Managing multiple usernames and passwords for different applications can be tiring and confusing for users. Federated Identity Management (FIM) tackles this issue by allowing users to access several systems through a single set of login credentials. This method not only streamlines the user experience but also reinforces security across organizational boundaries.
What is Federated Identity Management?
Federated Identity Management is a system that enables users to use one set of login credentials to access multiple applications across different organizations or domains. Instead of creating separate accounts for each service, users authenticate through a trusted Identity Provider (IdP), which then grants access to various Service Providers (SPs) without requiring additional logins.
How Does Federated Identity Work?
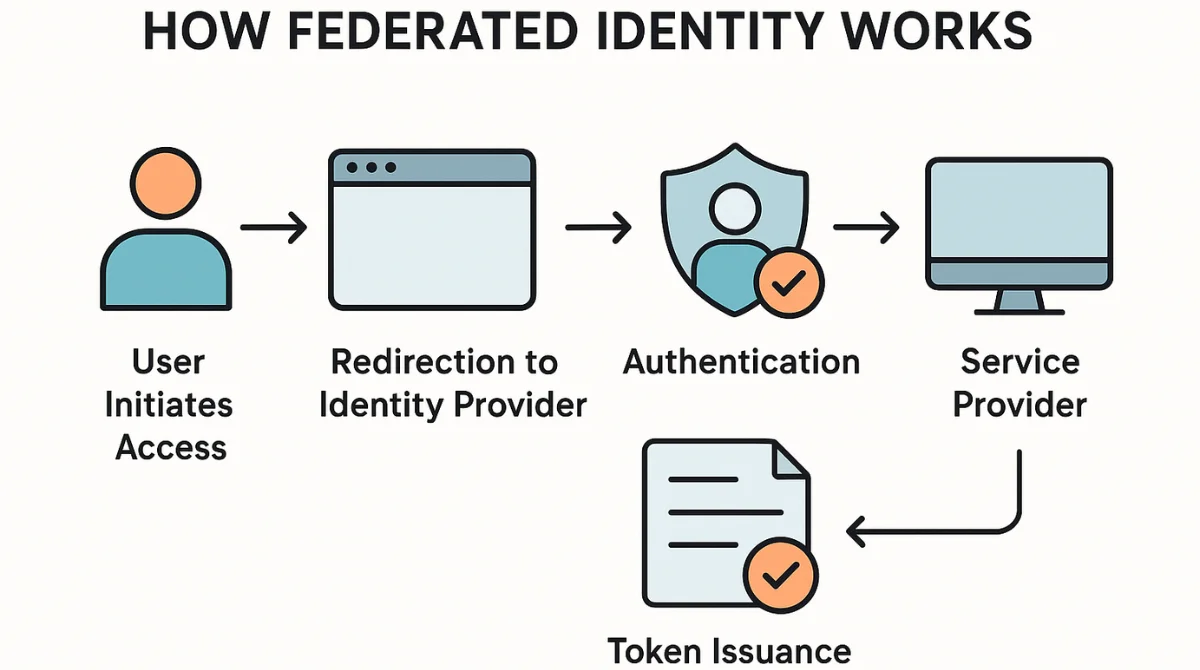
At the heart of Federated Identity Management (FIM) is the trust established between Identity Providers and Service Providers. Here’s a simplified flow:
- User Initiates Access: The user attempts to access an application or service.
- Redirection to Identity Provider: The application redirects the user to the IdP for authentication.
- Authentication: The IdP verifies the user’s credentials.
- Token Issuance: The IdP issues a security token with user data after a successful authentication.
- Access Granted: The token is presented to the Service Provider, which grants accessbased on the information provided.
This process allows seamless access to multiple services without repeated logins, enhancing both convenience and security.
Key Features
1. Single Sign-On (SSO)
SSO lets users log in once and access multiple apps without repeating credentials. This reduces password fatigue and enhances overall productivity.
2. Interoperability
Federated Identity Management works with standard protocols like SAML, OAuth, and OpenID Connect. This guarantees seamless operation across various platforms.
3. Centralized Identity Management
Organizations can control all user identities from a single place. This makes adding, updating, or removing users much easier.
4. Attribute-Based Access Control
Access is granted based on user attributes like job role or department. This allows precise and flexible control over who sees what.
5. Enhanced Privacy
Instead of sharing personal info, FIM uses secure tokens for login. This keeps sensitive data safer from leaks or misuse.
Benefits of Federated Identity Management
- Improved User Experience: Users benefit from a streamlined login process, reducing the need to remember multiple passwords and decreasing login-related frustrations.
- Enhanced Security: Centralized authentication reduces the risk of password-related breaches and allows for the implementation of stronger security measures.
- Cost Savings: Organizations can lower IT support costs by reducing password reset requests and simplifying user management.
