Mobile networks have significantly transformed the way we live, work, and stay connected in today’s digital world. From the early days of slow internet on our phones to today’s high-speed streaming and cloud access, a great deal has changed. One of the most important changes in this journey is Long Term Evolution, commonly known as LTE. LTE helped bridge the gap between 3G and 5G, offering faster speeds, more stable connections, and better performance overall.
What Was 3G All About?
The third generation of mobile network technology, known as 3G, introduced mobile internet to the mainstream. It was introduced in the early 2000s and made mobile internet widely usable. Before 3G, phones were mostly used for calling and texting. With 3G, people could:
- Browse the internet faster
- Send and receive emails easily
- Use apps like WhatsApp and Facebook
- Make video calls and stream low-quality videos
But 3G had its limits. While it improved mobile data compared to 2G, it was still slow for tasks like HD video streaming or large downloads. Plus, as more users joined the network, it became crowded and less reliable.
The Arrival of LTE: A Game Changer
Following that, Long Term Evolution (LTE), commonly branded as 4G LTE, ushered in a new era of high-speed mobile connectivity. LTE is not exactly 4G in its purest form, but it was much faster and more efficient than 3 G. It became the main step between 3 G and 5G and gave mobile users a big upgrade.
Here’s how LTE changed the game:
- Speed Advantage: Under optimal conditions, LTE could deliver download speeds reaching up to 100 Mbps significantly faster than 3G.
- Reduced Latency: In networking terms, latency refers to the delay that occurs before data transmission begins. LTE reduced latency, making streaming, gaming, and video calling smoother.
- Better Voice Quality: With VoLTE (Voice over LTE), users get clearer calls and faster connection times.
- Efficient Use of Spectrum: LTE used radio frequencies more smartly, allowing better coverage and capacity.
LTE made mobile internet feel more like using home Wi-Fi. Apps loaded quickly, videos played without buffering, and even work tasks like file sharing and cloud access became easier on the go.
How LTE Works Behind the Scenes?
Even though we experience LTE as fast internet on our phones, there’s a lot of tech behind it. LTE works by sending data in small blocks over radio waves. It uses something called OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing), which splits signals into smaller parts to avoid interference and ensure smooth delivery.
It also uses MIMO (Multiple Input, Multiple Output), which means both the phone and the tower use multiple antennas to send and receive data. This improves speed and reliability, especially in crowded areas.
LTE-Advanced: An Even Better Version
To push things further, an improved version called LTE-Advanced was developed. It offered even faster speeds (up to 1 Gbps in theory) and could combine multiple frequencies to handle more users. Features like carrier aggregation helped boost network performance by combining different bands to increase data rates.
LTE’s Impact on Daily Life
LTE didn’t just improve mobile browsing. It made many modern services possible or better:
- Streaming Services: Watching Netflix or YouTube in HD while on the go became normal.
- Ride-Sharing Apps: Apps like Uber and Careem need stable and fast internet to work smoothly.
- Mobile Banking: Secure, real-time transactions have become easier.
- Video Conferencing: LTE allowed smoother Zoom or Google Meet calls without Wi-Fi.
- Remote Work and Learning: Students and workers could join online classes or meetings from anywhere.
The Shift Toward 5G
Today, the spotlight is on 5G, the fifth generation of mobile technology, which aims to deliver even greater speeds, ultra-low latency, and seamless connectivity for countless devices simultaneously. It’s expected to power innovations like:
- Smart cities
- Self-driving cars
- Remote surgery
- Real-time virtual reality
But here’s the catch: 5G coverage is still limited in many parts of the world. This is precisely where LTE still holds substantial importance. Many 5G phones still rely on LTE fallback when 5G signals aren’t available. Most current mobile networks are built using both LTE and 5G layers to ensure wide coverage.
