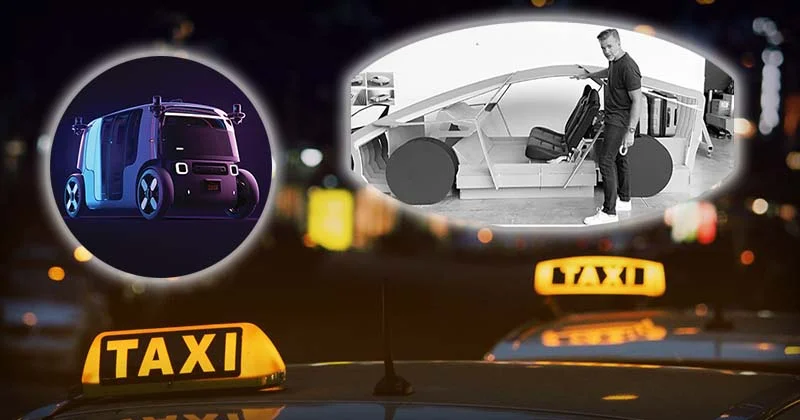
The concept of robotaxis is also referred to as robotaxi, self-driving taxis or driverless taxis, has been a prominent topic in the realm of autonomous vehicles. These vehicles are operating at SAE automation levels 4 or 5, are deployed by ridesharing companies to provide a glimpse into the future of transportation.
The potential benefits of robotaxi extend beyond convenience, promising positive impacts on road safety, traffic congestion, and parking challenges in urban areas.
RoboTaxi Advantages and Challenges
Studies suggest that widespread adoption of robotaxis, especially in urban settings, could revolutionize mobility. The anticipated benefits include enhanced road safety, reduced traffic congestion and a positive environmental impact.
The Robotaxis are expected to contribute to pollution reduction, given the likely use of electric cars. Additionally, the shift from individual car ownership to Transportation-as-a-Service (TaaS) could lead to cost savings, making robotaxis an affordable mode of transportation. However, this transition raises concerns about job displacement and operator liabilities. Notably, there have been instances of robotaxis causing road blockages and interfering with emergency vehicles, highlighting challenges that need addressing.
Evolution of Robotaxis: A Historical Perspective
First Trials
The journey of robotaxis began in August 2016 when NuTonomy: a MIT spinoff, initiated the first public robotaxi service in Singapore. This marked the beginning of a transformative era in transportation. Subsequently, partnerships with companies like Grab, Groupe PSA and Lyft signaled a growing interest in the potential of autonomous taxi services.
Testing and Revenue Service Timeline
The development of robotaxis has seen several trials and challenges. From Uber’s initial robotaxi trials in Pittsburgh in 2016 to Waymo’s large-scale tests in Phoenix starting in April 2017, the industry has experienced both successes and setbacks. Notably, incidents such as the Uber self-driving car accident in Tempe, Arizona, in March 2018, raised questions about the safety of autonomous vehicles.
Robotaxi Commercial Ventures
Uber’s Advanced Technologies Group (ATG), Waymo and GM Cruise have been key players in the commercialization of robotaxi. Uber’s journey, marked by trials, accidents and eventually selling its self-driving division to Aurora Innovation in 2021, reflects the challenges faced by the industry. Waymo’s Waymo One service in Arizona and GM Cruise’s driverless taxi service in San Francisco demonstrate the progress made in recent years.
The Road Ahead Robotaxi
Several automakers and technology providers have entered partnerships to develop robotaxis before 2025. Zoox, Daimler AG, Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance and others are exploring the potential of autonomous taxi services. These collaborations aim to integrate robotaxis into the fabric of urban transportation, offering a glimpse into a future where self-driving cars are an integral part of our daily lives.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the evolution of robotaxis is a fascinating journey, marked by technological advancements, trials and collaborative efforts. While challenges persist, the vision of a future with safer, more efficient and environmentally friendly transportation through robotaxis remains a compelling one. The industry’s ability to address concerns and continue innovating will determine the extent of its impact on the way we travel.