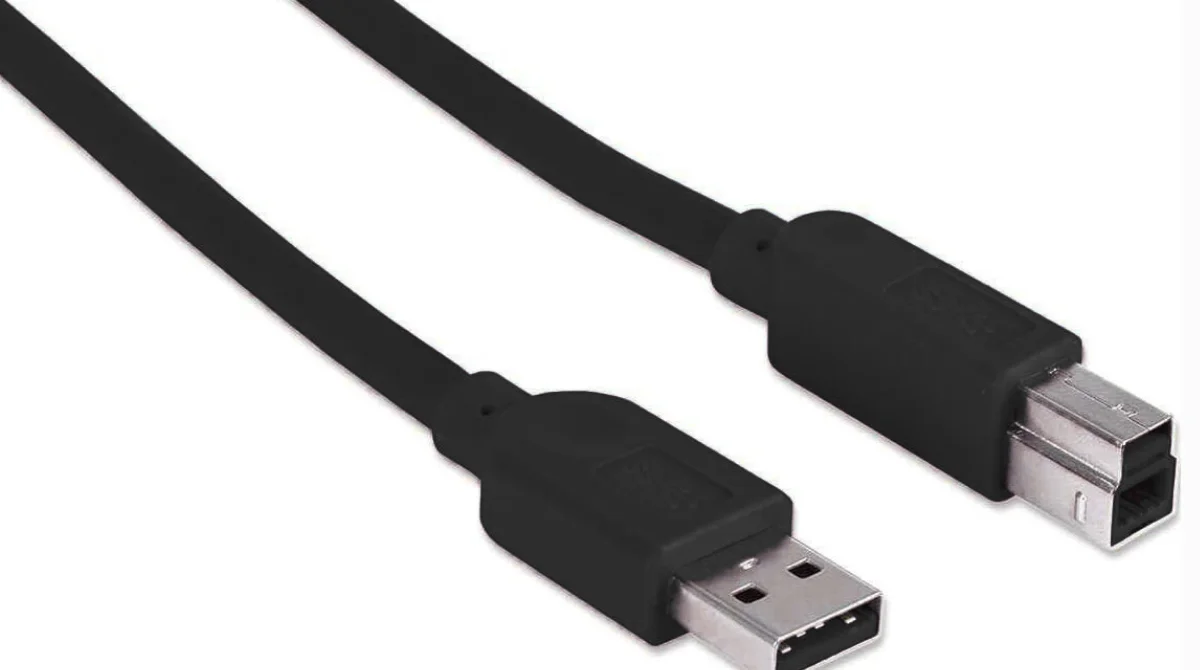
2. USB 3.0 Type-B
This connector is square-shaped with a little notch on top. It’s often used with larger devices that receive power and transfer data, like printers or scanners.
- Where you see it: Printers, external hard drives, and some monitors
- Tip: USB 3.0 Type-B is bulkier than the USB 2.0 version because it has extra pins for faster data transfer.
3. USB 3.0 Micro-B
This type is used mainly with portable devices. It looks like two connectors merged into one – a small standard Micro-USB plus an extra part for more speed.
- Where you see it: External portable hard drives and some older Android phones
- Tip: It’s wider than regular micro-USB connectors due to its extra pins.
4. USB 3.0 Type-C (Introduced with USB 3.1 but often supports USB 3.0 speed)
Though technically part of newer standards, Type-C connectors are often used with USB 3.0 speeds too. It’s small, reversible, and becoming very common.
- Where you see it: New smartphones, laptops, tablets, and other modern gadgets
- Tip: You can plug it in any way—there’s no “wrong side up.”
Conclusion
USB 3.0 has revolutionized the way we transfer data and power our devices. With its significantly faster data transfer speeds, improved power efficiency, and backward compatibility, it has become an essential part of modern computing. Whether you’re a professional handling large files or just someone looking for quicker charging and smoother performance from your peripherals, USB 3.0 offers a reliable and efficient solution.
Even as newer versions like USB 3.1, USB 3.2, and USB4 emerge, USB 3.0 remains highly relevant and widely supported. Understanding how it works, its benefits, and how to identify it can help you make the most out of your tech gear. In an age where speed and efficiency matter more than ever, USB 3.0 continues to be a game-changer for both everyday users and tech enthusiasts alike.
Related Topics:



