In our daily lives, we often take precautions to avoid problems like locking our doors or saving money for emergencies. Similarly, businesses use a system called a Risk Management Framework (RMF) to identify and handle potential issues that could disrupt their operations. This guide will explain what an RMF is, why it’s important, and how it works, using straightforward language.
What Is a Risk Management Framework?
A Risk Management Framework is a structured approach that helps organizations identify, assess, and address risks that could impact their goals. Think of it as a roadmap that guides a company in recognizing potential problems and deciding how to deal with them effectively.
Why Is Risk Management Important?
Every organization faces uncertainties like market fluctuations, cyber threats, or natural disasters that can affect their performance. By implementing an RMF, companies can:
- Anticipate potential issues before they occur.
- Make informed decisions to minimize negative impacts.
- Ensure compliance with laws and regulations.
- Protect their reputation and financial stability.
Key Components of a Risk Management Framework
An effective RMF typically includes the following steps:
1. Risk Identification
This process entails identifying possible hazards that might have an impact on the company. These hazards may be external (such as downturns in the economy) or internal (such as mistakes made by employees). Early risk identification enables proactive management.
2. Risk Assessment and Analysis
After hazards have been identified, they must be assessed to determine their likelihood and possible impact. This evaluation aids in setting priorities for which dangers need to be addressed right now and which can wait.
3. Risk Mitigation
Following risk assessment, firms create management plans. This could involve:
- Avoiding the risk entirely.
- Reducing the risk’s impact or likelihood.
- Transferring the risk to a different person (for example, by purchasing insurance).
- Accepting the risk if it’s within the organization’s tolerance levels.
4. Monitoring and Review
Risk management is an ongoing process. Regularly monitoring risks and reviewing mitigation strategies ensures that the organization adapts to new challenges and maintains effective controls.
5. Communication and Reporting
Clear communication about risks and how they’re being managed is crucial. This involves reporting to stakeholders, training employees, and fostering a culture where risk awareness is part of everyday operations.
6. Governance and Compliance
Establishing clear roles and responsibilities ensures that everyone understands their part in managing risks. Compliance with legal and regulatory requirements is also a key aspect of governance.
7. Continuous Improvement
Organizations should regularly evaluate and improve their risk management processes. Learning from past experiences and staying updated on best practices helps in refining the RMF over time.
Popular Risk Management Frameworks
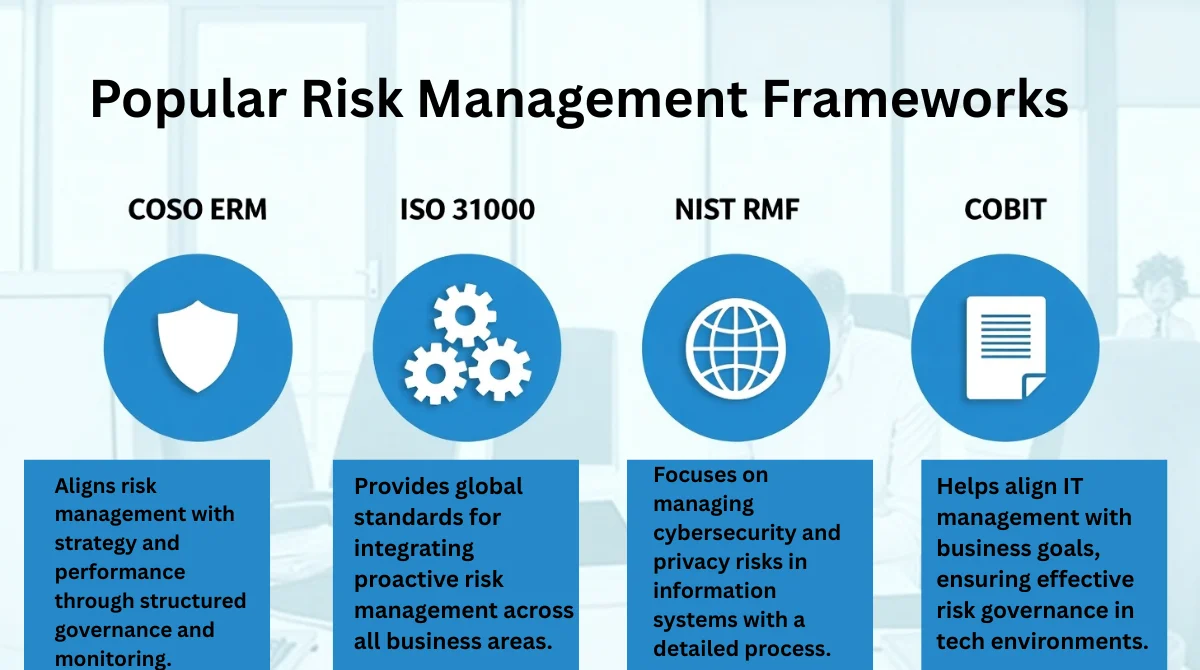
Several established frameworks provide guidelines for managing risks:
1. COSO ERM Framework
Developed by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO), this framework emphasizes aligning risk management with an organization’s strategy and performance. It includes components like governance, strategy setting, and performance monitoring.
2. ISO 31000
Principles and criteria for efficient risk management are provided by this international standard. It focuses on integrating risk management into all aspects of an organization, promoting a proactive approach to identifying and addressing risks.
3. NIST Risk Management Framework
Created by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), this framework provides a structured process for managing cybersecurity and privacy risks, particularly in information systems.
4. COBIT
COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies) is a framework for IT management and governance. It helps organizations align their IT goals with business objectives, ensuring effective risk management in technology processes.
Implementing a Risk Management Framework
To effectively implement an RMF, organizations should:
- Understand their context: Recognize internal and external factors that influence risks.
- Engage stakeholders: Involve employees, management, and other relevant parties in the risk management process.
- Establish clear policies: Define procedures and responsibilities for managing risks.
- Provide training: Instruct staff members on risk management and awareness.
- Use appropriate tools: Leverage technology and methodologies suitable for the organization’s size and industry.
Role of Technology in Risk Management
A significant part of contemporary risk management involves technology. It helps businesses track, analyze, and respond to risks quickly. Here’s how:
- Automation tools can handle repetitive tasks like monitoring data or sending alerts
- Dashboards show real-time risk data so you can act fast
- Cloud platforms offer secure backups and disaster recovery options
- AI and machine learning are able to identify anomalous activity and forecast patterns.
- Risk Management Software (like LogicManager, Resolver, and RiskWatch) helps track and manage risk activities in one place
Even small businesses can start with free or low-cost tools like Google Sheets or project management apps to track risks.
FAQ
1: Is a risk management framework only for big companies?
No. Small and medium businesses benefit just as much, even from a simple checklist or spreadsheet-based approach.
2: How frequently should a framework for risk management be reviewed?
At least once a year or after any major change in your business, such as launching a new product or entering a new market.
3: What’s the easiest way to start risk management?
Start by listing risks you already know, assess how likely and harmful they are, and plan simple ways to reduce them.
4: Is ISO 31000 suitable for small businesses?
Yes, it offers flexible guidelines that can be adapted to organizations of any size or industry.
5: What happens if a business ignores risk management?
It can face unplanned costs, damaged reputation, legal issues, or even business failure due to unpreparedness.
Conclusion
Managing risks is essential for any organization’s success and longevity. A Risk Management Framework provides a systematic approach to identifying, assessing, and addressing potential issues, enabling companies to navigate uncertainties confidently. By understanding and implementing an RMF, organizations can protect their assets, ensure compliance, and achieve their objectives more effectively.