LTE and 5G: Working Together
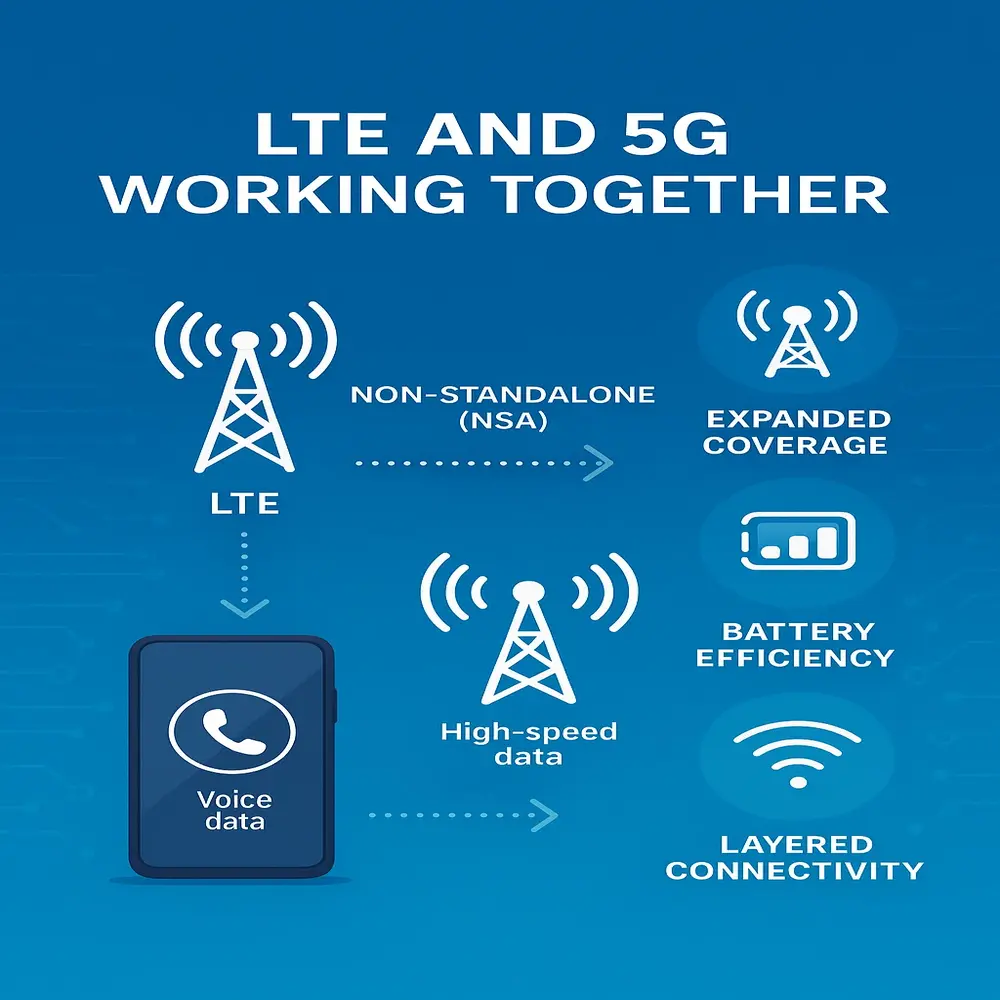
Instead of completely replacing LTE, 5G builds on it. Many mobile networks use Non-Standalone (NSA) 5G, which uses LTE for tasks like connecting calls or managing devices, while 5G handles high-speed data.
This teamwork helps:
- Expand 5G quickly using existing LTE infrastructure
- Ensure coverage even in areas where 5G is weak
- Reduce battery use on 5G devices by offloading some work to LTE
So even as 5G grows, LTE remains a strong part of the mobile world.
Why LTE Still Matters?
You might think LTE is old now, but it’s far from outdated. Long Term Evolution is still the primary mobile network for millions around the globe. Many low-cost phones and budget data plans are LTE-only. Even high-end devices use LTE when 5G isn’t available. And in places where 5G won’t reach for years, like rural regions or developing countries, Long Term Evolution will continue to connect people.
How LTE Differs from 3G and 5G?
While LTE improved over 3 G, it also laid the groundwork for 5 G. Let’s take a side-by-side glance at the differences between these network technologies.
| Feature | 3G | LTE (4G) | 5G |
| Speed | Up to 2 Mbps | Up to 100 Mbps (theoretical) | 1–10 Gbps |
| Latency | 100–500 ms | 30–50 ms | Under 10 ms |
| Use Cases | Basic browsing, email | Streaming, video calls, cloud apps | Smart cities, autonomous cars, industrial IoT |
Key Takeaway: LTE is the middle bridge, faster and more stable than 3G, and still very capable where 5G isn’t available.
Summary of LTE’s Role Between 3G and 5G
Here’s a quick summary of how LTE has supported mobile connectivity:
- Acted as a powerful upgrade over slow 3G
- Enabled real-time internet services on the go
- Set the base for 5G rollouts with modern infrastructure
- Continues to support mobile users even in 5G times
Final Thoughts
The journey from 3 G to 5G wouldn’t have been possible without Long Term Evolution. It brought mobile internet to a level where we could rely on it daily, for fun, work, learning, and staying connected. Although 5G represents the future of wireless communication, Long Term Evolution remains the solid backbone of current mobile experiences. So the next time your phone says “LTE” in the corner, remember it’s not just a network. It’s a major part of mobile history and still doing a great job.