- Scalability: FIM systems can easily scale to accommodate growing numbers of users and applications, making them suitable for organizations of all sizes.
- Regulatory Compliance: By centralizing identity management and implementing standardized protocols, organizations can more easily comply with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
Technologies Behind Federated Identity
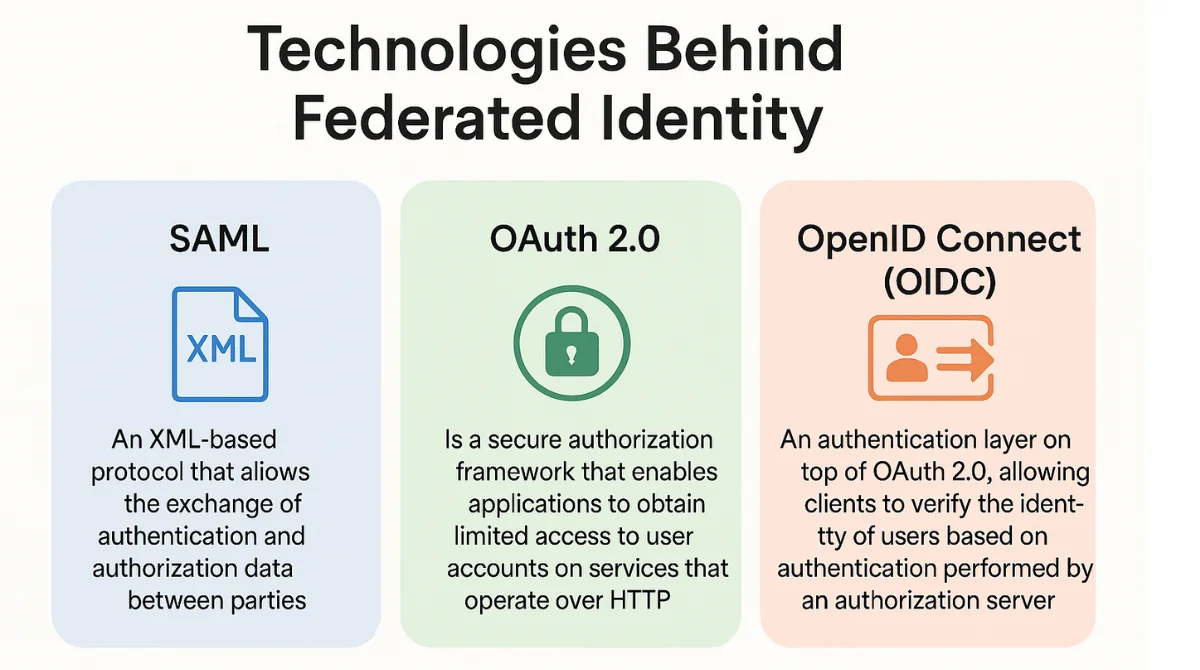
- SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language): An XML-based protocol that allows the exchange of authentication and authorization data between parties.
- OAuth 2.0:Is a secure authorization framework that enables applications to obtain limited access to user accounts on services that operate over HTTP, without exposing user credentials.
- OpenID Connect (OIDC): An authentication layer on top of OAuth 2.0, allowing clients to verify the identity of users based on authentication performed by an authorization server.
Real-World Applications
- Corporate Collaborations: Companies can grant partners access to internal resources without creating separate accounts.
- Educational Institutions: Students and staff can access shared resources across universities using a single login.
- Government Services: Citizens can access various government portals with one set of credentials.
- Healthcare Systems: Medical professionals can securely access patient records across different hospitals.
Challenges and Considerations
While FIM offers numerous benefits, there are challenges to consider:
- Single Point of Failure: Can occur if the Identity Provider (IdP) becomes unavailable, potentially preventing users from accessing multiple connected services.
- Implementation Complexity: Integrating FIM requires careful planning and coordination between different organizations and systems.
- Trust Management: Establishing and maintaining trust relationships between Identity Providers and Service Providers is crucial.
- Privacy Concerns: It is crucial to manage user data responsibly and ensure compliance with relevant privacy regulations.
Is Federated Identity Secure?
Yes, Federated Identity is secure when properly implemented. It reduces password-related risks, supports multi-factor authentication, and uses encrypted protocols like SAML and OpenID Connect. Centralized access makes it easier to monitor and revoke user rights. However, the Identity Provider must be well-protected, as it becomes a key target. With proper safeguards, FIM offers strong, reliable security.
Conclusion
Federated Identity Management streamlines user access across various systems, strengthens overall security, and delivers a more seamless user experience. By centralizing authentication and leveraging standard protocols, organizations can provide seamless and secure access to resources, both internally and with trusted partners. While implementation requires careful consideration, the benefits of FIM make it a valuable solution in today’s interconnected digital landscape.